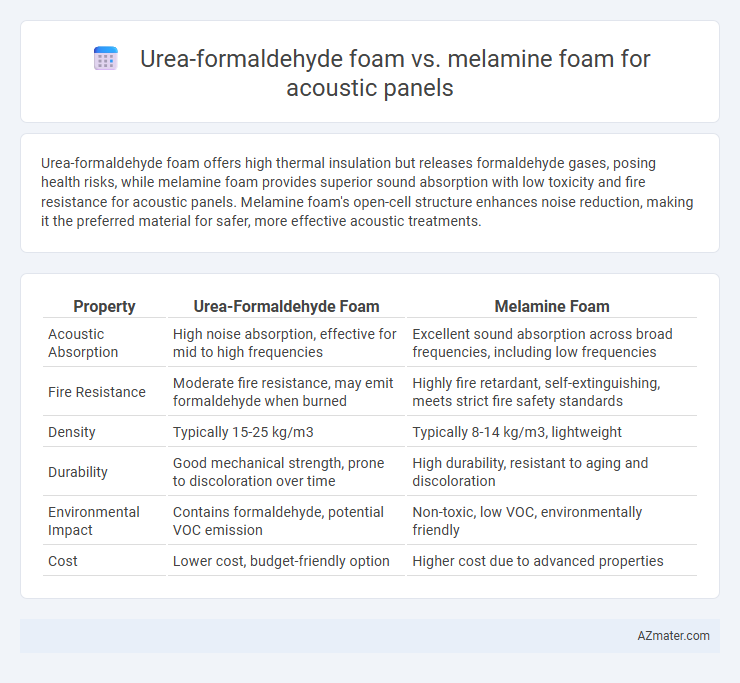
Urea-formaldehyde foam offers high thermal insulation but releases formaldehyde gases, posing health risks, while melamine foam provides superior sound absorption with low toxicity and fire resistance for acoustic panels. Melamine foam's open-cell structure enhances noise reduction, making it the preferred material for safer, more effective acoustic treatments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Urea-Formaldehyde Foam | Melamine Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Acoustic Absorption | High noise absorption, effective for mid to high frequencies | Excellent sound absorption across broad frequencies, including low frequencies |
| Fire Resistance | Moderate fire resistance, may emit formaldehyde when burned | Highly fire retardant, self-extinguishing, meets strict fire safety standards |
| Density | Typically 15-25 kg/m3 | Typically 8-14 kg/m3, lightweight |
| Durability | Good mechanical strength, prone to discoloration over time | High durability, resistant to aging and discoloration |
| Environmental Impact | Contains formaldehyde, potential VOC emission | Non-toxic, low VOC, environmentally friendly |
| Cost | Lower cost, budget-friendly option | Higher cost due to advanced properties |
Introduction to Acoustic Panel Materials
Urea-formaldehyde foam and melamine foam are common materials used in acoustic panels with distinct properties and applications. Urea-formaldehyde foam offers excellent thermal insulation and moderate sound absorption but has limited fire resistance. Melamine foam provides superior sound absorption, fire retardancy, and durability, making it ideal for high-performance acoustic treatments in various environments.
Overview of Urea-Formaldehyde Foam
Urea-formaldehyde foam is a rigid, thermosetting plastic widely utilized in acoustic panels for its excellent sound insulation properties and cost-effectiveness. This foam exhibits low thermal conductivity, high compressive strength, and resistance to moisture, making it suitable for soundproofing applications in residential and commercial buildings. Its dense cellular structure effectively absorbs mid to high-frequency sound waves, enhancing overall acoustic performance.
Overview of Melamine Foam
Melamine foam offers superior sound absorption due to its open-cell structure and lightweight properties, making it ideal for acoustic panels in environments requiring high noise reduction. Unlike urea-formaldehyde foam, melamine foam provides enhanced fire resistance and better thermal insulation, contributing to safer and more efficient soundproofing solutions. Its durability and resistance to moisture also extend the lifespan of acoustic treatments in both residential and commercial applications.
Acoustic Performance Comparison
Urea-formaldehyde foam exhibits moderate acoustic absorption with a noise reduction coefficient (NRC) typically ranging from 0.30 to 0.60, making it effective for reducing mid to high-frequency sound reflections. Melamine foam offers superior acoustic performance, characterized by an NRC often exceeding 0.85, due to its open-cell structure that enhances sound wave dissipation across a broader frequency range. The higher porosity and density differentiation in melamine foam allow for improved broadband noise attenuation compared to the more rigid and chemically bound urea-formaldehyde foam.
Fire Resistance and Safety
Urea-formaldehyde foam, commonly used in acoustic panels, has limited fire resistance and emits toxic gases when exposed to high temperatures, posing significant safety risks. Melamine foam offers superior fire resistance due to its inherent flame-retardant properties and produces minimal smoke and toxic fumes during combustion. For applications demanding enhanced fire safety and compliance with strict building codes, melamine foam is a safer and more reliable choice for acoustic paneling.
Durability and Lifespan
Urea-formaldehyde foam exhibits moderate durability with a typical lifespan of 10-15 years, making it susceptible to degradation from moisture and UV exposure. Melamine foam offers superior durability and can maintain acoustic performance for over 20 years due to its high resistance to heat, moisture, and microbial growth. The longer lifespan and enhanced resilience of melamine foam make it a preferred choice for long-term acoustic panel applications in diverse environments.
Environmental Impact and Emissions
Urea-formaldehyde foam emits formaldehyde, a volatile organic compound contributing to indoor air pollution and respiratory issues, raising concerns about its environmental and health impact. Melamine foam, composed of melamine resin, offers lower emissions of harmful chemicals and is more environmentally friendly due to its non-toxic nature and better recyclability. Selecting melamine foam for acoustic panels supports sustainable indoor air quality and reduces ecological footprint compared to urea-formaldehyde alternatives.
Cost Analysis
Urea-formaldehyde foam offers a lower initial cost compared to melamine foam, making it a budget-friendly option for acoustic panels in large-scale projects. Melamine foam, while more expensive upfront, provides superior fire resistance and durability, potentially reducing long-term replacement and maintenance expenses. Considering lifecycle costs, melamine foam may deliver better value despite its higher price point due to enhanced acoustic performance and safety benefits.
Installation and Maintenance
Urea-formaldehyde foam acoustic panels offer lightweight installation with ease of cutting and shaping but require careful handling due to potential formaldehyde emissions, making proper ventilation essential during setup. Melamine foam panels provide straightforward installation through adhesive or mechanical fixing, benefiting from inherent fire resistance and minimal off-gassing, which reduces indoor air quality concerns during and after installation. Maintenance for urea-formaldehyde panels involves cautious cleaning to avoid degradation and potential emission release, whereas melamine foam demands low maintenance with resistance to mold, moisture, and simple surface cleaning.
Best Applications and Recommendations
Urea-formaldehyde foam offers excellent thermal insulation and is ideal for basic soundproofing in residential and office environments where cost efficiency is a priority. Melamine foam provides superior acoustic absorption and fire resistance, making it the best choice for professional recording studios, theaters, and high-performance acoustic panel applications. For environments requiring enhanced fire safety and clear sound diffusion, melamine foam panels are strongly recommended over urea-formaldehyde foam.
Infographic: Urea-formaldehyde foam vs Melamine foam for Acoustic panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com