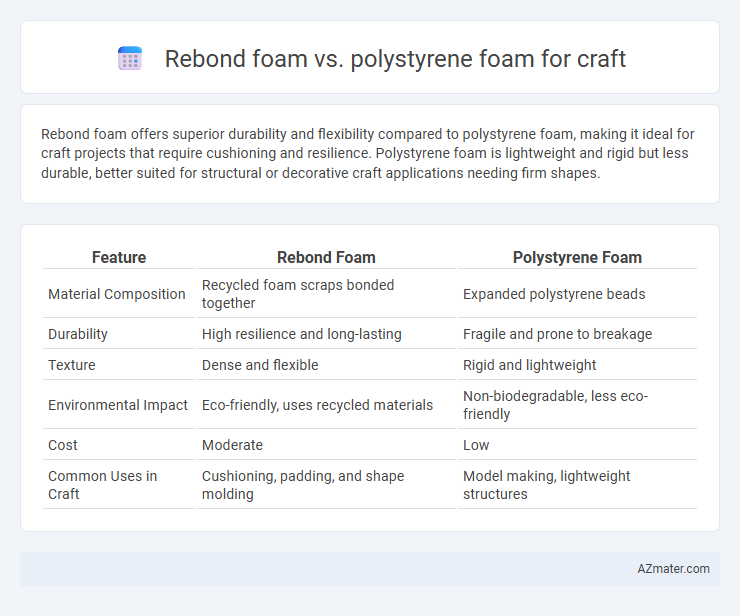
Rebond foam offers superior durability and flexibility compared to polystyrene foam, making it ideal for craft projects that require cushioning and resilience. Polystyrene foam is lightweight and rigid but less durable, better suited for structural or decorative craft applications needing firm shapes.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Rebond Foam | Polystyrene Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Recycled foam scraps bonded together | Expanded polystyrene beads |
| Durability | High resilience and long-lasting | Fragile and prone to breakage |
| Texture | Dense and flexible | Rigid and lightweight |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, uses recycled materials | Non-biodegradable, less eco-friendly |
| Cost | Moderate | Low |
| Common Uses in Craft | Cushioning, padding, and shape molding | Model making, lightweight structures |
Introduction to Rebond Foam and Polystyrene Foam
Rebond foam, composed of shredded scrap foam bonded together under heat and pressure, offers enhanced durability and flexibility for craft projects requiring cushioning and structural integrity. Polystyrene foam, a lightweight, rigid material made from expanded beads, provides excellent insulation and shape retention, ideal for model making and lightweight sculptures. Both foams serve distinct purposes in crafting, with rebond foam favored for impact absorption and polystyrene valued for its ease of carving and painting.
Key Properties of Rebond Foam
Rebond foam, made from shredded foam scraps bonded together, offers superior density and durability compared to lightweight polystyrene foam, making it ideal for high-impact craft projects. Its excellent cushioning properties and resistance to compression ensure long-lasting support and shape retention, unlike brittle polystyrene which can easily crack. Rebond foam also provides better thermal insulation and sound absorption, enhancing both comfort and functional performance in craft applications.
Key Properties of Polystyrene Foam
Polystyrene foam features a lightweight, rigid structure and excellent moisture resistance, making it ideal for precise craft applications requiring durability and shape retention. Its low thermal conductivity and high compressive strength provide effective insulation and protection for delicate projects. This foam's smooth surface allows easy painting and detailed finishing, enhancing its versatility in artistic and craft uses.
Durability Comparison: Rebond vs Polystyrene Foam
Rebond foam exhibits superior durability compared to polystyrene foam due to its dense and resilient composition made from recycled foam scraps bonded together under heat and pressure. Polystyrene foam, while lightweight and cost-effective, tends to be more brittle and prone to cracking or crumbling under stress or prolonged use. The enhanced toughness and compression resistance of rebond foam make it a preferred choice for craft projects requiring long-lasting structural integrity.
Weight and Flexibility Differences
Rebond foam is denser and heavier compared to polystyrene foam, making it more suitable for applications requiring durability and cushioning. Polystyrene foam offers superior flexibility and lighter weight, ideal for lightweight craft projects that need easy shaping and cutting. Weight differences play a significant role in project choice, with rebond foam providing sturdiness while polystyrene ensures ease of manipulation.
Cost Analysis for Craft Applications
Rebond foam offers a cost-effective alternative to polystyrene foam in craft applications due to its utilization of recycled foam scraps, reducing raw material expenses by up to 30%. Polystyrene foam, while lightweight and easy to shape, often incurs higher costs due to its petroleum-based production and limited recyclability. Evaluating long-term expenses, rebond foam's durability and potential for reuse can further lower overall craft project budgets compared to single-use polystyrene foam.
Suitability for Sculpting and Shaping
Rebond foam offers superior flexibility and density, making it ideal for detailed sculpting and shaping in craft projects where precision and durability are crucial. Polystyrene foam, being lightweight and rigid, is easier to cut but less adaptable for intricate contours or smoothing, often requiring additional coating for finishing. For crafts demanding fine detail and resilience, rebond foam provides enhanced suitability over polystyrene foam.
Adhesion and Painting Compatibility
Rebond foam offers superior adhesion due to its porous texture that allows glues and primers to bond effectively, making it ideal for craft projects requiring strong attachment. Polystyrene foam, while lightweight and easy to shape, often repels water-based paints and adhesives, necessitating the use of specialized primers or paint designed for non-porous surfaces. The choice between rebond and polystyrene foam depends largely on the intended finish and durability of the craft, with rebond foam providing better compatibility for multi-layer adhesion and painting.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Rebond foam, made from recycled foam scraps, offers a sustainable alternative to polystyrene foam, which is derived from petroleum-based non-biodegradable materials. The recycling process of rebond foam significantly reduces landfill waste and lowers carbon emissions compared to the energy-intensive production and disposal challenges associated with polystyrene foam. Choosing rebond foam for crafts supports environmental conservation by promoting material reuse and reducing plastic pollution.
Choosing the Best Foam for Your Craft Project
Rebond foam offers high durability and excellent cushioning, making it ideal for craft projects that require long-lasting, resilient materials. Polystyrene foam, lightweight and easy to shape, suits intricate designs and model-making where precision and detail are essential. Selecting the best foam depends on the specific craft requirements: rebond foam for robust support and impact resistance, or polystyrene foam for versatility and ease of carving.
Infographic: Rebond foam vs Polystyrene foam for Craft
 azmater.com
azmater.com