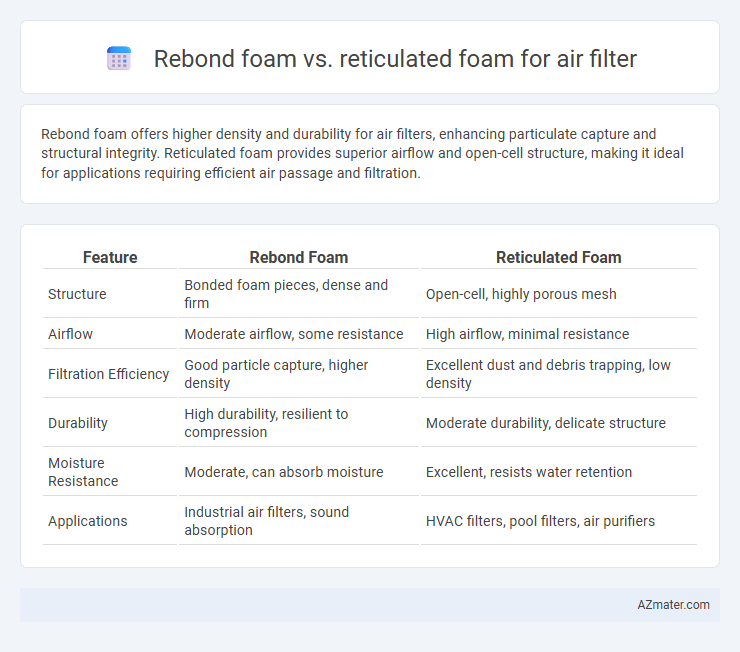
Rebond foam offers higher density and durability for air filters, enhancing particulate capture and structural integrity. Reticulated foam provides superior airflow and open-cell structure, making it ideal for applications requiring efficient air passage and filtration.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Rebond Foam | Reticulated Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Bonded foam pieces, dense and firm | Open-cell, highly porous mesh |
| Airflow | Moderate airflow, some resistance | High airflow, minimal resistance |
| Filtration Efficiency | Good particle capture, higher density | Excellent dust and debris trapping, low density |
| Durability | High durability, resilient to compression | Moderate durability, delicate structure |
| Moisture Resistance | Moderate, can absorb moisture | Excellent, resists water retention |
| Applications | Industrial air filters, sound absorption | HVAC filters, pool filters, air purifiers |
Introduction to Air Filter Foams
Air filter foams play a crucial role in trapping airborne particles while allowing optimal airflow to engines and HVAC systems. Rebond foam, made from shredded polyurethane scraps bonded together, offers durability and effective particle capture due to its dense structure. Reticulated foam features an open-cell network that enhances air permeability and filtration efficiency, making it ideal for high-performance air filters requiring minimal airflow resistance.
What is Rebond Foam?
Rebond foam is a durable, dense material made by bonding shredded foam scraps together using adhesive and heat, resulting in a firm structure ideal for air filter applications requiring high filtration efficiency and mechanical strength. It offers superior airflow resistance and excellent dust-holding capacity, making it suitable for industrial and HVAC air filtration systems. Unlike reticulated foam, which features an open-cell structure for maximum porosity, rebond foam balances filtration performance with structural integrity for long-lasting use.
What is Reticulated Foam?
Reticulated foam is a highly porous, open-cell polyurethane material designed for efficient air filtration, allowing maximum airflow while capturing airborne particles. Its structure results from a chemical searing process that removes cell membranes, creating an interconnected web ideal for air filter applications. Compared to rebond foam, reticulated foam offers superior filtration performance and better breathability, making it a preferred choice in HVAC and automotive air filters.
Structural Differences Between Rebond and Reticulated Foam
Rebond foam is composed of shredded PU foam pieces fused together, creating a dense and resilient structure with limited airflow, ideal for heavy-duty air filtration applications. Reticulated foam features an open-cell network formed by removing cell membranes, resulting in a highly porous material that promotes superior air permeability and particulate capture. The structural difference, where rebond foam exhibits closed-cell density and reticulated foam possesses interconnected pores, directly affects filtration efficiency and pressure drop in air filter systems.
Filtration Efficiency: Rebond vs Reticulated Foam
Rebond foam offers moderate filtration efficiency due to its dense, closed-cell structure that traps larger particles but allows finer particles to pass through, making it suitable for general dust filtration. Reticulated foam exhibits superior filtration efficiency with an open-cell, porous structure that effectively captures fine particles and promotes high airflow, ideal for high-performance air filter applications. Reticulated foam's enhanced permeability and particle retention make it the preferred choice in environments requiring precise air quality control.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
Rebond foam and reticulated foam differ significantly in durability and lifespan when used in air filters. Rebond foam is denser and more resilient, offering superior structural integrity and longer service life under high-stress or harsh environmental conditions. Reticulated foam features an open-cell structure that enhances airflow but tends to degrade faster, resulting in shorter durability compared to the robust performance of rebond foam in prolonged filtration applications.
Cost Analysis: Which Foam Is More Economical?
Rebond foam typically costs less than reticulated foam due to its production process involving shredded foam pieces bonded together, making it a budget-friendly option for air filters. Reticulated foam, with its open-cell structure and higher filtration efficiency, generally commands a higher price but may reduce maintenance expenses over time. Evaluating total cost of ownership, rebond foam offers upfront savings, while reticulated foam can be more economical in applications requiring frequent air cleaning and longevity.
Applications: Where Each Foam Excels
Rebond foam excels in applications requiring high-density cushioning and soundproofing, making it ideal for HVAC filters where vibration dampening and structural support are critical. Reticulated foam outperforms in air filtration systems demanding maximum airflow and efficient particle capture due to its open-cell structure and high porosity. Both materials are chosen based on specific filtration environments, with rebond foam suited for heavy-duty filtering and reticulated foam preferred in high-ventilation scenarios.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Rebond foam and reticulated foam differ significantly in environmental impact and sustainability for air filters, with rebond foam often derived from recycled foam scraps, promoting waste reduction and circular economy practices. Reticulated foam typically features higher porosity and durability, but its manufacturing process may involve petrochemical-based materials with limited biodegradability, influencing its ecological footprint. Choosing rebond foam supports eco-friendly initiatives by reusing materials, while reticulated foam offers performance advantages that require careful disposal or recycling strategies to minimize environmental harm.
Choosing the Right Foam for Your Air Filter Needs
Rebond foam offers dense, durable filtration with excellent dust-trapping capabilities, ideal for industrial or heavy-duty air filter applications requiring high particle retention. Reticulated foam provides a porous, open-cell structure that maximizes airflow while effectively capturing larger debris, making it suitable for HVAC systems and environments needing superior ventilation. Selecting the right foam depends on balancing filtration efficiency, airflow requirements, and environmental conditions to optimize air quality and filter lifespan.
Infographic: Rebond foam vs Reticulated foam for Air filter
 azmater.com
azmater.com