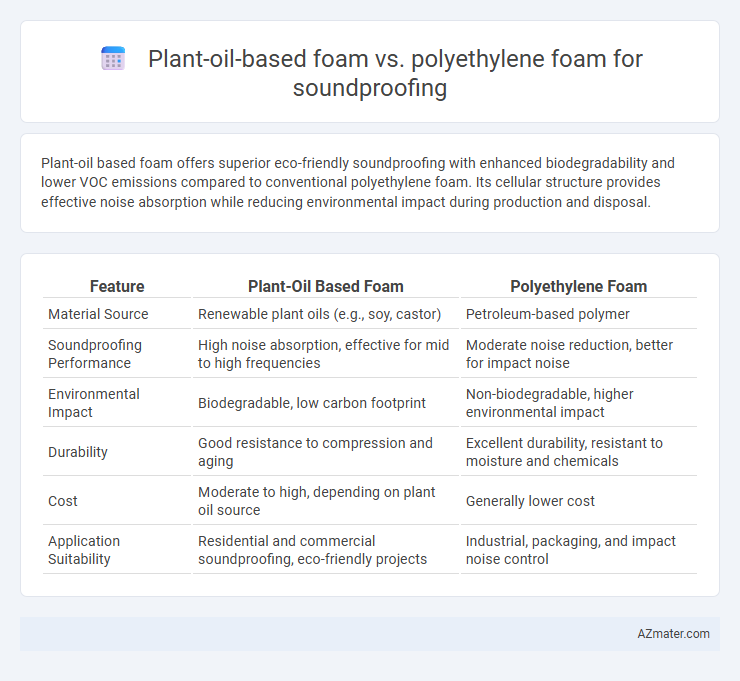
Plant-oil based foam offers superior eco-friendly soundproofing with enhanced biodegradability and lower VOC emissions compared to conventional polyethylene foam. Its cellular structure provides effective noise absorption while reducing environmental impact during production and disposal.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Plant-Oil Based Foam | Polyethylene Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Renewable plant oils (e.g., soy, castor) | Petroleum-based polymer |
| Soundproofing Performance | High noise absorption, effective for mid to high frequencies | Moderate noise reduction, better for impact noise |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, low carbon footprint | Non-biodegradable, higher environmental impact |
| Durability | Good resistance to compression and aging | Excellent durability, resistant to moisture and chemicals |
| Cost | Moderate to high, depending on plant oil source | Generally lower cost |
| Application Suitability | Residential and commercial soundproofing, eco-friendly projects | Industrial, packaging, and impact noise control |
Introduction to Plant-Oil Based and Polyethylene Foams
Plant-oil based foam is an eco-friendly alternative derived from renewable resources such as soybean or castor oil, offering enhanced biodegradability and lower environmental impact compared to traditional materials. Polyethylene foam, a widely used synthetic polymer, provides excellent sound absorption and durability but is typically non-biodegradable and relies on petrochemical sources. Both materials serve acoustic insulation purposes, with plant-oil based foam increasingly favored for sustainable construction and green building certifications.
Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Plant-oil based foam is derived from bio-based polyols sourced from renewable plant oils, such as soy or castor, and undergoes a chemical reaction with isocyanates to create a polyurethane foam matrix, emphasizing sustainability and eco-friendliness. Polyethylene foam, made from polymerized ethylene gas, involves extrusion or molding processes that produce a closed-cell foam structure reputed for its durability and high resistance to moisture. The manufacturing of plant-oil based foam integrates greener chemistry principles, reducing reliance on fossil fuels, while polyethylene foam manufacturing prioritizes thermoplastic processing techniques suitable for mass production and stability.
Acoustic Performance Comparison
Plant-oil based foam demonstrates superior sound absorption coefficients across mid-to-high frequency ranges compared to traditional polyethylene foam, enhancing its effectiveness in reducing echo and reverberation. Its open-cell structure contributes to higher noise reduction coefficients (NRC), typically ranging from 0.65 to 0.80, whereas polyethylene foam often exhibits NRC values between 0.40 and 0.55. Moreover, plant-oil based foam offers improved damping characteristics, making it a more efficient material for acoustic insulation in soundproofing applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Plant-oil based foam offers a significantly lower environmental impact compared to traditional polyethylene foam, as it is derived from renewable resources and is often biodegradable, reducing landfill waste and microplastic pollution. Its production process typically generates fewer greenhouse gas emissions and consumes less non-renewable energy, enhancing sustainability in building materials. In contrast, polyethylene foam relies on fossil fuels, is non-biodegradable, and contributes to persistent environmental pollution, making plant-oil based foam a more eco-friendly choice for soundproofing applications.
Cost and Economic Considerations
Plant-oil based foam typically offers a higher upfront cost compared to traditional polyethylene foam due to sustainable raw materials and eco-friendly manufacturing processes. However, its biodegradability and lower environmental impact can result in long-term economic benefits such as reduced waste management expenses and potential tax incentives. Polyethylene foam remains cheaper initially and widely available, making it a common choice for budget-sensitive soundproofing projects despite lesser sustainability credentials.
Installation and Handling Differences
Plant-oil based foam offers easier cutting and shaping due to its softer, more pliable texture compared to polyethylene foam, reducing installation time and effort. Its lightweight nature allows for simple handling and positioning in tight spaces, while polyethylene foam demands more precision tools and protective equipment because of its denser, tougher composition. The biodegradable properties of plant-oil foam also simplify disposal after installation, contrasting with the non-biodegradable waste generated by polyethylene foam.
Durability and Lifespan
Plant-oil based foam exhibits enhanced durability due to its natural resilience and resistance to compression over time, maintaining soundproofing performance effectively. In contrast, polyethylene foam tends to degrade faster under prolonged exposure to environmental stressors, leading to reduced lifespan and diminished acoustic insulation capability. The sustainable composition of plant-oil based foam contributes to longer-lasting soundproofing applications, making it a superior choice for durability-focused projects.
Health and Safety Implications
Plant-oil based foam offers a non-toxic, biodegradable alternative to traditional polyethylene foam, reducing exposure to harmful volatile organic compounds (VOCs) during installation and use. Polyethylene foam often emits VOCs and may contain chemical additives that pose long-term respiratory risks and flammability concerns. Using plant-oil based foam enhances indoor air quality and minimizes environmental impact, making it a safer choice for soundproofing in residential and commercial settings.
Market Availability and Applications
Plant-oil based foam offers a sustainable alternative to traditional polyethylene foam in soundproofing, gaining traction in eco-conscious markets due to its biodegradable properties and renewable raw materials. Polyethylene foam remains widely available and extensively used across automotive, construction, and packaging industries for its durability, moisture resistance, and cost-effectiveness. While polyethylene foam dominates general soundproofing applications, plant-oil based foam is expanding its presence in niche markets prioritizing green building standards and indoor air quality improvements.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Foam for Soundproofing
Plant-oil based foam offers eco-friendly advantages with effective sound absorption and reduced environmental impact compared to traditional polyethylene foam. Polyethylene foam provides superior durability, moisture resistance, and cost-efficiency, making it suitable for long-term or industrial applications. Selecting the right foam depends on balancing environmental goals with performance needs and budget constraints for optimal soundproofing results.
Infographic: Plant-oil based foam vs Polyethylene foam for Soundproofing
 azmater.com
azmater.com