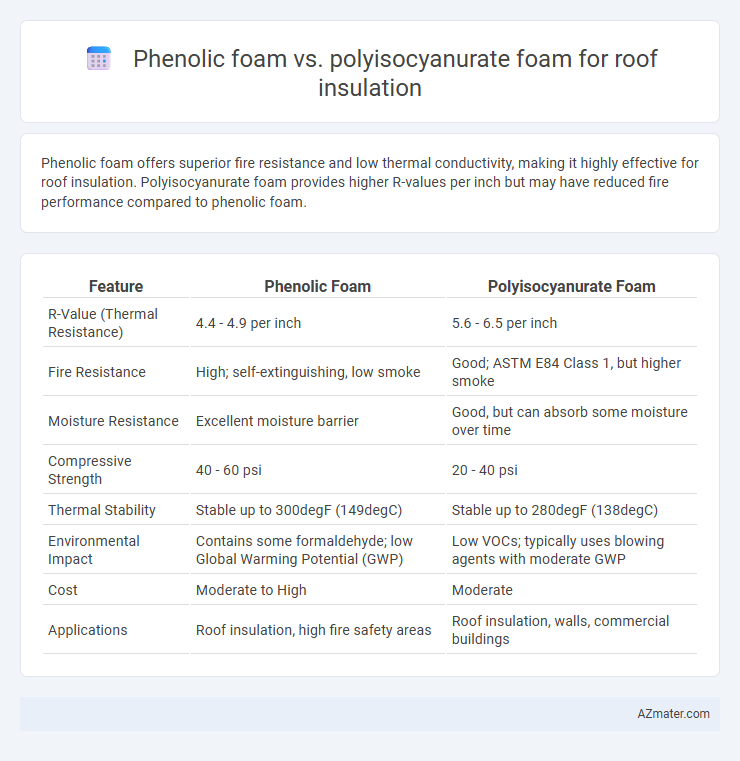
Phenolic foam offers superior fire resistance and low thermal conductivity, making it highly effective for roof insulation. Polyisocyanurate foam provides higher R-values per inch but may have reduced fire performance compared to phenolic foam.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Phenolic Foam | Polyisocyanurate Foam |
|---|---|---|
| R-Value (Thermal Resistance) | 4.4 - 4.9 per inch | 5.6 - 6.5 per inch |
| Fire Resistance | High; self-extinguishing, low smoke | Good; ASTM E84 Class 1, but higher smoke |
| Moisture Resistance | Excellent moisture barrier | Good, but can absorb some moisture over time |
| Compressive Strength | 40 - 60 psi | 20 - 40 psi |
| Thermal Stability | Stable up to 300degF (149degC) | Stable up to 280degF (138degC) |
| Environmental Impact | Contains some formaldehyde; low Global Warming Potential (GWP) | Low VOCs; typically uses blowing agents with moderate GWP |
| Cost | Moderate to High | Moderate |
| Applications | Roof insulation, high fire safety areas | Roof insulation, walls, commercial buildings |
Introduction to Roof Insulation Materials
Phenolic foam and polyisocyanurate foam are both advanced roof insulation materials known for their high thermal resistance and fire retardant properties. Phenolic foam offers a low thermal conductivity of approximately 0.021 W/m*K, making it highly efficient in reducing heat transfer, while polyisocyanurate foam provides thermal resistance typically ranging from R-6 to R-8 per inch. Selection between these materials depends on factors such as required insulation performance, fire ratings, moisture resistance, and compatibility with roofing systems.
Overview of Phenolic Foam
Phenolic foam is a rigid, closed-cell insulation material known for its superior fire resistance, low smoke emission, and excellent thermal performance with R-values typically ranging from 3.8 to 4.2 per inch. Its high compressive strength and dimensional stability make it ideal for roof insulation applications where durability and long-term performance are critical. Phenolic foam's low thermal conductivity and moisture resistance contribute to enhanced energy efficiency and building envelope protection compared to conventional insulation options.
Overview of Polyisocyanurate (PIR) Foam
Polyisocyanurate (PIR) foam is a rigid, closed-cell insulation material widely used in roofing systems due to its high thermal resistance, typically boasting R-values between 6 and 7 per inch. Its superior fire resistance and moisture tolerance make PIR foam an ideal choice over phenolic foam for flat and pitched roof applications requiring long-term durability. PIR foam also offers enhanced structural integrity while maintaining lightweight properties that contribute to easy installation and reduced roof load.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Phenolic foam exhibits a thermal conductivity typically around 0.020 W/m*K, offering superior insulation efficiency compared to polyisocyanurate foam, which ranges from 0.022 to 0.028 W/m*K. The closed-cell structure of phenolic foam provides exceptional thermal resistance and better long-term dimensional stability under varying temperatures. Polyisocyanurate foam, while slightly less efficient in thermal performance, offers higher fire resistance and greater structural rigidity, making it suitable for specific roof insulation requirements despite its marginally higher thermal conductivity.
Fire Resistance and Safety
Phenolic foam offers superior fire resistance compared to polyisocyanurate foam due to its low flame spread and smoke development indices, making it a safer option for roof insulation in fire-prone areas. Polyisocyanurate foam typically exhibits higher thermal insulation values but can produce toxic gases when exposed to high temperatures, posing fire safety concerns. Choosing phenolic foam enhances overall roof safety by minimizing flame propagation and reducing harmful smoke emissions during fires.
Moisture and Water Resistance
Phenolic foam exhibits superior moisture resistance compared to polyisocyanurate foam, making it highly effective in preventing water absorption and maintaining insulation performance in damp conditions. Polyisocyanurate foam, while offering good thermal insulation, tends to absorb more moisture over time, which can compromise its structural integrity and R-value. The closed-cell structure of phenolic foam provides enhanced water repellency and durability, critical for long-term roof insulation in moist environments.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Phenolic foam outperforms polyisocyanurate foam in environmental impact due to its lower global warming potential and reduced ozone depletion potential. Phenolic foam contains fewer harmful blowing agents, leading to decreased greenhouse gas emissions throughout its lifecycle. Sustainability is enhanced by phenolic foam's superior thermal durability, which extends roof lifespan and reduces energy consumption for heating and cooling.
Installation Process and Handling
Phenolic foam offers a lightweight and rigid structure, making it easier to cut and shape during roof insulation installation, with minimal dust generation and a low risk of skin irritation. Polyisocyanurate foam requires careful handling due to its susceptibility to moisture absorption and brittleness, often necessitating protective gear and precision cutting tools to maintain its thermal efficiency. Both materials demand proper sealing and joint treatment to prevent heat loss and moisture ingress, but phenolic foam typically allows faster installation due to its uniform density and ease of customization on-site.
Cost Analysis and Long-Term Value
Phenolic foam generally offers lower initial costs compared to polyisocyanurate foam, making it a budget-friendly option for roof insulation projects. Polyisocyanurate foam, while more expensive upfront, provides superior thermal performance and higher R-values, resulting in better energy savings and reduced long-term utility costs. Over time, the enhanced durability and moisture resistance of polyisocyanurate foam contribute to greater longevity and overall value, potentially offsetting the higher initial investment.
Choosing the Right Foam for Your Roof
Phenolic foam offers superior fire resistance and low smoke emission, making it ideal for roofs requiring enhanced safety standards, while polyisocyanurate foam provides higher R-values per inch, ensuring better thermal insulation for energy-efficient buildings. Polyisocyanurate's moisture resistance and dimensional stability suit varied climates, whereas phenolic foam excels in sound dampening and chemical resistance. Selecting the right foam depends on balancing thermal performance, fire safety, moisture control, and budget constraints specific to your roofing project.
Infographic: Phenolic foam vs Polyisocyanurate foam for Roof insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com