Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam offers excellent chemical resistance and durability, making it suitable for gasket applications in harsh environments. Nitrile rubber foam provides superior oil and fuel resistance along with enhanced flexibility, ideal for sealing in automotive and industrial settings.
Table of Comparison
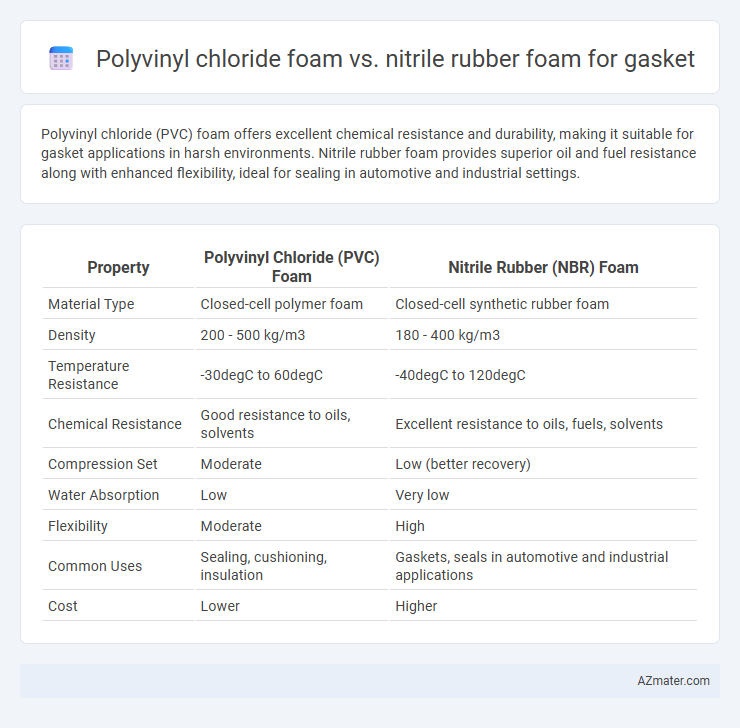
| Property | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Foam | Nitrile Rubber (NBR) Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Closed-cell polymer foam | Closed-cell synthetic rubber foam |
| Density | 200 - 500 kg/m3 | 180 - 400 kg/m3 |
| Temperature Resistance | -30degC to 60degC | -40degC to 120degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to oils, solvents | Excellent resistance to oils, fuels, solvents |
| Compression Set | Moderate | Low (better recovery) |
| Water Absorption | Low | Very low |
| Flexibility | Moderate | High |
| Common Uses | Sealing, cushioning, insulation | Gaskets, seals in automotive and industrial applications |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Gasket Material Selection
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam and nitrile rubber foam are widely used materials for gasket applications due to their unique physical and chemical properties. PVC foam offers excellent resistance to moisture, chemicals, and abrasion, making it suitable for environments requiring durability and flexibility. Nitrile rubber foam demonstrates superior oil, fuel, and chemical resistance, combined with high compressibility and recovery, ideal for sealing in automotive and industrial machinery.
Overview of Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Foam
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam is a lightweight, closed-cell material known for its excellent chemical resistance, durability, and ease of fabrication, making it ideal for gasket applications in automotive and construction industries. PVC foam provides superior compression set resistance and good thermal insulation, maintaining performance across a wide temperature range from -15degC to 80degC. Compared to nitrile rubber foam, PVC foam offers better resistance to moisture and UV exposure, enhancing gasket longevity in outdoor environments.
Overview of Nitrile Rubber Foam
Nitrile rubber foam offers excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals, making it ideal for gasket applications in automotive and industrial settings. Its closed-cell structure provides superior compressibility and cushioning compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam, which tends to have lower chemical resistance and durability. The temperature tolerance of nitrile rubber foam ranges from -40degC to 120degC, ensuring reliable performance in demanding environments where PVC foam may degrade.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam gaskets offer excellent rigidity, high tensile strength, and moderate compression set resistance, making them suitable for applications requiring durability and shape retention under mechanical stress. Nitrile rubber foam gaskets provide superior elasticity, excellent resistance to abrasion, and better tensile elongation, which enhances sealing performance in dynamic or vibrating environments. Compared to PVC foam, nitrile foam's enhanced mechanical flexibility and resilience to oil and chemical exposure make it more adaptable for industrial equipment and automotive sealing applications.
Chemical Resistance: PVC Foam vs Nitrile Rubber Foam
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam exhibits superior resistance to acids, alkalis, and oils, making it ideal for chemical environments involving solvents and corrosive substances. In contrast, nitrile rubber (NBR) foam offers exceptional resistance to petroleum-based oils, fuels, and greases, excelling in automotive and industrial applications where hydrocarbon exposure is frequent. PVC foam's chemical stability is generally broader, while nitrile foam is preferred for applications requiring high resistance to oil and fuel-based chemicals.
Temperature Performance and Stability
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam offers good chemical resistance and moderate temperature stability, typically performing well in temperature ranges from -15degC to 60degC, making it suitable for general gasket applications with limited heat exposure. Nitrile rubber foam exhibits superior temperature performance and stability, enduring temperatures from -40degC to 120degC while maintaining excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and abrasion, which enhances its suitability for demanding industrial gasket applications. The choice depends on the specific thermal and chemical environment, with nitrile foam preferred for higher temperature resistance and PVC foam favored for cost-effective, moderate temperature seals.
Compression Set and Recovery
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam gaskets exhibit moderate compression set resistance, typically around 20-35%, making them suitable for static sealing but less ideal for applications requiring frequent compression cycles. Nitrile rubber (NBR) foam gaskets demonstrate superior compression set performance, often below 15%, due to their elastomeric properties, which enable rapid recovery and maintain seal integrity under dynamic stress. The enhanced recovery of nitrile foam ensures longer gasket lifespan and better sealing reliability, especially in environments involving oil exposure and mechanical movement.
Applications and Industry Usage
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam is widely used in automotive, construction, and marine industries due to its excellent weather resistance, durability, and chemical stability, making it ideal for sealing and cushioning gaskets exposed to harsh environments. Nitrile rubber foam, favored in aerospace, oil and gas, and manufacturing sectors, offers superior oil and fuel resistance along with excellent compression recovery, crucial for dynamic sealing applications in engine compartments and machinery. Both materials provide effective sealing solutions, but PVC foam is preferred for static sealing in exterior conditions, while nitrile rubber foam excels in applications requiring high resilience and fluid exposure resistance.
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam offers superior cost-effectiveness for gasket applications due to its lower material and manufacturing expenses compared to nitrile rubber (NBR) foam. PVC foam provides adequate resistance to water, chemicals, and moderate temperatures, making it an economical choice for general-purpose sealing without sacrificing durability. Nitrile rubber foam, while more expensive, excels in oil, fuel, and high-temperature resistance, justifying higher costs in specialized industrial environments where performance requirements demand enhanced chemical and thermal stability.
Choosing the Right Foam for Your Gasket Needs
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam offers excellent chemical resistance and durability, making it ideal for environments exposed to oils, acids, and solvents, while nitrile rubber foam excels in oil resistance and flexibility under varying temperatures. When choosing the right foam for your gasket needs, consider PVC foam for applications requiring rigidity and long-term weather resistance, whereas nitrile rubber foam suits dynamic seals needing high elasticity and superior compression set recovery. Evaluating factors like temperature range, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress ensures optimal gasket performance and longevity.
Infographic: Polyvinyl chloride foam vs Nitrile rubber foam for Gasket
 azmater.com
azmater.com