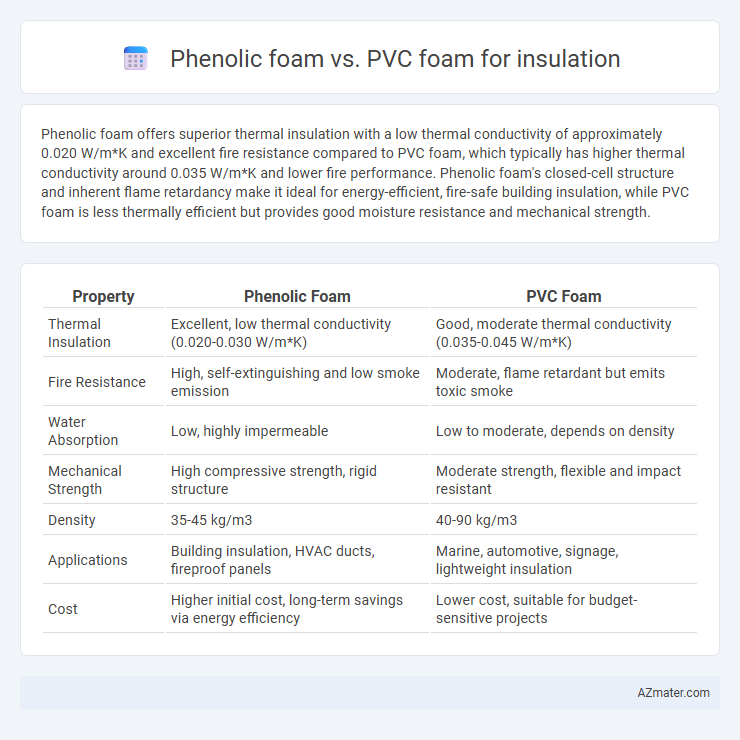
Phenolic foam offers superior thermal insulation with a low thermal conductivity of approximately 0.020 W/m*K and excellent fire resistance compared to PVC foam, which typically has higher thermal conductivity around 0.035 W/m*K and lower fire performance. Phenolic foam's closed-cell structure and inherent flame retardancy make it ideal for energy-efficient, fire-safe building insulation, while PVC foam is less thermally efficient but provides good moisture resistance and mechanical strength.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Phenolic Foam | PVC Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Insulation | Excellent, low thermal conductivity (0.020-0.030 W/m*K) | Good, moderate thermal conductivity (0.035-0.045 W/m*K) |
| Fire Resistance | High, self-extinguishing and low smoke emission | Moderate, flame retardant but emits toxic smoke |
| Water Absorption | Low, highly impermeable | Low to moderate, depends on density |
| Mechanical Strength | High compressive strength, rigid structure | Moderate strength, flexible and impact resistant |
| Density | 35-45 kg/m3 | 40-90 kg/m3 |
| Applications | Building insulation, HVAC ducts, fireproof panels | Marine, automotive, signage, lightweight insulation |
| Cost | Higher initial cost, long-term savings via energy efficiency | Lower cost, suitable for budget-sensitive projects |
Introduction to Phenolic Foam and PVC Foam Insulation
Phenolic foam insulation offers exceptional thermal resistance due to its closed-cell structure and low thermal conductivity, making it highly efficient for energy-saving applications in buildings and refrigeration. PVC foam insulation provides good durability, chemical resistance, and moderate thermal performance, often utilized in areas requiring moisture resistance and mechanical strength. Both materials serve distinct insulation needs, with phenolic foam excelling in fire retardancy and high thermal efficiency, while PVC foam is preferred for its versatility and environmental resistance.
Composition and Manufacturing Process
Phenolic foam is composed primarily of phenol-formaldehyde resin, produced through a polymerization process that creates a rigid, closed-cell structure with excellent fire resistance and low smoke emission. PVC foam consists of polyvinyl chloride resin combined with blowing agents to form a lightweight, closed-cell cellular structure, offering good chemical resistance and durability. The manufacturing of phenolic foam typically involves a two-step curing and foaming process, while PVC foam is produced through extrusion or molding methods that expand the resin into a foam form.
Thermal Insulation Properties
Phenolic foam offers superior thermal insulation performance with a low thermal conductivity of approximately 0.020-0.025 W/m*K, making it highly effective in reducing heat transfer. PVC foam typically has higher thermal conductivity values around 0.035-0.045 W/m*K, resulting in less efficient insulation compared to phenolic foam. The closed-cell structure of phenolic foam also contributes to better moisture resistance and consistent thermal properties over time.
Fire Resistance and Safety Performance
Phenolic foam offers superior fire resistance with a high limiting oxygen index (LOI) typically above 30%, producing minimal smoke and toxic gases during combustion, making it ideal for stringent safety standards. PVC foam, while providing decent insulation, has a lower LOI and tends to generate more smoke and harmful fumes under fire conditions. The enhanced fire safety performance of phenolic foam significantly reduces risks in residential and commercial insulation applications.
Moisture Resistance and Water Absorption
Phenolic foam exhibits superior moisture resistance and minimal water absorption, making it highly effective for insulation in humid environments. PVC foam also offers good moisture resistance but tends to absorb slightly more water than phenolic foam, which can reduce its insulating efficiency over time. The closed-cell structure of phenolic foam provides enhanced durability against moisture-related degradation compared to the more porous nature of PVC foam.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Phenolic foam offers superior mechanical strength with high compressive resistance and excellent fire retardant properties, making it ideal for structural insulation applications requiring durability over time. PVC foam exhibits moderate mechanical strength but excels in moisture resistance and dimensional stability, contributing to long-term durability in humid environments. Choosing between phenolic and PVC foam depends on performance priorities, where phenolic foam suits high-load conditions and PVC foam is preferred for flexible, water-resistant insulation solutions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Phenolic foam offers superior fire resistance and lower smoke emissions compared to PVC foam, making it a safer choice for building insulation with reduced environmental hazards. PVC foam, derived from polyvinyl chloride, involves chlorine-based production processes that release harmful dioxins and pose recycling challenges, impacting its sustainability negatively. Phenolic foam features higher thermal efficiency, leading to less energy consumption over time and a smaller carbon footprint, positioning it as a more eco-friendly insulation option.
Cost Comparison and Installation Considerations
Phenolic foam insulation typically offers a higher upfront cost compared to PVC foam due to its superior fire resistance and thermal performance, making it more cost-effective in long-term energy savings. PVC foam insulation is generally less expensive and easier to install, with lower labor costs attributed to its lightweight and flexible properties. Installation considerations include phenolic foam requiring precise handling to prevent damage, while PVC foam's moisture resistance can reduce the need for additional vapor barriers, impacting overall project expenses.
Common Applications in Construction and Industry
Phenolic foam is widely used for thermal insulation in cold storage facilities, HVAC ductwork, and industrial pipelines due to its excellent fire resistance and low smoke emission. PVC foam is preferred for lightweight structural insulation, wall panels, and decorative cladding in commercial buildings because of its moisture resistance and ease of fabrication. Both materials serve critical roles in balancing thermal performance and safety requirements across construction and industrial applications.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Foam Insulation
Phenolic foam offers superior thermal performance with a lower thermal conductivity of approximately 0.020 W/m*K, making it ideal for high-efficiency insulation needs. PVC foam provides better moisture resistance and structural strength, suitable for environments with high humidity or mechanical stress. Selecting between phenolic and PVC foam depends on balancing priorities like thermal insulation efficiency, moisture resistance, fire retardancy, and application-specific requirements.
Infographic: Phenolic foam vs PVC foam for Insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com