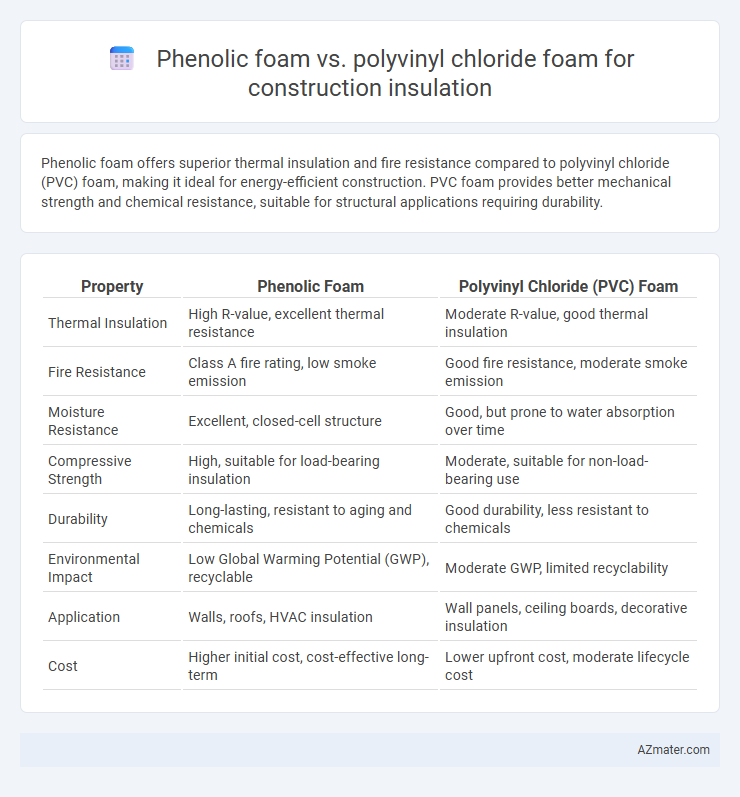
Phenolic foam offers superior thermal insulation and fire resistance compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam, making it ideal for energy-efficient construction. PVC foam provides better mechanical strength and chemical resistance, suitable for structural applications requiring durability.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Phenolic Foam | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Insulation | High R-value, excellent thermal resistance | Moderate R-value, good thermal insulation |
| Fire Resistance | Class A fire rating, low smoke emission | Good fire resistance, moderate smoke emission |
| Moisture Resistance | Excellent, closed-cell structure | Good, but prone to water absorption over time |
| Compressive Strength | High, suitable for load-bearing insulation | Moderate, suitable for non-load-bearing use |
| Durability | Long-lasting, resistant to aging and chemicals | Good durability, less resistant to chemicals |
| Environmental Impact | Low Global Warming Potential (GWP), recyclable | Moderate GWP, limited recyclability |
| Application | Walls, roofs, HVAC insulation | Wall panels, ceiling boards, decorative insulation |
| Cost | Higher initial cost, cost-effective long-term | Lower upfront cost, moderate lifecycle cost |
Introduction to Construction Insulation Materials
Phenolic foam offers superior thermal insulation with a low thermal conductivity of approximately 0.02 W/m*K, making it highly efficient for reducing energy consumption in buildings. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam provides durable, moisture-resistant insulation with excellent fire-retardant properties, featuring a density range between 40-80 kg/m3. Both materials contribute to enhanced building performance, but phenolic foam excels in thermal resistance while PVC foam is favored for its resilience and versatility in diverse construction applications.
Overview of Phenolic Foam
Phenolic foam is a high-performance insulation material known for its superior fire resistance, low smoke emission, and excellent thermal insulation properties, making it ideal for construction applications demanding stringent safety standards. Its closed-cell structure provides high compressive strength and excellent dimensional stability, ensuring durability and long-term energy efficiency in building envelopes. Compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam, phenolic foam exhibits greater resistance to heat and chemical exposure, positioning it as a premium choice for fire-rated walls and ceilings.
Overview of Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Foam
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam is a lightweight, closed-cell material widely used in construction insulation due to its excellent thermal resistance, moisture barrier properties, and fire retardancy. This foam exhibits high durability, chemical resistance, and dimensional stability, making it suitable for applications such as wall panels, roofing, and HVAC systems. Compared to phenolic foam, PVC foam offers enhanced mechanical strength and better resistance to water absorption, contributing to longer-lasting insulation performance in various environmental conditions.
Thermal Insulation Performance Comparison
Phenolic foam exhibits superior thermal insulation performance compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam, with a lower thermal conductivity typically around 0.020 to 0.025 W/m*K, which ensures better energy efficiency in construction applications. PVC foam generally has a higher thermal conductivity approximately between 0.035 to 0.045 W/m*K, resulting in less effective insulation properties. The closed-cell structure of phenolic foam also provides enhanced fire resistance and dimensional stability, making it a preferred choice for high-performance thermal insulation in buildings.
Fire Resistance and Safety Aspects
Phenolic foam exhibits superior fire resistance compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam, boasting a low flame spread index and the ability to self-extinguish, which significantly enhances building safety. It releases minimal toxic smoke and no halogenated gases during combustion, reducing health hazards in fire scenarios. PVC foam, while offering moderate fire resistance, produces more smoke and hazardous gases like hydrogen chloride, raising concerns for occupant safety in construction insulation applications.
Moisture Resistance and Durability
Phenolic foam offers superior moisture resistance in construction insulation due to its closed-cell structure, preventing water absorption and maintaining thermal performance over time. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam is less resistant to prolonged moisture exposure, which can lead to degradation and reduced insulation efficiency. Phenolic foam's enhanced durability under humid conditions makes it a preferred choice for applications requiring long-term moisture resistance and dimensional stability.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Phenolic foam offers superior thermal insulation with low smoke and toxicity levels, making it an environmentally preferable choice due to its fire-resistant properties and recyclability. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam, while effective in insulation, poses sustainability challenges because of its reliance on chlorine-based compounds and difficulties in recycling, which contribute to environmental pollution. Choosing phenolic foam supports greener building practices by reducing harmful emissions and enhancing energy efficiency over the building lifecycle.
Installation Ease and Flexibility
Phenolic foam offers superior installation ease due to its lightweight structure and excellent dimensional stability, allowing for quick and precise fitting in complex architectural designs. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam provides enhanced flexibility, accommodating irregular surfaces and dynamic building movements without compromising insulation performance. Both materials present distinct advantages, with phenolic foam excelling in straightforward application and PVC foam preferred for adaptability in diverse construction environments.
Cost Analysis and Long-term Value
Phenolic foam offers superior fire resistance and higher thermal efficiency but typically comes at a higher initial cost compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam. PVC foam provides a cheaper upfront investment and decent moisture resistance but may require more frequent replacement or maintenance, affecting long-term value. Evaluating lifecycle costs, phenolic foam often delivers better return on investment due to durability and energy savings in construction insulation projects.
Choosing the Right Foam for Your Construction Project
Phenolic foam offers superior fire resistance, low smoke emission, and excellent thermal insulation with a low thermal conductivity of around 0.020 W/m*K, making it ideal for high-safety construction projects. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam provides good chemical resistance, durability, and moisture resistance but generally has a higher thermal conductivity, approximately 0.035 W/m*K, which affects its insulation efficiency. Selecting phenolic foam enhances fire safety and energy efficiency, while PVC foam suits applications requiring robust resistance to chemicals and moisture.
Infographic: Phenolic foam vs Polyvinyl chloride foam for Construction insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com