Open-cell foam offers superior breathability and cushioning due to its porous structure, ideal for pressure relief padding. Polyethylene foam provides higher durability and water resistance, making it better suited for impact absorption and long-term use.
Table of Comparison
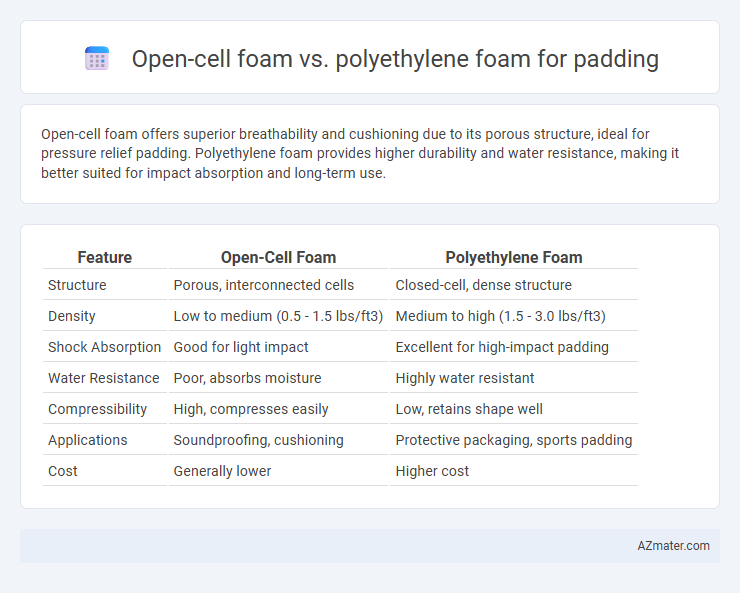
| Feature | Open-Cell Foam | Polyethylene Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Porous, interconnected cells | Closed-cell, dense structure |
| Density | Low to medium (0.5 - 1.5 lbs/ft3) | Medium to high (1.5 - 3.0 lbs/ft3) |
| Shock Absorption | Good for light impact | Excellent for high-impact padding |
| Water Resistance | Poor, absorbs moisture | Highly water resistant |
| Compressibility | High, compresses easily | Low, retains shape well |
| Applications | Soundproofing, cushioning | Protective packaging, sports padding |
| Cost | Generally lower | Higher cost |
Understanding Open-Cell Foam and Polyethylene Foam
Open-cell foam features interconnected air pockets making it softer, more compressible, and highly breathable, ideal for cushioning and sound absorption in padding applications. Polyethylene foam consists of closed cells filled with gas, providing higher density, excellent impact resistance, and superior moisture and chemical resistance, suitable for protective packaging and industrial padding. Understanding these material properties is essential for selecting the right foam based on factors like comfort, durability, and environmental exposure.
Key Properties and Structure Comparison
Open-cell foam offers excellent breathability and cushioning due to its interconnected porous structure, making it ideal for applications requiring softness and flexibility. Polyethylene foam features a closed-cell structure, providing superior moisture resistance, higher density, and better impact absorption, which is essential for protective padding and insulation. The key difference lies in the open-cell foam's lightweight, compressible nature versus polyethylene foam's durability and rigidity, affecting their suitability for various padding uses.
Durability and Longevity Differences
Open-cell foam offers superior cushioning and breathability but tends to wear out faster due to its softer structure, making it less durable for long-term padding applications. Polyethylene foam features a closed-cell design with higher density, providing excellent resistance to compression, moisture, and impact, which translates to enhanced durability and longer lifespan in padding solutions. For applications demanding sustained performance and durability, polyethylene foam is generally the preferred choice over open-cell foam.
Comfort and Cushioning Performance
Open-cell foam offers superior breathability and conformability, making it ideal for applications requiring enhanced comfort and pressure relief in padding. Polyethylene foam provides higher density and resilience, delivering excellent shock absorption and durability for long-lasting cushioning performance. Choosing between the two depends on the balance needed between softness and support in specific padding applications.
Moisture Resistance and Breathability
Open-cell foam offers superior breathability due to its interconnected cell structure, allowing air and moisture vapor to pass through easily, which reduces sweat buildup and enhances comfort in padding applications. Polyethylene foam, characterized by its closed-cell structure, provides excellent moisture resistance by preventing water absorption and acting as a barrier against liquids, making it ideal for environments prone to dampness. Choosing between open-cell and polyethylene foam depends on the requirement for ventilation versus waterproofing in padding materials.
Weight and Flexibility Considerations
Open-cell foam is significantly lighter and more flexible than polyethylene foam, making it ideal for applications requiring cushioning with minimal weight. Polyethylene foam offers greater density and rigidity, providing superior impact resistance but sacrificing some flexibility. When prioritizing lightweight, adaptable padding, open-cell foam excels, whereas polyethylene foam is better suited for durable, firm support.
Insulation and Thermal Properties
Open-cell foam offers superior breathability and moisture permeability but has lower thermal insulation compared to polyethylene foam, which provides excellent thermal resistance due to its closed-cell structure. Polyethylene foam's dense cellular makeup traps air effectively, minimizing heat transfer and making it ideal for thermal insulation applications. In contrast, open-cell foam is better suited for cushioning where airflow and moisture control are priorities, but it provides less effective insulation against temperature variations.
Common Applications in Padding
Open-cell foam is commonly used for cushioning in furniture, mattresses, and seat padding due to its softness and breathability, allowing air circulation and enhanced comfort. Polyethylene foam is frequently applied in packaging, protective padding for electronics, and sports equipment because of its high impact resistance, rigidity, and moisture resistance. Both materials serve crucial roles in padding, with open-cell foam favored for comfort applications and polyethylene foam chosen for durability and protection.
Cost Analysis: Which Is More Economical?
Open-cell foam typically offers a lower upfront cost compared to polyethylene foam due to its less dense structure and simpler manufacturing process. Polyethylene foam, although more expensive initially, provides greater durability and longer lifespan, potentially reducing replacement frequency and long-term expenses. Evaluating total cost of ownership, open-cell foam suits budget-sensitive applications, while polyethylene foam excels in high-impact or moisture-prone environments where durability offsets higher initial investment.
Choosing the Right Foam for Your Padding Needs
Open-cell foam offers superior breathability and cushioning, making it ideal for applications requiring comfort and airflow, such as seating and sensitive padding. Polyethylene foam provides excellent impact resistance, moisture resistance, and durability, suitable for protective packaging and heavy-duty padding in industrial settings. Selecting the right foam depends on specific needs: prioritize open-cell foam for softness and ventilation, while polyethylene foam is best for robust protection and environmental resistance.
Infographic: Open-cell foam vs Polyethylene foam for Padding
 azmater.com
azmater.com