High-density foam mattresses provide superior durability and support by maintaining shape and resilience over time, making them ideal for deep compression and long-term use. Low-density foam offers softer cushioning and better airflow but tends to wear out faster, making it suitable for budget-friendly or temporary sleeping solutions.
Table of Comparison
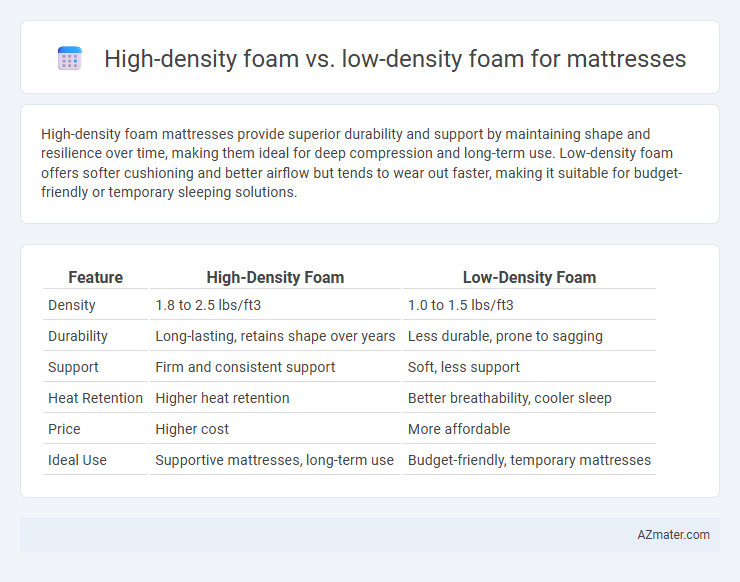
| Feature | High-Density Foam | Low-Density Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 1.8 to 2.5 lbs/ft3 | 1.0 to 1.5 lbs/ft3 |
| Durability | Long-lasting, retains shape over years | Less durable, prone to sagging |
| Support | Firm and consistent support | Soft, less support |
| Heat Retention | Higher heat retention | Better breathability, cooler sleep |
| Price | Higher cost | More affordable |
| Ideal Use | Supportive mattresses, long-term use | Budget-friendly, temporary mattresses |
Introduction to Foam Density in Mattresses
Foam density in mattresses measures the weight of foam per cubic foot, influencing durability, support, and comfort. High-density foam typically ranges from 4 to 6 pounds per cubic foot, offering enhanced longevity and better support for heavier body weights. Low-density foam, usually under 3 pounds per cubic foot, provides a softer feel and quicker responsiveness but may degrade faster over time.
What is High-Density Foam?
High-density foam is a type of polyurethane foam characterized by its higher mass per cubic foot, typically exceeding 5 pounds per cubic foot, providing greater durability and support in mattresses. It offers enhanced resilience and longevity, maintaining its shape and firmness over time compared to low-density foam, which usually weighs less than 3 pounds per cubic foot and tends to compress faster. High-density foam mattresses are ideal for sleepers seeking optimal spinal alignment and pressure relief due to their superior load-bearing capacity.
What is Low-Density Foam?
Low-density foam is a lightweight, soft material commonly used in mattresses for enhanced comfort and pressure relief. It typically has a density below 3 pounds per cubic foot, providing greater breathability and a plush feel but less durability compared to high-density foam. This type of foam is ideal for those seeking a softer sleeping surface with quicker response to movement.
Key Differences Between High and Low-Density Foam
High-density foam typically ranges from 1.8 to 3.0 pounds per cubic foot, offering superior durability, support, and motion isolation compared to low-density foam, which is usually under 1.5 pounds per cubic foot and tends to compress faster. High-density foam provides better pressure relief and longevity, making it ideal for sleepers seeking firm support and long-term use, while low-density foam is softer, more breathable, but less resilient. These differences significantly impact mattress lifespan, comfort levels, and suitability for various sleep positions and body weights.
Comfort and Support Comparison
High-density foam mattresses provide superior support by maintaining firmness and durability, making them ideal for individuals requiring consistent spinal alignment and pressure relief. Low-density foam offers greater initial softness and contouring comfort but tends to compress faster, potentially resulting in less long-term support. Choosing between high-density and low-density foam depends on balancing immediate comfort preferences with the need for sustained support and mattress lifespan.
Durability and Longevity
High-density foam mattresses offer superior durability and longevity due to their compact cell structure, which resists sagging and maintains firmness over time, typically lasting 8 to 10 years or more. Low-density foam mattresses tend to break down faster, often losing their support within 3 to 5 years because of their less robust material composition. Choosing high-density foam enhances mattress lifespan and provides consistent support for extended periods.
Breathability and Temperature Regulation
High-density foam mattresses offer superior durability but tend to retain more heat due to their compact cellular structure, which can impact breathability and lead to less effective temperature regulation. Low-density foam features a more open-cell design, promoting better airflow and enhanced breathability, which helps dissipate heat and maintain a cooler sleeping surface. Choosing between high-density and low-density foam involves balancing support requirements with personal preferences for temperature control and breathability.
Suitability for Different Sleep Types
High-density foam mattresses offer superior support and durability, making them ideal for back and stomach sleepers who require firm spinal alignment and pressure relief. Low-density foam mattresses provide a softer, more contouring feel, better suited for side sleepers who benefit from cushioning at shoulders and hips to reduce pressure points. Choosing the right foam density aligns with individual sleep positions, enhancing comfort and overall sleep quality.
Cost and Value Analysis
High-density foam mattresses typically cost more due to higher material quality and longer durability, offering better support and resilience over time. Low-density foam mattresses are more affordable upfront but tend to compress faster, reducing overall lifespan and value. Investing in high-density foam provides greater long-term cost efficiency through enhanced comfort and reduced need for replacement.
Choosing the Right Foam Density for Your Mattress
High-density foam offers superior durability and support, making it ideal for individuals seeking long-lasting comfort and pressure relief in a mattress. Low-density foam provides a softer, more breathable sleep surface, suitable for those prioritizing plushness and budget-friendly options. Selecting the right foam density depends on factors like body weight, sleeping position, and personal comfort preferences to ensure optimal spinal alignment and mattress longevity.
Infographic: High-density foam vs Low-density foam for Mattress
 azmater.com
azmater.com