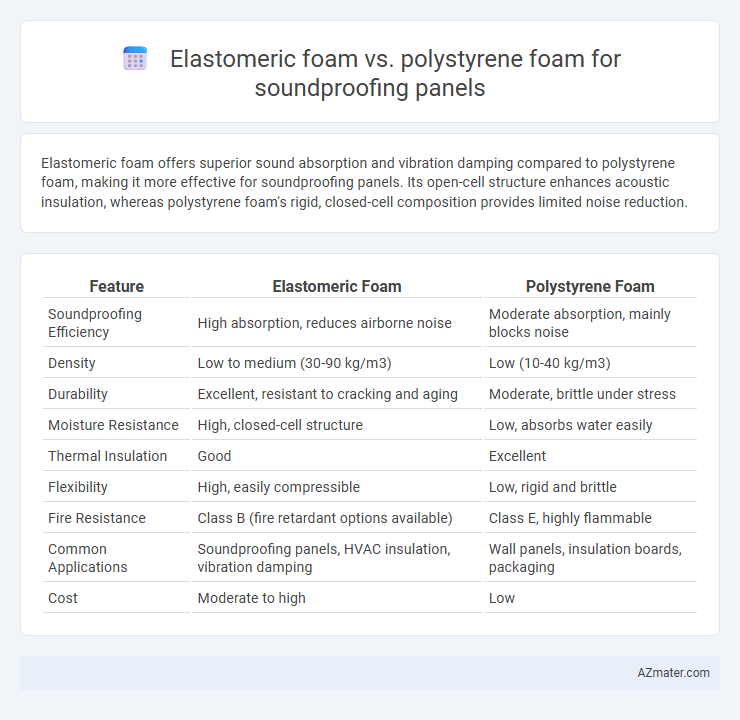
Elastomeric foam offers superior sound absorption and vibration damping compared to polystyrene foam, making it more effective for soundproofing panels. Its open-cell structure enhances acoustic insulation, whereas polystyrene foam's rigid, closed-cell composition provides limited noise reduction.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Elastomeric Foam | Polystyrene Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Soundproofing Efficiency | High absorption, reduces airborne noise | Moderate absorption, mainly blocks noise |
| Density | Low to medium (30-90 kg/m3) | Low (10-40 kg/m3) |
| Durability | Excellent, resistant to cracking and aging | Moderate, brittle under stress |
| Moisture Resistance | High, closed-cell structure | Low, absorbs water easily |
| Thermal Insulation | Good | Excellent |
| Flexibility | High, easily compressible | Low, rigid and brittle |
| Fire Resistance | Class B (fire retardant options available) | Class E, highly flammable |
| Common Applications | Soundproofing panels, HVAC insulation, vibration damping | Wall panels, insulation boards, packaging |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Low |
Introduction: Understanding Soundproofing Materials
Elastomeric foam and polystyrene foam serve distinct roles in soundproofing panels due to their differing acoustic properties and material structures. Elastomeric foam offers superior sound absorption and vibration damping, making it highly effective in reducing airborne and impact noise in various environments. Polystyrene foam, while lightweight and moisture-resistant, provides limited sound absorption but is often used for thermal insulation rather than primary soundproofing.
Overview of Elastomeric Foam
Elastomeric foam is a flexible, closed-cell material known for its excellent sound absorption and vibration damping properties, making it ideal for soundproofing panels. Its cellular structure effectively reduces noise transmission by trapping and dissipating sound waves, outperforming rigid materials like polystyrene foam in impact noise reduction. Elastomeric foam also offers superior durability, moisture resistance, and thermal insulation, enhancing overall acoustic performance in various environments.
Overview of Polystyrene Foam
Polystyrene foam, commonly known as expanded polystyrene (EPS), offers rigid structure and excellent thermal insulation properties, making it less flexible but effective for basic soundproofing applications. Its closed-cell composition provides moderate sound absorption by minimizing air gaps, while its lightweight nature simplifies installation in wall and ceiling panels. However, compared to elastomeric foam, polystyrene foam has lower resilience and acoustic damping capabilities, which can limit its performance in environments requiring advanced noise reduction.
Acoustic Performance Comparison
Elastomeric foam exhibits superior acoustic performance compared to polystyrene foam due to its higher density and flexibility, which enhance sound absorption and vibration damping. Its open-cell structure effectively reduces mid to high-frequency noise, making it ideal for soundproofing panels in environments requiring noise control. Polystyrene foam, with its rigid closed-cell composition, offers limited sound absorption and primarily insulates against thermal transfer rather than acoustic energy.
Thermal Insulation Capabilities
Elastomeric foam exhibits superior thermal insulation capabilities compared to polystyrene foam due to its closed-cell structure that minimizes heat transfer and provides excellent resistance to temperature fluctuations. Polystyrene foam, while effective for thermal insulation, tends to have higher thermal conductivity and may degrade faster under prolonged heat exposure. The enhanced thermal barrier of elastomeric foam ensures improved energy efficiency and consistent performance in soundproofing applications exposed to varying temperature conditions.
Moisture Resistance and Durability
Elastomeric foam offers superior moisture resistance compared to polystyrene foam, making it ideal for environments prone to humidity and condensation. Its closed-cell structure prevents water absorption, enhancing durability and maintaining soundproofing effectiveness over time. Polystyrene foam tends to absorb moisture, which can degrade its structural integrity and reduce acoustic performance in damp conditions.
Installation Process and Flexibility
Elastomeric foam offers superior flexibility and ease of installation for soundproofing panels due to its lightweight and compressible nature, allowing it to conform to irregular surfaces and reduce gaps effectively. Polystyrene foam, while rigid and less adaptable, requires more precise cutting and fitting during installation, often necessitating adhesives or mechanical fasteners for secure placement. The flexible properties of elastomeric foam enhance acoustic performance by maintaining consistent contact with surfaces, preventing sound leaks commonly found with the stiff structure of polystyrene panels.
Fire Resistance and Safety Considerations
Elastomeric foam offers superior fire resistance compared to polystyrene foam, exhibiting higher ignition temperatures and lower smoke emission during combustion. Polystyrene foam, while lightweight and cost-effective, is highly flammable and generates toxic fumes, posing significant safety hazards in soundproofing applications. Fire safety regulations often favor elastomeric foam due to its enhanced durability under high temperatures and compliance with stringent building codes.
Cost Analysis and Long-Term Value
Elastomeric foam typically has a higher upfront cost compared to polystyrene foam but offers superior durability and enhanced sound absorption properties, leading to greater long-term value in soundproofing panel applications. Polystyrene foam is more affordable initially but may degrade faster, requiring more frequent replacement and potentially increasing lifecycle expenses. Evaluating total cost of ownership highlights elastomeric foam's advantage in sustained performance and reduced maintenance over time.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Foam for Soundproofing Panels
Elastomeric foam offers superior sound absorption and flexibility, making it ideal for reducing mid to high-frequency noise in soundproofing panels. Polystyrene foam is more rigid and cost-effective but provides limited sound dampening, best suited for thermal insulation with minimal acoustic requirements. Selecting the right foam depends on balancing acoustic performance, durability, and budget constraints for the specific soundproofing application.
Infographic: Elastomeric foam vs Polystyrene foam for Soundproofing panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com