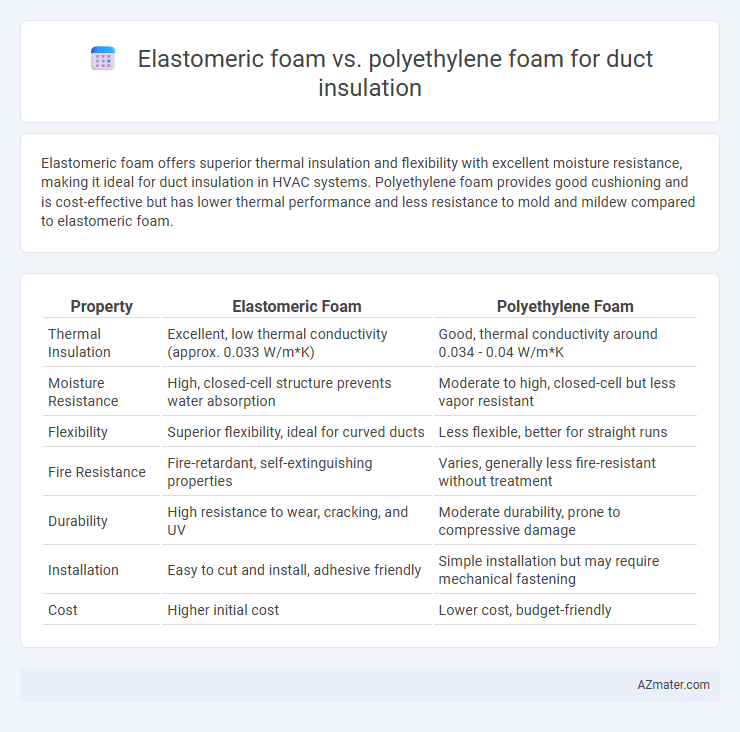
Elastomeric foam offers superior thermal insulation and flexibility with excellent moisture resistance, making it ideal for duct insulation in HVAC systems. Polyethylene foam provides good cushioning and is cost-effective but has lower thermal performance and less resistance to mold and mildew compared to elastomeric foam.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Elastomeric Foam | Polyethylene Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Insulation | Excellent, low thermal conductivity (approx. 0.033 W/m*K) | Good, thermal conductivity around 0.034 - 0.04 W/m*K |
| Moisture Resistance | High, closed-cell structure prevents water absorption | Moderate to high, closed-cell but less vapor resistant |
| Flexibility | Superior flexibility, ideal for curved ducts | Less flexible, better for straight runs |
| Fire Resistance | Fire-retardant, self-extinguishing properties | Varies, generally less fire-resistant without treatment |
| Durability | High resistance to wear, cracking, and UV | Moderate durability, prone to compressive damage |
| Installation | Easy to cut and install, adhesive friendly | Simple installation but may require mechanical fastening |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower cost, budget-friendly |
Overview of Duct Insulation Materials
Elastomeric foam and polyethylene foam are common duct insulation materials known for their thermal and acoustic properties. Elastomeric foam excels in durability, moisture resistance, and high thermal efficiency, making it ideal for HVAC systems that require vapor barriers. Polyethylene foam offers lightweight insulation with good flexibility and cost-effectiveness, but typically has lower thermal resistance and less moisture resistance compared to elastomeric foam.
What is Elastomeric Foam?
Elastomeric foam is a flexible, closed-cell insulation material widely used for duct insulation due to its excellent thermal resistance and moisture barrier properties. It offers superior flexibility and durability compared to polyethylene foam, allowing better conformity to irregular duct shapes and minimizing heat loss. The material's resistance to mold, mildew, and UV degradation enhances its suitability for HVAC applications over traditional polyethylene foam options.
What is Polyethylene Foam?
Polyethylene foam is a closed-cell, lightweight thermal insulation material known for its excellent moisture resistance and compressive strength, making it ideal for duct insulation applications. It provides effective thermal insulation by minimizing heat transfer and is resistant to chemicals, mold, and mildew, enhancing the durability of HVAC systems. Compared to elastomeric foam, polyethylene foam typically offers superior resistance to water absorption but may have lower flexibility and UV resistance.
Key Properties Comparison
Elastomeric foam insulation offers superior thermal resistance with an R-value ranging from 4.0 to 5.0 per inch, providing excellent energy efficiency compared to polyethylene foam, which typically has an R-value around 3.0 to 4.0 per inch. Elastomeric foam features closed-cell structure that delivers outstanding vapor barrier properties and flexibility, making it ideal for HVAC duct insulation exposed to condensation and temperature fluctuations. In contrast, polyethylene foam, while cost-effective and lightweight, has lower moisture resistance and durability, limiting its performance in high humidity environments.
Thermal Insulation Performance
Elastomeric foam exhibits superior thermal insulation performance for duct applications due to its low thermal conductivity, typically around 0.035 to 0.040 W/m*K, effectively reducing heat transfer and energy loss. Polyethylene foam, while offering moderate insulation with thermal conductivity values near 0.034 to 0.038 W/m*K, is less efficient in vapor resistance and temperature range compared to elastomeric foam. Elastomeric foam's closed-cell structure and inherent vapor barrier properties enhance its insulation efficiency, making it a preferred choice for HVAC duct insulation in diverse environmental conditions.
Moisture Resistance and Vapor Barrier Effectiveness
Elastomeric foam offers superior moisture resistance compared to polyethylene foam, effectively preventing water absorption and condensation buildup in duct insulation. Its closed-cell structure also provides a more reliable vapor barrier, reducing the risk of mold growth and corrosion within HVAC systems. Polyethylene foam, while cost-effective, generally has higher permeability to water vapor, making it less effective in maintaining a consistent and durable vapor barrier in humid environments.
Fire Safety and Flame Retardancy
Elastomeric foam offers superior fire safety and flame retardancy compared to polyethylene foam due to its closed-cell structure and inherent resistance to combustion, often meeting stringent UL 94 FMVSS 302 standards. Polyethylene foam is more flammable and prone to higher smoke generation during combustion, posing increased risks in duct insulation applications. Selecting elastomeric foam enhances fire protection and reduces flame propagation in HVAC duct systems, ensuring compliance with building codes and safety regulations.
Installation and Flexibility
Elastomeric foam offers superior flexibility and easy installation for duct insulation due to its closed-cell structure, allowing it to conform seamlessly around complex duct shapes and fittings. Polyethylene foam, while also lightweight and resistant to moisture, is less flexible and requires more cutting and joining during installation, potentially increasing labor time and cost. The resilience and compressibility of elastomeric foam enhance its sealing capabilities and reduce air leakage, making it a preferred choice for dynamic HVAC systems.
Cost Considerations
Elastomeric foam insulation typically presents a higher initial cost compared to polyethylene foam due to its superior thermal performance and flexibility. Polyethylene foam offers a more budget-friendly option but may require thicker layers to achieve similar insulation values, potentially increasing installation costs. Evaluating life cycle costs reveals elastomeric foam's durability and resistance to moisture often result in lower maintenance and replacement expenses over time.
Best Applications and Recommendations
Elastomeric foam offers superior thermal insulation and moisture resistance, making it ideal for HVAC ductwork in commercial and residential buildings where condensation control is critical. Polyethylene foam provides cost-effective cushioning and impact absorption, suitable for lightweight or non-temperature-sensitive duct insulation applications. For durable, long-term duct insulation exposed to variable temperatures and humidity, elastomeric foam is recommended, while polyethylene foam fits best in budget-conscious, low-moisture environments.
Infographic: Elastomeric foam vs Polyethylene foam for Duct insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com