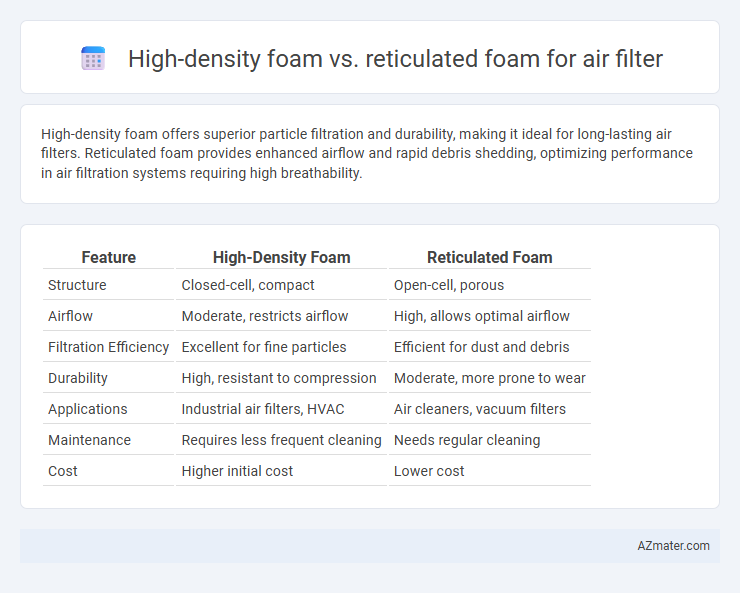
High-density foam offers superior particle filtration and durability, making it ideal for long-lasting air filters. Reticulated foam provides enhanced airflow and rapid debris shedding, optimizing performance in air filtration systems requiring high breathability.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | High-Density Foam | Reticulated Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Closed-cell, compact | Open-cell, porous |
| Airflow | Moderate, restricts airflow | High, allows optimal airflow |
| Filtration Efficiency | Excellent for fine particles | Efficient for dust and debris |
| Durability | High, resistant to compression | Moderate, more prone to wear |
| Applications | Industrial air filters, HVAC | Air cleaners, vacuum filters |
| Maintenance | Requires less frequent cleaning | Needs regular cleaning |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower cost |
Introduction to Foam Types in Air Filters
High-density foam in air filters provides superior particle capture due to its tightly packed structure, enhancing filtration efficiency for fine contaminants. Reticulated foam features an open-cell matrix that facilitates optimal airflow while trapping larger particles, making it ideal for applications requiring balanced air permeability and dirt holding capacity. Selecting between high-density and reticulated foam depends on the specific filtration requirements, including particle size, airflow resistance, and maintenance frequency.
What is High-Density Foam?
High-density foam is a type of polyurethane foam characterized by its compact cellular structure, offering superior durability and filtration efficiency in air filters. It provides excellent particle capture while maintaining airflow, making it ideal for industrial and automotive applications where robust filtration is required. Compared to reticulated foam, high-density foam delivers enhanced strength and prolonged lifespan under harsh operating conditions.
What is Reticulated Foam?
Reticulated foam is a porous, open-cell foam designed specifically for air filtration due to its high permeability and efficient particle capture. Unlike high-density foam, reticulated foam has a network of interconnected pores that allow maximum airflow while trapping contaminants, making it ideal for HVAC systems and industrial air filters. Its unique structure enables easy cleaning and durability, enhancing the lifespan and performance of air filtration systems.
Key Differences Between High-Density and Reticulated Foams
High-density foam for air filters features a compact cell structure that provides superior filtration efficiency by trapping finer particles, whereas reticulated foam contains an open-cell network allowing maximum airflow and quicker particle shedding. High-density foam excels in environments requiring cleaner air with higher particulate filtration, while reticulated foam is preferred when airflow and moisture drainage are critical. The key differences lie in pore size, filtration capability, airflow resistance, and durability under various operational conditions.
Filtration Efficiency Comparison
High-density foam offers superior filtration efficiency due to its tightly packed cells, effectively trapping fine particulate matter and airborne contaminants. Reticulated foam features an open-cell structure that allows higher airflow rates but with reduced filtration efficiency, as larger particles may pass through more easily. In air filter applications, high-density foam is preferred when maximizing particle capture is critical, whereas reticulated foam balances filtration with ventilation needs.
Airflow and Permeability Analysis
High-density foam offers lower airflow permeability due to its tightly packed cells, making it effective for trapping smaller particles but limiting air passage. Reticulated foam features a network of open cells that significantly enhances airflow and permeability, improving air filtration efficiency by allowing higher airflow rates with less resistance. Analyzing both materials, reticulated foam demonstrates superior permeability suitable for applications requiring optimal air exchange, while high-density foam is preferred where filtration of finer contaminants is critical.
Durability and Maintenance Needs
High-density foam offers superior durability and maintains structural integrity longer under heavy air filtration conditions compared to reticulated foam, which tends to degrade faster due to its open-cell structure. Reticulated foam, while easier to clean because of its porous design, requires more frequent maintenance to prevent clogging and ensure optimal airflow. Choosing high-density foam reduces replacement frequency and lowers long-term maintenance costs in air filtration systems.
Typical Applications for Each Foam Type
High-density foam excels in air filters for HVAC systems and automotive cabin air filters due to its superior particle capture efficiency and durability. Reticulated foam, characterized by its open-cell structure, is ideal for industrial air filtration and swimming pool filters where high airflow and effective particulate removal are critical. Typical applications for high-density foam prioritize fine filtration and longevity, while reticulated foam suits environments requiring maximum air permeability and rapid contaminant capture.
Cost Considerations
High-density foam for air filters generally offers a lower initial cost due to its widespread availability and simpler manufacturing process, making it a budget-friendly option for routine replacement. Reticulated foam, while more expensive upfront, provides enhanced airflow and superior filtration efficiency, potentially reducing long-term maintenance and energy costs. Evaluating cost considerations must include both the initial investment and the lifespan performance to determine the most economical choice for specific filtration applications.
Choosing the Right Foam for Your Air Filter
High-density foam offers excellent filtration efficiency and durability, making it ideal for capturing fine particles and providing long-lasting performance in air filters. Reticulated foam features an open-cell structure that promotes superior airflow and rapid particle removal, best suited for applications requiring high breathability and quick drying. Selecting the right foam depends on balancing filtration needs with airflow requirements, ensuring optimal air quality and filter lifespan for your specific environment.
Infographic: High-density foam vs Reticulated foam for Air filter
 azmater.com
azmater.com