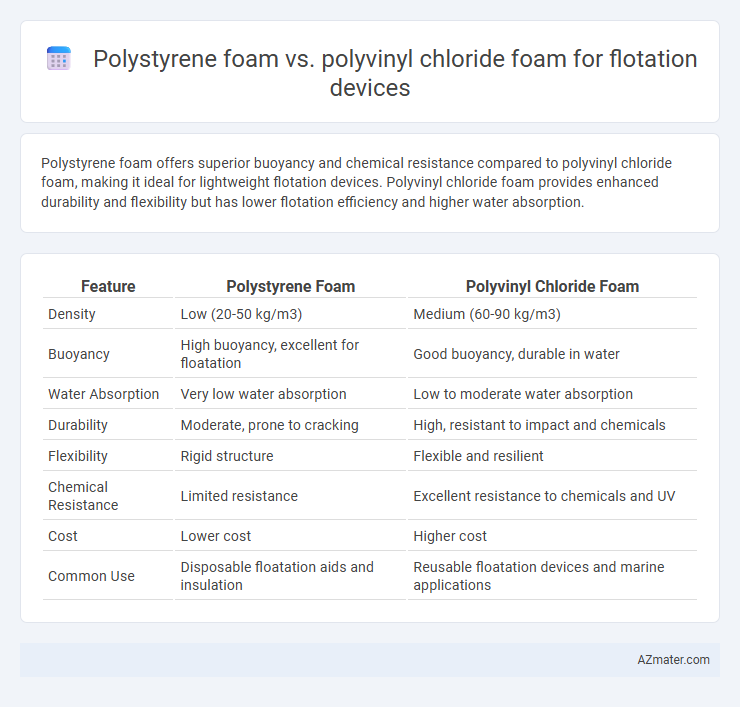
Polystyrene foam offers superior buoyancy and chemical resistance compared to polyvinyl chloride foam, making it ideal for lightweight flotation devices. Polyvinyl chloride foam provides enhanced durability and flexibility but has lower flotation efficiency and higher water absorption.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Polystyrene Foam | Polyvinyl Chloride Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Density | Low (20-50 kg/m3) | Medium (60-90 kg/m3) |
| Buoyancy | High buoyancy, excellent for floatation | Good buoyancy, durable in water |
| Water Absorption | Very low water absorption | Low to moderate water absorption |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to cracking | High, resistant to impact and chemicals |
| Flexibility | Rigid structure | Flexible and resilient |
| Chemical Resistance | Limited resistance | Excellent resistance to chemicals and UV |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
| Common Use | Disposable floatation aids and insulation | Reusable floatation devices and marine applications |
Introduction to Flotation Device Materials
Polystyrene foam offers lightweight buoyancy and excellent water resistance, making it a popular choice for flotation devices that require high rigidity and durability. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam provides enhanced flexibility, chemical resistance, and impact absorption, ideal for applications needing more adaptability and longevity under harsh conditions. Choosing between polystyrene and PVC foam fundamentally depends on the specific performance requirements, including density, buoyancy, and environmental exposure of the flotation device.
Overview of Polystyrene Foam
Polystyrene foam is a lightweight, rigid material with excellent buoyancy, making it ideal for flotation devices. Its closed-cell structure resists water absorption, enhancing durability in marine environments. Compared to polyvinyl chloride foam, polystyrene offers higher stiffness and cost-effectiveness but may have lower impact resistance.
Overview of Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Foam
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) foam is a closed-cell, lightweight material widely used in flotation devices due to its excellent buoyancy and durability. Its superior resistance to water absorption, chemicals, and UV degradation makes it ideal for marine and aquatic applications compared to Polystyrene foam. The structural stability and enhanced mechanical strength of PVC foam provide reliable long-term performance in harsh environmental conditions.
Comparative Buoyancy Performance
Polystyrene foam exhibits higher buoyancy due to its lower density and greater closed-cell structure, which traps more air compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam. PVC foam offers moderate buoyancy with enhanced durability and resistance to water absorption but typically weighs more, reducing overall flotation efficiency. For flotation devices, polystyrene foam ensures superior lift and prolonged buoyant performance in aquatic environments.
Durability and Lifespan
Polystyrene foam offers lightweight buoyancy but tends to degrade faster when exposed to UV radiation and moisture, resulting in a shorter lifespan for flotation devices. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam provides superior durability due to its resistance to water absorption, chemicals, and environmental stress, significantly extending the service life of flotation equipment. This enhanced resilience makes PVC foam the preferred material for long-term use in harsh marine and freshwater flotation applications.
Water Absorption and Resistance
Polystyrene foam exhibits low water absorption due to its closed-cell structure, making it highly effective for flotation devices by maintaining buoyancy and structural integrity in wet conditions. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam also offers excellent water resistance with superior durability and chemical resistance, ensuring long-term performance in marine environments. Both materials provide reliable flotation, but PVC foam outperforms polystyrene foam in resistance to water absorption and environmental degradation.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polystyrene foam, commonly used in flotation devices, is lightweight and provides excellent buoyancy but poses significant environmental challenges due to its slow degradation and difficulty in recycling, often contributing to microplastic pollution. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam offers durability and resistance to wear but contains chlorine, which can release harmful dioxins during production and disposal, complicating its environmental footprint. Recycling options for PVC foam remain limited and energy-intensive compared to emerging biodegradable alternatives, making polystyrene foam more prevalent despite its ecological drawbacks.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Polystyrene foam offers a lower cost solution for flotation devices due to its mass production and widespread availability, making it a budget-friendly option in the market. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam, while generally costlier, provides superior durability and chemical resistance, justifying its price in specialized applications. Market availability favors polystyrene foam with numerous suppliers and extensive distribution networks, whereas PVC foam is less common but preferred for high-performance flotation products.
Safety Standards and Regulatory Compliance
Polystyrene foam and Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam both meet industry safety standards for flotation devices, but PVC foam typically offers superior resistance to water absorption and chemical degradation, enhancing long-term buoyancy and durability. Regulatory compliance with standards such as ASTM F746 and ISO 12402 requires both materials to demonstrate adequate buoyancy, non-toxicity, and flame retardancy, where PVC foam often excels due to its inherent fire-resistant properties. Manufacturers prioritize these compliance benchmarks to ensure flotation devices provide reliable performance and meet national and international safety certifications.
Conclusion: Choosing the Ideal Foam for Flotation Devices
Polystyrene foam offers lightweight buoyancy and cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for disposable or short-term flotation devices. Polyvinyl chloride foam provides superior durability, resistance to water absorption, and enhanced structural integrity, suited for long-term or heavy-duty applications. Selecting the ideal foam depends on balancing weight, durability, and cost to meet specific flotation device requirements.
Infographic: Polystyrene foam vs Polyvinyl chloride foam for Floatation device
 azmater.com
azmater.com