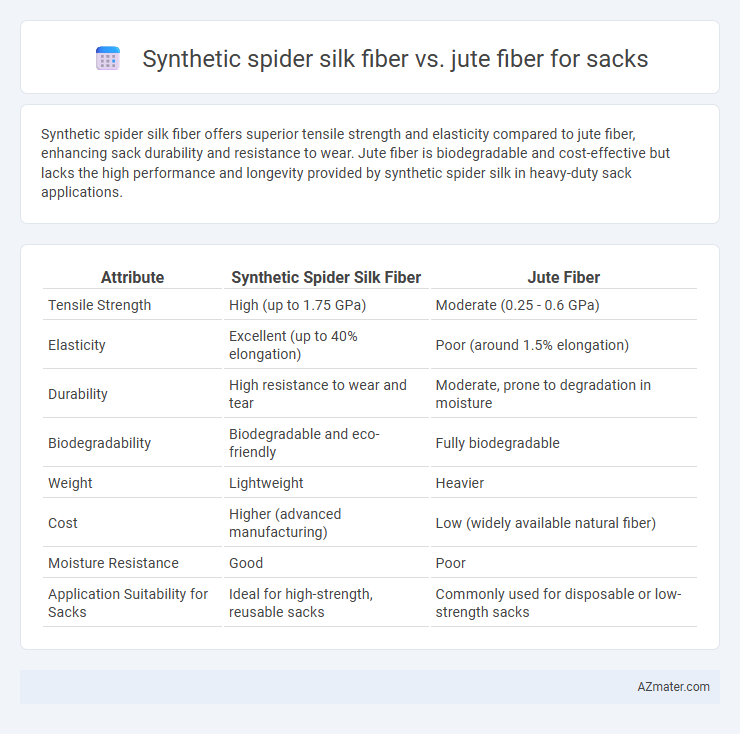
Synthetic spider silk fiber offers superior tensile strength and elasticity compared to jute fiber, enhancing sack durability and resistance to wear. Jute fiber is biodegradable and cost-effective but lacks the high performance and longevity provided by synthetic spider silk in heavy-duty sack applications.
Table of Comparison
| Attribute | Synthetic Spider Silk Fiber | Jute Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | High (up to 1.75 GPa) | Moderate (0.25 - 0.6 GPa) |
| Elasticity | Excellent (up to 40% elongation) | Poor (around 1.5% elongation) |
| Durability | High resistance to wear and tear | Moderate, prone to degradation in moisture |
| Biodegradability | Biodegradable and eco-friendly | Fully biodegradable |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier |
| Cost | Higher (advanced manufacturing) | Low (widely available natural fiber) |
| Moisture Resistance | Good | Poor |
| Application Suitability for Sacks | Ideal for high-strength, reusable sacks | Commonly used for disposable or low-strength sacks |
Introduction to Sack Fibers: An Overview
Synthetic spider silk fiber demonstrates exceptional tensile strength and elasticity, making it a promising alternative for sack materials that require durability and flexibility. Jute fiber, a traditional choice for sacks, offers natural biodegradability and cost-effectiveness but lacks the high mechanical performance of synthetic spider silk. Both fibers serve distinct roles in sack production, with synthetic spider silk advancing the potential for high-performance, lightweight sacks and jute maintaining its position in eco-friendly, sustainable packaging.
Origins and Composition: Synthetic Spider Silk vs Jute
Synthetic spider silk fiber originates from genetically engineered proteins that mimic the natural silk produced by spiders, offering exceptional strength, elasticity, and durability due to its beta-sheet nanocrystal structure. Jute fiber is a natural bast fiber obtained from the Corchorus plant, composed primarily of cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin, providing a coarse texture and moderate tensile strength suitable for traditional sack manufacturing. The synthetic spider silk's protein-based composition results in lightweight, high-performance materials, whereas jute's plant-based cellulose matrix favors biodegradability and cost-effectiveness in agricultural and packaging applications.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Synthetic spider silk fiber exhibits superior mechanical strength compared to jute fiber, with tensile strength reaching up to 1.2 GPa, significantly higher than jute's typical range of 400-800 MPa. The elasticity of synthetic spider silk, characterized by its strain at break of approximately 30%, surpasses jute fiber's lower elongation capacity, enabling better resilience under stress. Enhanced durability and resistance to wear make synthetic spider silk a promising alternative for high-performance sacks requiring lightweight yet robust material.
Durability and Longevity in Sack Applications
Synthetic spider silk fiber exhibits exceptional durability and longevity compared to jute fiber in sack applications, with superior tensile strength and resistance to abrasion, moisture, and UV degradation. Jute fiber, while biodegradable and cost-effective, tends to degrade faster under prolonged exposure to environmental elements, leading to reduced sack lifespan. The enhanced mechanical properties of synthetic spider silk fiber ensure sacks maintain structural integrity through extended use and challenging conditions, making it a premium choice for heavy-duty and reusable packaging.
Environmental Impact: Biodegradability and Sustainability
Synthetic spider silk fiber exhibits remarkable biodegradability and sustainability due to its bioengineered proteins that decompose naturally without releasing harmful toxins. Jute fiber is highly biodegradable and renewable, grown with minimal pesticides and water, making it an eco-friendly choice for sacks. However, synthetic spider silk offers superior environmental benefits through its potential for scalable production with lower land use and no reliance on agrochemical inputs.
Cost Efficiency in Production and Usage
Synthetic spider silk fiber demonstrates higher cost efficiency in production and usage compared to jute fiber for sacks due to its superior tensile strength and durability, reducing replacement frequency and maintenance costs. Though synthetic spider silk has a higher initial production cost, its enhanced longevity and resistance to environmental degradation lower overall lifecycle expenses. Jute fiber, while cheaper upfront, often incurs higher long-term costs due to its lower durability and susceptibility to moisture and pests, leading to more frequent sack replacements.
Moisture Resistance and Fiber Performance
Synthetic spider silk fiber demonstrates superior moisture resistance compared to jute fiber, making it ideal for sacks exposed to humid or wet conditions. Its advanced fiber performance includes high tensile strength, elasticity, and durability, which surpass the natural degradation tendencies of jute when exposed to moisture. Jute fiber, while biodegradable and cost-effective, tends to absorb water and weaken over time, limiting its performance in moisture-heavy environments.
Industrial Scalability and Availability
Synthetic spider silk fiber offers high tensile strength and elasticity, making it an innovative alternative for sacks, but its industrial scalability remains limited due to complex production processes and higher costs. Jute fiber is widely available, affordable, and easily scalable for industrial use, benefiting from established agricultural supply chains and eco-friendly properties. While synthetic spider silk is promising for specialized applications, jute remains the dominant choice for large-scale sack manufacturing due to its availability and cost-efficiency.
Potential Challenges and Limitations
Synthetic spider silk fiber offers superior tensile strength and elasticity compared to jute fiber but faces challenges such as high production costs and scalability issues limiting widespread sack manufacturing adoption. Jute fiber, while economical and biodegradable, suffers from lower durability and susceptibility to moisture damage, reducing sack lifespan in certain conditions. Both materials require improvements in processing techniques to balance performance, cost, and environmental impact for practical sack applications.
Future Prospects for Sack Manufacturing
Synthetic spider silk fiber offers superior tensile strength, elasticity, and biodegradability compared to traditional jute fiber, making it a promising material for eco-friendly sack manufacturing. Advances in biotechnology and large-scale production techniques are expected to reduce costs and enhance the availability of synthetic spider silk, positioning it as a sustainable alternative to jute. The integration of synthetic spider silk could revolutionize the sack industry by producing lightweight, durable, and compostable sacks that meet increasing demands for environmentally responsible packaging materials.
Infographic: Synthetic spider silk fiber vs Jute fiber for Sack
 azmater.com
azmater.com