Spider silk fiber offers exceptional tensile strength and lightweight flexibility, making it highly effective for protective clothing. Aramid fiber, such as Kevlar, provides superior heat resistance and cut protection, commonly used in bulletproof vests and firefighter suits.
Table of Comparison
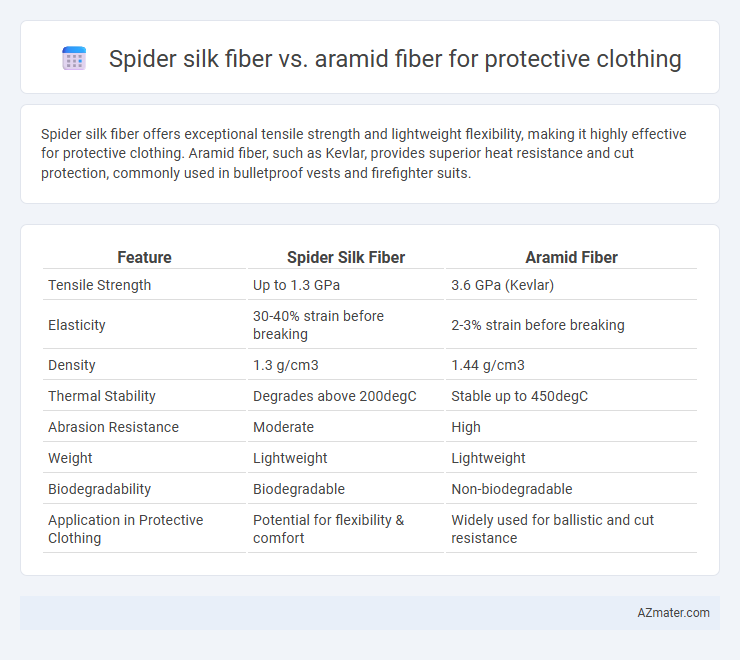
| Feature | Spider Silk Fiber | Aramid Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | Up to 1.3 GPa | 3.6 GPa (Kevlar) |
| Elasticity | 30-40% strain before breaking | 2-3% strain before breaking |
| Density | 1.3 g/cm3 | 1.44 g/cm3 |
| Thermal Stability | Degrades above 200degC | Stable up to 450degC |
| Abrasion Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Weight | Lightweight | Lightweight |
| Biodegradability | Biodegradable | Non-biodegradable |
| Application in Protective Clothing | Potential for flexibility & comfort | Widely used for ballistic and cut resistance |
Introduction to Protective Clothing Materials
Spider silk fiber exhibits exceptional tensile strength and elasticity, making it a promising material for protective clothing due to its lightweight and biodegradable properties. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, are well-established in protective gear for their high resistance to heat, abrasion, and impact, providing reliable durability and cut resistance. Comparing these materials highlights spider silk's potential for enhanced flexibility and comfort, while aramid fibers remain dominant for robust protection in extreme environments.
Overview of Spider Silk Fiber
Spider silk fiber exhibits exceptional tensile strength and elasticity, making it a promising material for protective clothing applications. Its lightweight and biodegradable nature provides advantages over synthetic fibers like aramid, used in kevlar, which are known for their high impact resistance but suffer from rigidity and environmental concerns. Advances in bioengineering have enhanced the production of spider silk, enabling scalable integration into protective textiles that require both durability and flexibility.
Overview of Aramid Fiber
Aramid fiber is a synthetic material known for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, making it ideal for protective clothing in hazardous environments. It exhibits excellent heat resistance, high tensile strength, and superior durability compared to traditional fibers, enhancing wearer safety against impacts and cuts. Commonly used in bulletproof vests and firefighting gear, aramid fiber's performance surpasses many natural fibers, including spider silk, especially in large-scale industrial applications.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Spider silk fiber demonstrates superior tensile strength and elasticity compared to aramid fibers, which contributes to its enhanced energy absorption and resistance to impact. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, are known for their high strength-to-weight ratio and excellent thermal stability but generally exhibit lower extensibility and toughness than spider silk. The combination of spider silk's combination of strength around 1.3 GPa with strain capacity up to 30% surpasses typical aramid fibers, which have tensile strengths of approximately 3.6 GPa but strain-to-failure below 5%, making spider silk more effective for dynamic protective clothing applications.
Flexibility and Comfort Differences
Spider silk fiber offers superior flexibility and exceptional softness compared to aramid fiber, enhancing wearer comfort in protective clothing by allowing greater range of motion and reduced stiffness. While aramid fibers like Kevlar provide excellent strength and heat resistance, their rigid structure can cause discomfort and restrict mobility during extended use. The lightweight and breathable nature of spider silk fiber makes it an ideal choice for applications demanding both protection and comfort, especially in high-performance environments.
Durability and Environmental Resistance
Spider silk fiber exhibits exceptional durability with tensile strength surpassing many synthetic fibers, maintaining flexibility under repetitive stress, making it ideal for protective clothing. Its natural protein structure provides excellent environmental resistance against UV radiation, moisture, and temperature fluctuations, outperforming many synthetic materials. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, offer high resistance to abrasion and heat but can degrade over prolonged UV exposure and moisture, limiting their long-term environmental resilience compared to spider silk.
Weight and Wearability Aspects
Spider silk fiber offers exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, making it significantly lighter than aramid fibers commonly used in protective clothing. Its superior flexibility and breathability enhance wearability, reducing fatigue during extended use compared to the stiffer, heavier aramid fibers like Kevlar. These properties make spider silk a promising material for lightweight, comfortable protective gear without compromising durability.
Manufacturing and Scalability
Spider silk fiber exhibits exceptional tensile strength and elasticity, but its natural production is limited by the difficulty of farming spiders, resulting in low manufacturing scalability. Aramid fiber, such as Kevlar, benefits from well-established synthetic polymerization processes, allowing mass production with consistent quality and scalability for protective clothing applications. Advances in recombinant DNA technology aim to enhance spider silk production, yet aramid fibers currently dominate manufacturing due to cost efficiency and large-scale availability.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Spider silk fiber offers exceptional sustainability due to its biodegradability and renewable production from genetically engineered organisms, resulting in low environmental impact compared to aramid fiber, which is synthetic and derived from petrochemicals. Aramid fibers like Kevlar provide excellent strength and heat resistance but involve energy-intensive manufacturing and generate non-biodegradable waste. The use of spider silk fiber in protective clothing significantly reduces carbon footprint and end-of-life environmental hazards, making it a greener alternative to conventional aramid-based textiles.
Future Prospects in Protective Clothing
Spider silk fiber exhibits remarkable tensile strength, elasticity, and biodegradability, making it a promising candidate for next-generation protective clothing designed to offer enhanced cut resistance and flexibility. Aramid fiber, widely used in current protective gear such as Kevlar, provides exceptional heat resistance and durability but lacks the biodegradability and stretchability inherent in spider silk. Future protective clothing developments are likely to integrate bioengineered spider silk fibers to create lightweight, sustainable, and high-performance materials that surpass the limitations of traditional aramid fibers.
Infographic: Spider silk fiber vs Aramid fiber for Protective clothing
 azmater.com
azmater.com