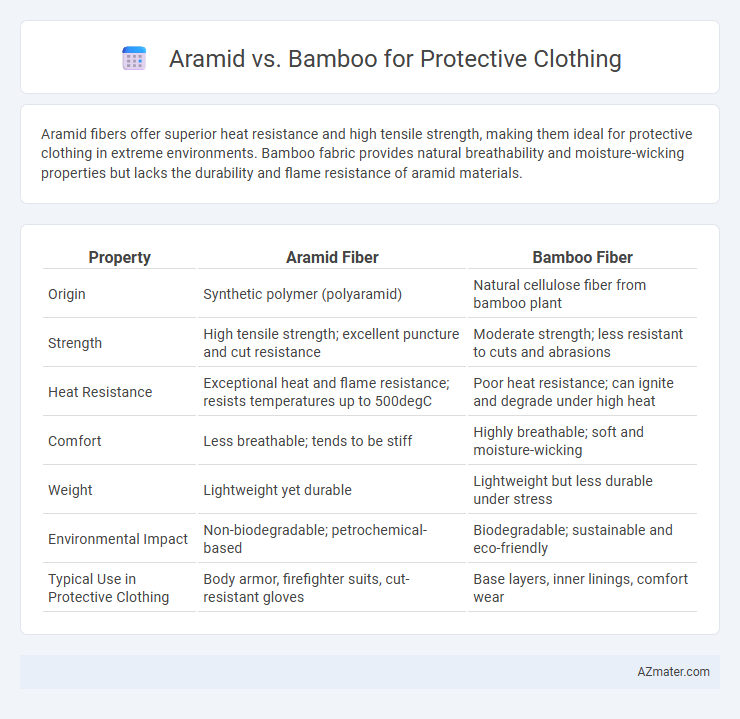
Aramid fibers offer superior heat resistance and high tensile strength, making them ideal for protective clothing in extreme environments. Bamboo fabric provides natural breathability and moisture-wicking properties but lacks the durability and flame resistance of aramid materials.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Aramid Fiber | Bamboo Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Synthetic polymer (polyaramid) | Natural cellulose fiber from bamboo plant |
| Strength | High tensile strength; excellent puncture and cut resistance | Moderate strength; less resistant to cuts and abrasions |
| Heat Resistance | Exceptional heat and flame resistance; resists temperatures up to 500degC | Poor heat resistance; can ignite and degrade under high heat |
| Comfort | Less breathable; tends to be stiff | Highly breathable; soft and moisture-wicking |
| Weight | Lightweight yet durable | Lightweight but less durable under stress |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable; petrochemical-based | Biodegradable; sustainable and eco-friendly |
| Typical Use in Protective Clothing | Body armor, firefighter suits, cut-resistant gloves | Base layers, inner linings, comfort wear |
Introduction to Protective Clothing Materials
Aramid fibers, known for their exceptional heat resistance and high tensile strength, are widely used in protective clothing to safeguard against flames and mechanical hazards. Bamboo fabric offers natural antibacterial properties, breathability, and eco-friendliness but lacks the thermal and abrasion resistance needed for high-risk environments. Combining aramid's durability with bamboo's comfort can enhance protective gear performance in diverse industrial applications.
Overview of Aramid Fibers
Aramid fibers, known for their exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and heat resistance, are widely used in protective clothing for industries such as firefighting, military, and law enforcement. These synthetic fibers, including Kevlar and Nomex, provide superior cut, abrasion, and flame resistance compared to natural fibers like bamboo. Their molecular structure enables high durability and thermal stability, making aramid fibers a preferred choice for advanced protective gear.
Characteristics of Bamboo Textiles
Bamboo textiles are prized for their natural moisture-wicking and antibacterial properties, making them highly breathable and comfortable in protective clothing applications. The fibers exhibit excellent softness and elasticity, contributing to enhanced flexibility and wearer comfort compared to traditional synthetic materials like aramid. Bamboo fabrics also offer eco-friendly benefits due to their renewable source and biodegradability, although they typically lack the high heat resistance and durability provided by aramid fibers in flame-retardant environments.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, exhibit exceptional tensile strength and superior resistance to heat and abrasion, making them a premier choice for protective clothing in extreme environments. Bamboo fibers, while naturally antibacterial and biodegradable, lack comparable strength and durability, limiting their use to lighter protective applications or blended fabrics. The inherent molecular structure of aramid promotes long-term durability under stress, whereas bamboo fibers degrade more rapidly when exposed to heavy mechanical or thermal loads.
Thermal and Flame Resistance
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar and Nomex, provide superior thermal and flame resistance, making them a preferred choice for protective clothing in high-heat environments. Bamboo fabric, while naturally breathable and soft, lacks inherent flame-retardant properties and requires chemical treatments to meet safety standards. The intrinsic heat stability and self-extinguishing characteristics of aramid materials deliver enhanced protection, durability, and compliance with industry regulations in fire-resistant apparel.
Comfort and Breathability
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, offer exceptional strength and heat resistance but tend to be less breathable and can feel stiffer against the skin compared to bamboo fabric. Bamboo fibers provide superior comfort due to their natural softness and high moisture-wicking properties, enhancing breathability and reducing heat buildup in protective clothing. Manufacturers often balance aramid's protective performance with bamboo's comfort to create hybrid garments that optimize both safety and wearability.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, are petroleum-based and present challenges in biodegradability and resource depletion, whereas bamboo is a rapidly renewable resource with natural biodegradability and lower ecological footprint. Bamboo cultivation requires minimal pesticides and water, making it a more sustainable option compared to the energy-intensive production of aramid fibers. However, chemical processing of bamboo into wearable fabric involves environmental concerns, balancing its natural advantages against industrial impacts.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Aramid fibers, known for their high strength and heat resistance, typically come with a higher cost and limited availability due to complex manufacturing processes and reliance on specialized suppliers. Bamboo fiber, while more affordable and widely accessible owing to its rapid renewability and natural abundance, lacks the same level of protective performance required for high-risk environments. Cost-effectiveness and supply chain stability make bamboo suitable for low-impact protective garments, whereas aramid remains the preferred choice for premium, high-performance protective clothing.
Typical Applications in Protective Clothing
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar and Nomex, are extensively used in protective clothing for applications requiring high cut and heat resistance, including firefighter suits, bulletproof vests, and industrial gloves. Bamboo fiber is valued for its natural antibacterial properties and moisture-wicking capabilities, making it suitable for lightweight protective wear and base layers that enhance comfort in hot environments. Combining aramid with bamboo can optimize protective gear by balancing durability and comfort in diverse occupational settings.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Aramid and Bamboo
Aramid fibers offer superior heat resistance and high tensile strength, making them ideal for protective clothing in extreme environments. Bamboo fabric provides natural breathability and moisture-wicking properties, enhancing comfort in less hazardous conditions. Selecting between aramid and bamboo depends on the specific safety requirements and comfort priorities of the wearer.
Infographic: Aramid vs Bamboo for Protective Clothing
 azmater.com
azmater.com