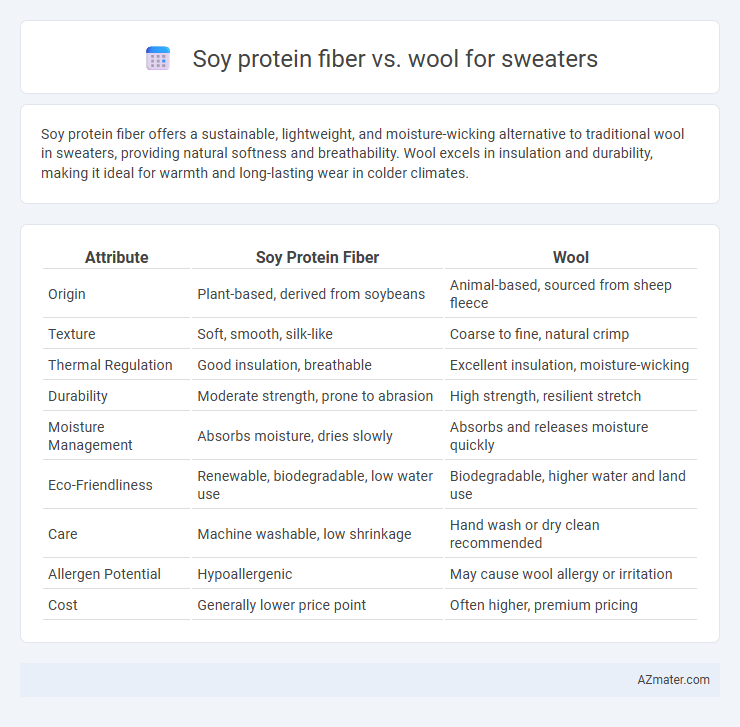
Soy protein fiber offers a sustainable, lightweight, and moisture-wicking alternative to traditional wool in sweaters, providing natural softness and breathability. Wool excels in insulation and durability, making it ideal for warmth and long-lasting wear in colder climates.
Table of Comparison
| Attribute | Soy Protein Fiber | Wool |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Plant-based, derived from soybeans | Animal-based, sourced from sheep fleece |
| Texture | Soft, smooth, silk-like | Coarse to fine, natural crimp |
| Thermal Regulation | Good insulation, breathable | Excellent insulation, moisture-wicking |
| Durability | Moderate strength, prone to abrasion | High strength, resilient stretch |
| Moisture Management | Absorbs moisture, dries slowly | Absorbs and releases moisture quickly |
| Eco-Friendliness | Renewable, biodegradable, low water use | Biodegradable, higher water and land use |
| Care | Machine washable, low shrinkage | Hand wash or dry clean recommended |
| Allergen Potential | Hypoallergenic | May cause wool allergy or irritation |
| Cost | Generally lower price point | Often higher, premium pricing |
Introduction to Soy Protein Fiber and Wool
Soy protein fiber, derived from soybean protein, offers a sustainable and biodegradable alternative to traditional fibers, boasting softness and moisture-wicking properties ideal for sweater production. Wool, sourced from sheep, is renowned for its excellent insulation, durability, and natural elasticity, making it a classic choice for warm and resilient sweaters. Both fibers present distinct benefits: soy protein fiber excels in comfort and eco-friendliness, while wool delivers superior warmth and long-lasting wear.
Fiber Origins: Plant-Based vs. Animal-Based
Soy protein fiber, derived from plant-based soybeans, offers a sustainable and hypoallergenic alternative to traditional wool, which originates from sheep's fleece, an animal-based fiber rich in natural warmth and moisture-wicking properties. Plant-based soy protein fibers are known for their softness, breathability, and biodegradability, making them eco-friendly options for sweater production. Wool fibers provide superior insulation and durability, benefiting from lanolin content that enhances water resistance and odor control in garments.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Soy protein fiber sweaters have a lower environmental impact compared to wool, as soy fibers are derived from renewable soybeans, requiring less water and producing fewer greenhouse gas emissions during cultivation and processing. Wool production involves methane emissions from sheep, significant land use, and water consumption, contributing to higher ecological footprints. Choosing soy protein fiber reduces reliance on animal agriculture, promoting a more sustainable and eco-friendly sweater option.
Comfort and Softness
Soy protein fiber offers exceptional softness and breathability, making sweaters lightweight and comfortable for all-day wear. Wool provides natural insulation and moisture-wicking properties but can feel coarse or itchy against sensitive skin. For ultimate comfort and softness, soy protein fiber sweaters are preferable, especially for those with skin sensitivities or seeking a smooth texture.
Thermal Insulation and Breathability
Soy protein fiber offers superior breathability compared to wool, allowing moisture to evaporate quickly and keeping the wearer dry. Wool provides excellent thermal insulation through its natural crimped structure, trapping air and maintaining warmth even when damp. Choosing between soy protein fiber and wool depends on prioritizing breathability for active wear or insulation for cold, static conditions.
Durability and Longevity
Soy protein fiber offers moderate durability with natural resistance to wrinkles and fading, making it suitable for lightweight sweaters but less resilient to frequent abrasion compared to wool. Wool excels in longevity due to its inherent elasticity, moisture-wicking properties, and resistance to tearing, maintaining shape and insulation over years of wear. For sweaters, wool provides superior durability and extended lifespan, ideal for harsh conditions and repeated use.
Moisture-Wicking Properties
Soy protein fiber offers excellent moisture-wicking properties due to its natural ability to absorb and release moisture quickly, keeping the skin dry and comfortable during wear. Wool also excels in moisture management with its unique hygroscopic structure, which can absorb up to 30% of its weight in moisture without feeling wet, making it highly breathable and temperature-regulating. Compared to wool, soy protein fiber is often lighter and smoother, providing a soft texture while maintaining efficient moisture control for active or casual sweaters.
Allergenicity and Skin Sensitivity
Soy protein fiber offers a hypoallergenic alternative to wool, making it ideal for individuals with sensitive skin or wool allergies. Unlike wool, which can cause itching or irritation due to lanolin and coarse fibers, soy protein fiber is smooth and gentle, minimizing skin redness and discomfort. Its natural moisture-wicking and breathable properties further enhance comfort for people prone to skin sensitivities or allergic reactions.
Care and Maintenance Requirements
Soy protein fiber sweaters require gentle washing with mild detergent and air drying to maintain their softness and prevent shrinking, as they are sensitive to high heat and agitation. Wool sweaters benefit from hand washing or dry cleaning, with cold water and specialized wool detergent to avoid felting and maintain elasticity, and should be dried flat to retain shape. Both fibers demand careful storage away from moisture and pests to preserve their texture and durability over time.
Cost and Market Availability
Soy protein fiber sweaters often come at a lower cost compared to wool due to the more sustainable and abundant raw material sourced from soybeans. Wool sweaters, although typically more expensive, have a well-established market presence with widespread availability in both luxury and mainstream fashion sectors. The growing demand for eco-friendly textiles boosts soy protein fiber's market availability, but wool remains dominant in traditional sweater markets.
Infographic: Soy protein fiber vs Wool for Sweater
 azmater.com
azmater.com