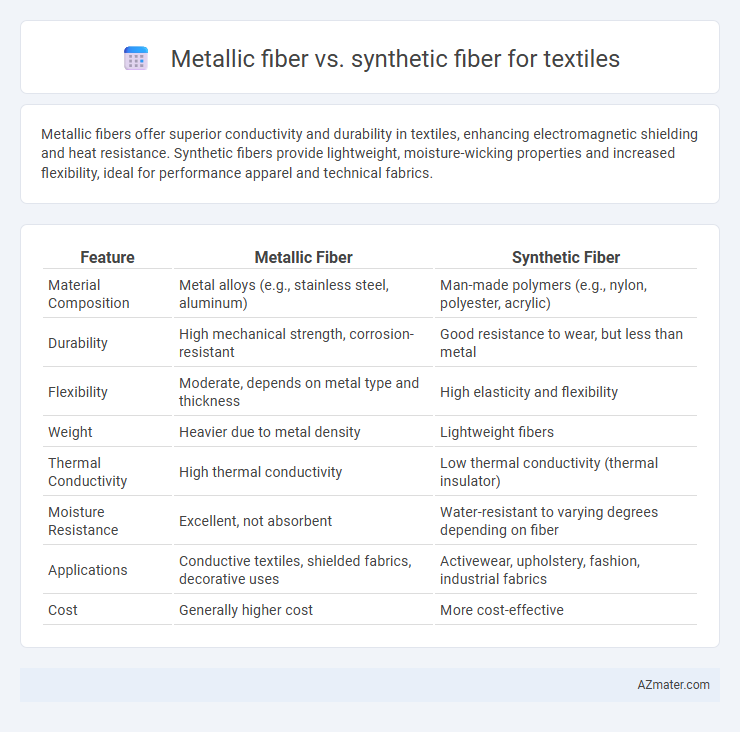
Metallic fibers offer superior conductivity and durability in textiles, enhancing electromagnetic shielding and heat resistance. Synthetic fibers provide lightweight, moisture-wicking properties and increased flexibility, ideal for performance apparel and technical fabrics.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Metallic Fiber | Synthetic Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Metal alloys (e.g., stainless steel, aluminum) | Man-made polymers (e.g., nylon, polyester, acrylic) |
| Durability | High mechanical strength, corrosion-resistant | Good resistance to wear, but less than metal |
| Flexibility | Moderate, depends on metal type and thickness | High elasticity and flexibility |
| Weight | Heavier due to metal density | Lightweight fibers |
| Thermal Conductivity | High thermal conductivity | Low thermal conductivity (thermal insulator) |
| Moisture Resistance | Excellent, not absorbent | Water-resistant to varying degrees depending on fiber |
| Applications | Conductive textiles, shielded fabrics, decorative uses | Activewear, upholstery, fashion, industrial fabrics |
| Cost | Generally higher cost | More cost-effective |
Introduction to Metallic and Synthetic Fibers
Metallic fibers are composed of metal-coated synthetic or natural fibers, offering enhanced conductivity, durability, and a unique reflective appearance often used in high-performance and decorative textiles. Synthetic fibers, such as polyester, nylon, and acrylic, are man-made polymers known for their strength, elasticity, and resistance to moisture, making them versatile choices in textile manufacturing. Both fiber types serve distinct functions in textiles, with metallic fibers providing specialized applications in electronics and fashion, while synthetic fibers dominate everyday apparel and industrial fabrics.
Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Metallic fibers are composed primarily of fine metal strands such as stainless steel, aluminum, or copper, produced through processes like wire drawing, swaging, and extrusion to achieve thin, flexible filaments. Synthetic fibers, including polyester, nylon, and acrylic, are derived from petrochemical polymers and manufactured using methods like melt spinning, dry spinning, or wet spinning to create continuous filaments or staple fibers. The production of metallic fibers involves mechanical deformation of metal materials, while synthetic fiber manufacturing relies on polymerization and controlled solidification of molten or dissolved polymers.
Physical Properties Comparison
Metallic fibers exhibit superior thermal conductivity, excellent electromagnetic shielding, and high tensile strength compared to synthetic fibers, which are generally more flexible and lightweight with better moisture resistance. While metallic fibers offer durability and a distinctive luster, synthetic fibers such as polyester and nylon provide enhanced elasticity, abrasion resistance, and ease of dyeing. The choice between metallic and synthetic fibers depends on application-specific requirements for strength, conductivity, flexibility, and environmental resistance in textile manufacturing.
Durability and Strength Factors
Metallic fibers exhibit superior durability and tensile strength compared to synthetic fibers, making them ideal for high-performance textile applications requiring resistance to wear, heat, and corrosion. Synthetic fibers, while generally less durable, offer greater flexibility and elasticity, contributing to their widespread use in stretchable and lightweight fabrics. The inherent strength of metallic fibers enhances longevity and structural integrity, whereas synthetic fibers rely on engineered polymers to achieve a balance between durability and comfort.
Aesthetic and Design Versatility
Metallic fibers offer a unique, reflective sheen that enhances the aesthetic appeal of textiles, creating eye-catching designs with a luxurious and futuristic vibe. Synthetic fibers provide greater design versatility through their wide range of colors, textures, and durability, allowing for innovative patterns and functional blends in fashion and interior applications. Combining metallic and synthetic fibers expands creative possibilities, balancing visual impact with practical performance in textile design.
Comfort and Wearability
Metallic fibers offer superior durability and a distinctive sheen but tend to be less breathable and flexible compared to synthetic fibers, which are engineered for enhanced comfort and moisture-wicking properties. Synthetic fibers such as polyester and nylon provide lightweight wearability, excellent elasticity, and quick-drying features, making them ideal for active and everyday apparel. The balance between metallic fiber's aesthetic appeal and synthetic fiber's comfort defines their suitability in textile applications targeting consumer wearability.
Applications in the Textile Industry
Metallic fibers are widely used in the textile industry for applications requiring enhanced durability, conductivity, and decorative effects, such as in performance wear, protective clothing, and anti-static fabrics. Synthetic fibers like polyester and nylon dominate in mass-produced textiles due to their strength, elasticity, moisture resistance, and cost-effectiveness, making them ideal for sportswear, home furnishings, and industrial fabrics. Combining metallic fibers with synthetic fibers creates hybrid textiles that balance aesthetics, functionality, and advanced performance in technical textile sectors.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Metallic fibers, often made from stainless steel or aluminum, offer durability and recyclability but require high energy consumption during production, contributing to a larger carbon footprint compared to synthetic fibers. Synthetic fibers such as polyester and nylon, derived from petrochemicals, contribute significantly to microplastic pollution and are less biodegradable, raising concerns over long-term environmental sustainability. Innovations in recycling technologies and the development of bio-based synthetics are crucial to mitigating the environmental impact associated with both fiber types in the textile industry.
Cost Analysis and Market Trends
Metallic fibers typically incur higher production and material costs compared to synthetic fibers due to their complex manufacturing processes and raw material expenses. Synthetic fibers, such as polyester and nylon, dominate the textile market because of their cost-effectiveness, durability, and versatile applications. Market trends indicate growing demand for sustainable synthetic fibers with recycled content, while metallic fibers maintain niche appeal in high-end fashion and technical textiles requiring conductive or decorative properties.
Future Innovations and Prospects
Metallic fibers in textiles offer superior durability, antimicrobial properties, and electromagnetic shielding, driving innovation in smart fabrics and wearable technology. Synthetic fibers continue to evolve with advancements in bio-based polymers and enhanced moisture-wicking capabilities, improving sustainability and performance. Future prospects involve hybrid materials combining metallic and synthetic fibers to create multifunctional textiles for healthcare, fashion, and industrial applications.
Infographic: Metallic fiber vs Synthetic fiber for Textile
 azmater.com
azmater.com