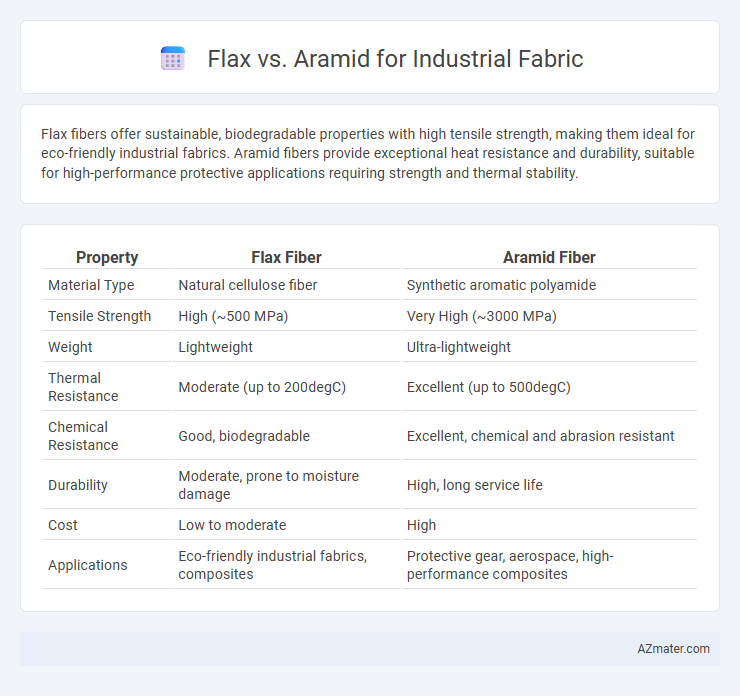
Flax fibers offer sustainable, biodegradable properties with high tensile strength, making them ideal for eco-friendly industrial fabrics. Aramid fibers provide exceptional heat resistance and durability, suitable for high-performance protective applications requiring strength and thermal stability.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Flax Fiber | Aramid Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Natural cellulose fiber | Synthetic aromatic polyamide |
| Tensile Strength | High (~500 MPa) | Very High (~3000 MPa) |
| Weight | Lightweight | Ultra-lightweight |
| Thermal Resistance | Moderate (up to 200degC) | Excellent (up to 500degC) |
| Chemical Resistance | Good, biodegradable | Excellent, chemical and abrasion resistant |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to moisture damage | High, long service life |
| Cost | Low to moderate | High |
| Applications | Eco-friendly industrial fabrics, composites | Protective gear, aerospace, high-performance composites |
Introduction to Flax and Aramid Fibers
Flax fibers, derived from the flax plant, are known for their biodegradability, high tensile strength, and resistance to UV degradation, making them a sustainable choice for industrial fabrics. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, are synthetic hydrocarbons celebrated for exceptional heat resistance, high strength-to-weight ratio, and superior impact protection. Comparing flax vs aramid in industrial applications highlights the trade-off between natural fiber sustainability and the engineered performance of high-performance aramid textiles.
Chemical and Physical Properties Comparison
Flax fibers exhibit superior biodegradability, excellent moisture absorption, and good tensile strength, making them suitable for eco-friendly industrial fabrics. Aramid fibers offer exceptional chemical resistance to acids and alkalis, along with high tensile strength, thermal stability up to 450degC, and flame retardancy, ideal for demanding industrial applications. The choice between flax and aramid depends on balancing environmental factors and performance requirements such as chemical exposure and mechanical stress resistance.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Flax fibers exhibit excellent tensile strength and natural rigidity, making them suitable for industrial fabric applications requiring moderate mechanical strength and biodegradability. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, provide superior mechanical strength with high tensile strength-to-weight ratio and exceptional resistance to abrasion, impact, and heat, ensuring enhanced durability in harsh industrial environments. The choice between flax and aramid depends on the need for sustainable, eco-friendly materials versus maximum durability and performance under extreme mechanical stress.
Weight and Flexibility Differences
Flax fabric is significantly lighter than aramid, with flax fibers weighing around 1.5 grams per cubic centimeter compared to aramid's 1.44 grams per cubic centimeter, offering better overall weight savings in industrial applications. In terms of flexibility, flax fibers provide moderate pliability due to their natural cellulose structure, while aramid fibers exhibit superior flexibility and elongation properties, making them more adaptable in dynamic environments. The choice between flax and aramid fabrics depends on whether priority is given to lightweight characteristics or enhanced flexibility for industrial performance.
Thermal and Flame Resistance
Flax fibers offer moderate thermal resistance, providing an eco-friendly option with natural insulating properties but lower flame resistance compared to aramid. Aramid fabrics, such as Kevlar, deliver superior thermal stability and exceptional flame retardancy, maintaining structural integrity at temperatures exceeding 400degC. Industrial applications demanding high-performance heat and fire resistance prioritize aramid for its durability and protective capabilities in extreme environments.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Flax fibers offer a renewable and biodegradable alternative in industrial fabrics, significantly reducing carbon footprint compared to synthetic aramid fibers derived from petrochemicals. Flax cultivation enhances soil health and requires less energy-intensive processing, whereas aramid production involves considerable chemical use and non-renewable resource depletion. Choosing flax-based fabrics supports sustainability goals through lower environmental impact and improved end-of-life biodegradability in industrial applications.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Flax industrial fabrics offer a cost-effective alternative to aramid, with lower raw material and production expenses contributing to reduced overall pricing. Aramid fabrics, such as Kevlar, provide superior strength and heat resistance but come at a significantly higher cost due to complex manufacturing and specialized applications in aerospace and defense. Economic considerations favor flax when budget constraints and sustainability are prioritized, whereas aramid remains the choice for performance-critical environments demanding enhanced durability and fire resistance.
Industrial Applications: Flax vs Aramid
Flax fibers offer natural breathability, biodegradability, and excellent vibration dampening properties, making them suitable for eco-friendly industrial fabrics used in automotive interiors and lightweight composites. Aramid fibers provide superior heat resistance, high tensile strength, and exceptional durability, ideal for protective clothing, conveyor belts, and insulation in harsh industrial environments. Industrial applications selecting between flax and aramid prioritize flax for sustainability and comfort, while aramid excels in safety and performance under extreme conditions.
Maintenance and Lifespan of Fabrics
Flax industrial fabrics offer natural breathability and biodegradability, requiring minimal chemical maintenance but are more susceptible to moisture damage and UV degradation, which can shorten their lifespan compared to synthetic options. Aramid fabrics, known for superior heat resistance and mechanical strength, demand specialized cleaning to maintain fiber integrity but typically provide a longer lifespan in harsh industrial environments. Proper maintenance routines tailored to each fabric type directly impact durability, with aramid yielding extended service life especially in high-stress applications.
Choosing the Right Fiber for Your Industrial Needs
Flax fibers offer natural strength, biodegradability, and excellent moisture-wicking properties, making them ideal for eco-friendly industrial applications requiring durability and breathability. Aramid fibers provide superior heat resistance, high tensile strength, and chemical stability, suitable for demanding environments like firefighting gear and ballistic protection. Selecting the right fiber depends on specific industrial requirements such as thermal resistance, environmental impact, and mechanical performance.
Infographic: Flax vs Aramid for Industrial fabric
 azmater.com
azmater.com