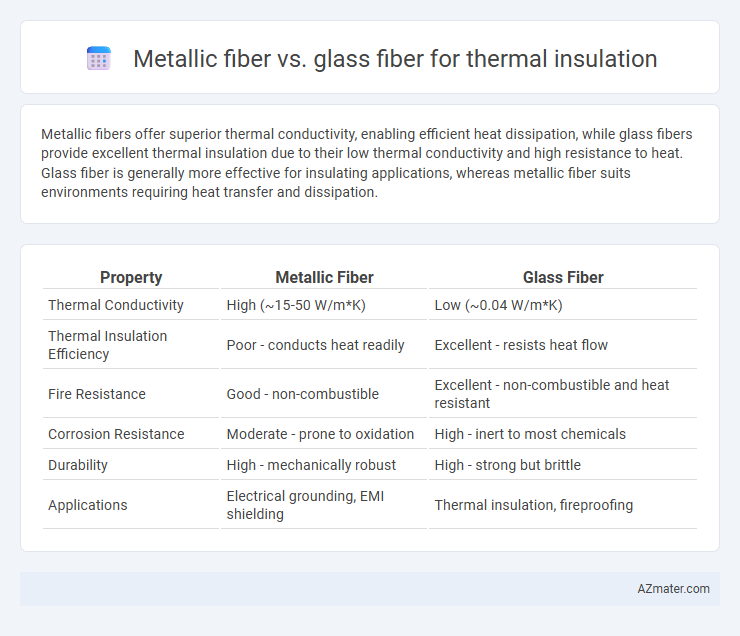
Metallic fibers offer superior thermal conductivity, enabling efficient heat dissipation, while glass fibers provide excellent thermal insulation due to their low thermal conductivity and high resistance to heat. Glass fiber is generally more effective for insulating applications, whereas metallic fiber suits environments requiring heat transfer and dissipation.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Metallic Fiber | Glass Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | High (~15-50 W/m*K) | Low (~0.04 W/m*K) |
| Thermal Insulation Efficiency | Poor - conducts heat readily | Excellent - resists heat flow |
| Fire Resistance | Good - non-combustible | Excellent - non-combustible and heat resistant |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate - prone to oxidation | High - inert to most chemicals |
| Durability | High - mechanically robust | High - strong but brittle |
| Applications | Electrical grounding, EMI shielding | Thermal insulation, fireproofing |
Introduction to Thermal Insulation Materials
Thermal insulation materials such as metallic fiber and glass fiber differ significantly in thermal conductivity and durability, impacting their efficiency in heat retention and loss prevention. Metallic fibers provide superior heat resistance and conductivity, making them suitable for high-temperature applications, whereas glass fibers offer excellent thermal insulation with low thermal conductivity and resistance to chemical corrosion. The choice between metallic and glass fiber depends on specific insulation requirements, including temperature ranges, environmental conditions, and mechanical stability.
What Are Metallic Fibers?
Metallic fibers are fine strands of metal, typically made from stainless steel, aluminum, or copper, used in thermal insulation for their excellent heat resistance and conductivity. Unlike glass fibers, which insulate by trapping air, metallic fibers provide superior durability and thermal stability in high-temperature environments. Their ability to withstand extreme heat and mechanical stress makes them ideal for specialized insulation applications in industrial settings.
What Are Glass Fibers?
Glass fibers are fine strands of glass used primarily for thermal insulation due to their low thermal conductivity and excellent resistance to heat. Compared to metallic fibers, glass fibers offer superior non-conductive properties, making them ideal for reducing heat transfer in various applications. Their lightweight nature and resistance to corrosion enhance durability in insulation systems where temperature regulation is critical.
Thermal Conductivity: Metallic vs Glass Fiber
Metallic fibers generally exhibit higher thermal conductivity, typically ranging from 10 to 400 W/m*K depending on the metal type, which results in less effective thermal insulation compared to glass fibers. Glass fibers have low thermal conductivity values, usually around 0.04 W/m*K, allowing superior resistance to heat transfer and better insulation performance. The low thermal conductivity of glass fibers makes them more suitable for applications requiring efficient thermal insulation.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Metallic fibers exhibit superior mechanical strength compared to glass fibers, offering higher tensile strength and impact resistance ideal for robust thermal insulation applications. Glass fibers provide excellent thermal insulation with lower density but tend to be more brittle and susceptible to damage under mechanical stress. Durability-wise, metallic fibers resist corrosion and maintain structural integrity in harsh environments, while glass fibers can degrade over time when exposed to moisture and thermal cycling.
Fire and Heat Resistance Properties
Metallic fibers offer superior fire resistance and maintain structural integrity at temperatures exceeding 1,000degC, making them ideal for extreme heat insulation applications. Glass fibers provide excellent thermal insulation with melting points around 850degC but can lose strength and degrade under prolonged high-temperature exposure. The choice between metallic and glass fibers depends on the specific thermal and fire resistance requirements, with metallic fibers favored for high-temperature environments demanding durability and safety.
Weight and Flexibility Considerations
Metallic fiber thermal insulation offers superior flexibility and lower weight compared to glass fiber, making it ideal for applications requiring lightweight, adaptable materials. Glass fiber insulation is typically heavier and more rigid, limiting its use in environments where bending or shaping is necessary. The combination of low density and high tensile strength in metallic fibers enhances thermal performance without compromising material flexibility.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Metallic fibers, often made from steel or aluminum, provide good thermal insulation but have a higher environmental impact due to energy-intensive manufacturing and limited recyclability compared to glass fibers. Glass fibers, derived from abundant natural silica, offer excellent thermal resistance with lower embodied energy and greater potential for recycling and reuse, enhancing sustainability in insulation applications. Choosing glass fiber insulation reduces carbon footprint and resource depletion, aligning better with sustainable building practices.
Cost-Effectiveness: Metallic vs Glass Fiber
Metallic fiber insulation generally incurs higher initial costs compared to glass fiber due to expensive raw materials and complex manufacturing processes. Glass fiber offers superior cost-effectiveness, as it is widely produced with abundant raw materials, lower energy requirements, and easier installation, leading to reduced overall expenses. While metallic fiber provides enhanced durability and heat resistance, the significant price difference often makes glass fiber the preferred choice for budget-conscious thermal insulation projects.
Choosing the Right Fiber for Thermal Insulation Applications
Metallic fibers offer superior thermal conductivity and durability, making them ideal for applications requiring rapid heat dissipation and resistance to high temperatures. Glass fibers provide excellent thermal insulation with low thermal conductivity, lightweight properties, and resistance to chemical corrosion, suitable for energy efficiency and fire safety. Selecting the right fiber depends on specific thermal performance needs, environmental exposure, and mechanical strength requirements in insulation systems.
Infographic: Metallic fiber vs Glass fiber for Thermal insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com