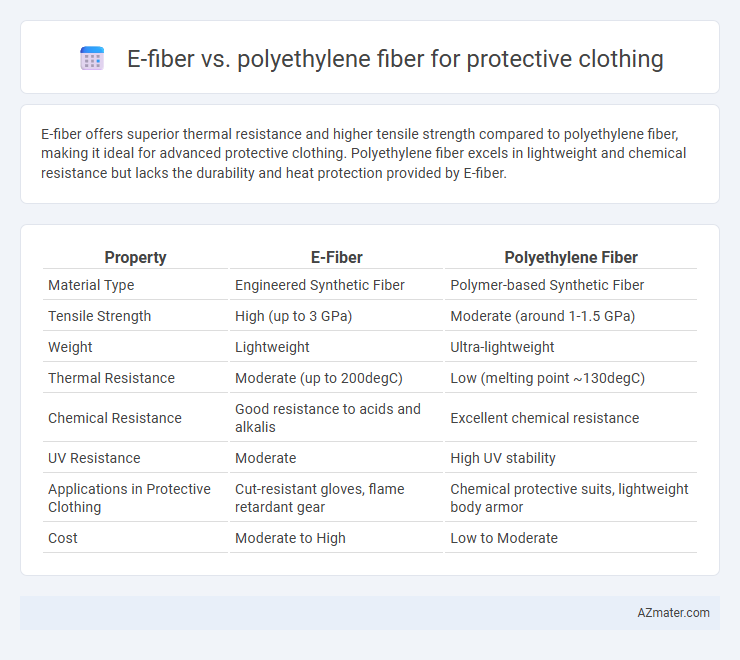
E-fiber offers superior thermal resistance and higher tensile strength compared to polyethylene fiber, making it ideal for advanced protective clothing. Polyethylene fiber excels in lightweight and chemical resistance but lacks the durability and heat protection provided by E-fiber.
Table of Comparison
| Property | E-Fiber | Polyethylene Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Engineered Synthetic Fiber | Polymer-based Synthetic Fiber |
| Tensile Strength | High (up to 3 GPa) | Moderate (around 1-1.5 GPa) |
| Weight | Lightweight | Ultra-lightweight |
| Thermal Resistance | Moderate (up to 200degC) | Low (melting point ~130degC) |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to acids and alkalis | Excellent chemical resistance |
| UV Resistance | Moderate | High UV stability |
| Applications in Protective Clothing | Cut-resistant gloves, flame retardant gear | Chemical protective suits, lightweight body armor |
| Cost | Moderate to High | Low to Moderate |
Introduction to Protective Clothing Fibers
E-fiber and polyethylene fiber are essential materials in the development of protective clothing, each offering unique advantages in performance and durability. E-fiber, known for its high tensile strength and low weight, provides excellent resistance to heat and abrasion, making it ideal for environments requiring enhanced mechanical protection. Polyethylene fiber excels in chemical resistance and moisture repellency, contributing to lightweight, flexible garments designed for hazardous chemical exposures and ballistic protection.
Overview of E-Fiber Technology
E-fiber technology utilizes electrospun nanofibers that provide superior strength, lightweight properties, and excellent moisture vapor transmission, making it highly effective for protective clothing. Compared to polyethylene fiber, E-fibers exhibit enhanced barrier protection against chemical and biological hazards due to their fine fiber diameter and high surface area. This technology enables the production of durable, breathable fabrics that improve wearer comfort and safety in extreme environments.
Understanding Polyethylene Fiber Properties
Polyethylene fiber is characterized by its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, high chemical resistance, and excellent moisture-wicking capabilities, making it ideal for protective clothing applications. Its low density ensures lightweight comfort while providing superior protection against abrasions and chemical exposure compared to E-fiber. The hydrophobic nature of polyethylene fibers enhances durability and reduces absorption of hazardous substances, critical for maintaining safety in demanding environments.
Key Differences between E-Fiber and Polyethylene Fiber
E-fiber, a type of aramid fiber, offers superior heat resistance and flame retardancy compared to polyethylene fiber, which excels in lightweight and chemical resistance. Polyethylene fibers, often used in high-performance protective clothing, provide exceptional cut and abrasion resistance but lack the thermal stability found in E-fibers. The choice between E-fiber and polyethylene fiber depends on specific protective requirements, balancing thermal protection with physical durability.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
E-fiber exhibits superior tensile strength and higher modulus compared to polyethylene fiber, making it more resistant to mechanical stress and deformation in protective clothing applications. Unlike polyethylene fiber, which offers excellent flexibility and impact resistance, E-fiber provides enhanced durability against cuts and abrasions due to its rigid molecular structure. This mechanical advantage makes E-fiber ideal for high-performance protective gear requiring both strength and resistance to mechanical wear.
Thermal and Chemical Resistance
E-fiber offers superior thermal resistance with a melting point exceeding 550degC, making it ideal for protective clothing exposed to extreme heat, while polyethylene fiber typically melts around 130degC, limiting its thermal protection. Chemically, polyethylene fiber demonstrates excellent resistance to acids and solvents, rendering it effective against various chemical hazards, whereas E-fiber exhibits moderate chemical resistance but excels in retaining structural integrity under high-temperature chemical exposure. Protective clothing combining E-fiber and polyethylene fiber can optimize performance by leveraging E-fiber's thermal stability and polyethylene's chemical protection.
Comfort and Wearability Factors
E-fiber offers superior moisture-wicking properties and enhanced breathability compared to polyethylene fiber, significantly improving comfort in protective clothing. Polyethylene fiber is lightweight and resistant to chemicals but can trap heat and moisture, reducing overall wearability during extended use. The advanced thermal regulation of E-fiber supports prolonged wear, making it ideal for environments requiring both protection and comfort.
Cost and Environmental Impact Analysis
E-fiber protective clothing offers higher thermal resistance and durability but comes at a significantly higher cost compared to polyethylene fiber, which remains more affordable for large-scale production. Polyethylene fibers provide a lower environmental footprint due to easier recyclability and reduced resource consumption during manufacturing, whereas E-fibers involve energy-intensive processes leading to greater carbon emissions. Choosing between the two depends on balancing cost-efficiency with sustainability goals, as E-fiber excels in performance but imposes heavier environmental and financial burdens.
Best Applications for E-Fiber vs Polyethylene
E-fiber excels in protective clothing requiring high thermal resistance and flame retardancy, making it ideal for firefighting gear and industrial heat protection. Polyethylene fiber offers superior cut resistance and lightweight durability, suited for applications like cut-resistant gloves and ballistic vests. Selecting E-fiber or polyethylene depends on specific hazards, with E-fiber preferred for heat and flame exposure, while polyethylene targets impact and abrasion threats.
Future Trends in Protective Clothing Materials
E-fiber offers exceptional tensile strength and thermal resistance, making it a prime candidate for next-generation protective clothing designed to withstand extreme conditions. Polyethylene fiber provides lightweight, cut-resistant, and chemical-resistant properties, increasingly integrated into protective gear for enhanced mobility and safety. Future trends emphasize hybrid fabrics combining E-fiber's durability with polyethylene's flexibility, aiming to maximize protection while improving wearer comfort and performance.
Infographic: E-fiber vs Polyethylene fiber for Protective clothing
 azmater.com
azmater.com