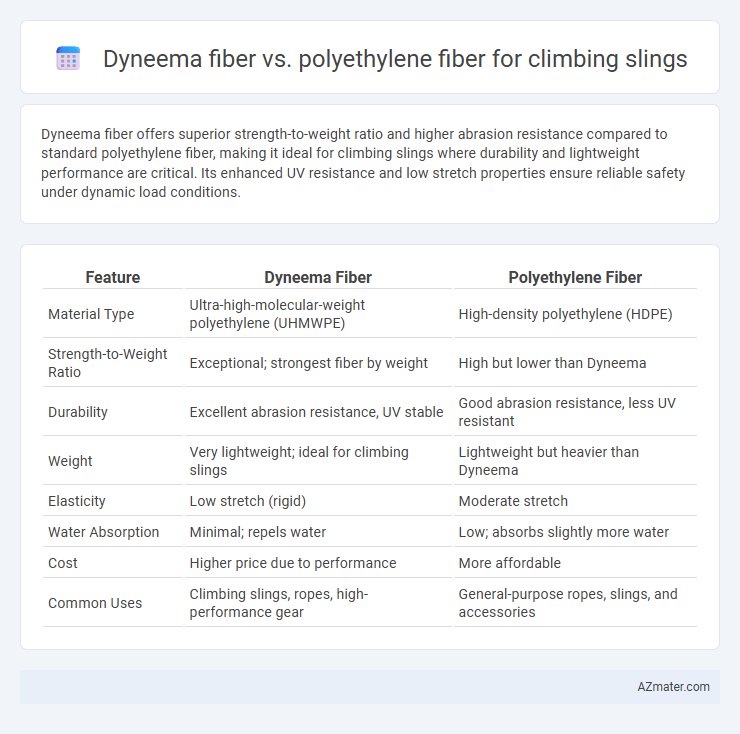
Dyneema fiber offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and higher abrasion resistance compared to standard polyethylene fiber, making it ideal for climbing slings where durability and lightweight performance are critical. Its enhanced UV resistance and low stretch properties ensure reliable safety under dynamic load conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Dyneema Fiber | Polyethylene Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) | High-density polyethylene (HDPE) |
| Strength-to-Weight Ratio | Exceptional; strongest fiber by weight | High but lower than Dyneema |
| Durability | Excellent abrasion resistance, UV stable | Good abrasion resistance, less UV resistant |
| Weight | Very lightweight; ideal for climbing slings | Lightweight but heavier than Dyneema |
| Elasticity | Low stretch (rigid) | Moderate stretch |
| Water Absorption | Minimal; repels water | Low; absorbs slightly more water |
| Cost | Higher price due to performance | More affordable |
| Common Uses | Climbing slings, ropes, high-performance gear | General-purpose ropes, slings, and accessories |
Introduction: Understanding Dyneema and Polyethylene Fibers
Dyneema fiber, a brand of ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE), offers exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and high resistance to abrasion, making it ideal for climbing slings. Polyethylene fiber, including other UHMWPE variants, shares similar properties but may vary in durability and elongation, affecting performance under dynamic loads. Understanding the molecular structure and mechanical properties of both fibers helps climbers choose slings that optimize safety, weight, and durability.
Material Composition: Dyneema vs. Standard Polyethylene
Dyneema fiber consists of ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) with a highly aligned molecular structure, offering exceptional tensile strength and abrasion resistance compared to standard polyethylene fibers. Standard polyethylene used in climbing slings typically has lower molecular weight and less orientation, resulting in reduced strength and durability under load. Dyneema's optimized molecular alignment and density provide superior performance in climbing gear, making it a preferred choice for high-strength, lightweight slings.
Strength and Load-Bearing Capacity Comparison
Dyneema fiber, known for its ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) composition, offers exceptional tensile strength with a breaking strength exceeding 3,480 MPa, making it one of the strongest materials used in climbing slings. Polyethylene fiber, although similar in base material, generally exhibits lower strength levels and reduced load-bearing capacity compared to Dyneema, often translating to decreased durability under dynamic climbing loads. The superior strength-to-weight ratio of Dyneema fibers provides climbers with reliable, lightweight slings capable of sustaining high impact forces and prolonged wear in demanding climbing scenarios.
Weight and Packability Differences
Dyneema fiber, also known as UHMWPE (Ultra-High-Molecular-Weight Polyethylene), is renowned for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, making climbing slings made from Dyneema significantly lighter than those made from traditional polyethylene fibers. This lightweight characteristic enhances packability as Dyneema slings compress easily into compact sizes, reducing bulk in a climber's gear. In contrast, polyethylene fibers tend to be heavier and less compressible, which can increase the overall weight and decrease the packability of climbing slings.
Abrasion and UV Resistance: Which Lasts Longer?
Dyneema fiber exhibits superior abrasion resistance compared to polyethylene fiber, making it more durable for climbing slings exposed to rough surfaces. Its excellent UV resistance ensures that Dyneema retains strength and integrity longer under prolonged sunlight exposure. Polyethylene fiber, while strong, degrades faster under UV rays and wears down more quickly with abrasion, resulting in a shorter lifespan for climbing slings made from this material.
Flexibility and Handling Performance in Climbing
Dyneema fiber offers superior flexibility and lightweight handling, enhancing climbers' grip and knotability in slings compared to traditional polyethylene fiber. Polyethylene fiber, while durable and high-strength, tends to be stiffer, which can reduce maneuverability and comfort during technical climbs. The enhanced flexibility of Dyneema slings improves overall performance by allowing smoother rope management and quicker adjustments on demanding routes.
Moisture Absorption and Weather Resistance
Dyneema fiber exhibits extremely low moisture absorption, typically less than 0.01%, ensuring minimal weight gain and maintaining tensile strength in wet conditions, which is crucial for climbing slings exposed to varying weather. Polyethylene fiber also offers low water absorption but tends to absorb slightly more moisture compared to Dyneema, potentially affecting drying time and sling performance over prolonged exposure. In terms of weather resistance, Dyneema outperforms polyethylene with superior UV resistance and corrosion resistance, making it more durable for outdoor climbing applications.
Knotting Security: Dyneema vs. Polyethylene in Practice
Dyneema fiber exhibits superior knotting security compared to standard polyethylene fiber in climbing slings, as its ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) structure provides higher tensile strength and reduced elongation, enhancing knot stability under load. Polyethylene fibers, while strong and lightweight, tend to have higher slippage and less secure knots, which can compromise sling reliability during critical climbing maneuvers. Practical applications favor Dyneema slings for consistent knot integrity, especially in dynamic climbing environments where secure load-bearing connections are vital.
Lifespan and Durability of Climbing Slings
Dyneema fiber offers exceptional lifespan and durability for climbing slings due to its high resistance to abrasion, UV exposure, and moisture, maintaining strength over extended use. Polyethylene fiber, while lightweight and strong, tends to degrade faster under repeated mechanical stress and UV exposure, reducing the overall lifespan of slings. Climbers prioritize Dyneema slings for long-term reliability, especially in harsh outdoor conditions where sustained performance and durability are critical.
Price and Value: Which Fiber Offers More for Climbers?
Dyneema fiber, renowned for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and low stretch, typically comes at a higher price point compared to traditional polyethylene fibers used in climbing slings. Polyethylene fiber, while more affordable, generally offers lower durability and tensile strength, potentially impacting long-term value for serious climbers seeking reliability and safety. Climbers prioritizing cost-effective solutions might lean towards polyethylene, but those valuing superior performance and longevity often find Dyneema's premium price justified by enhanced safety and reduced sling weight.
Infographic: Dyneema fiber vs Polyethylene fiber for Climbing sling
 azmater.com
azmater.com