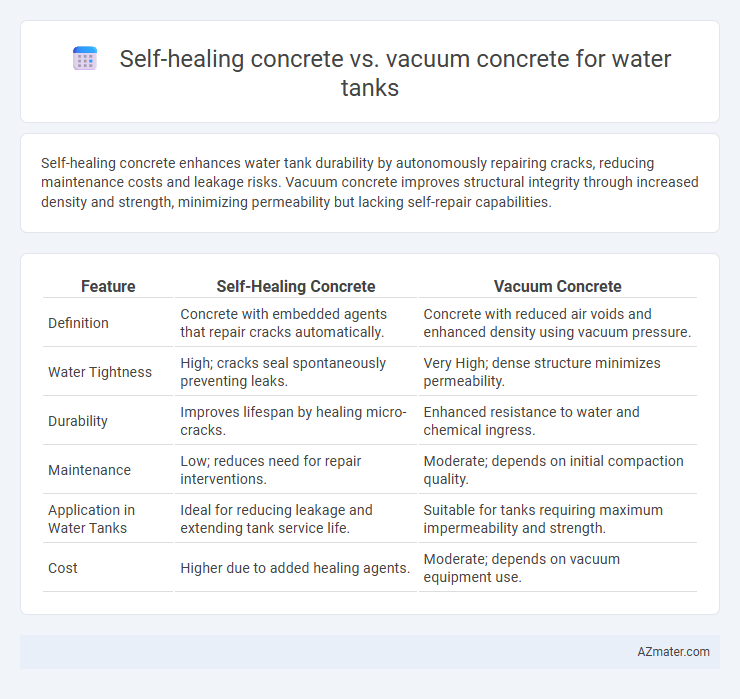
Self-healing concrete enhances water tank durability by autonomously repairing cracks, reducing maintenance costs and leakage risks. Vacuum concrete improves structural integrity through increased density and strength, minimizing permeability but lacking self-repair capabilities.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Self-Healing Concrete | Vacuum Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Concrete with embedded agents that repair cracks automatically. | Concrete with reduced air voids and enhanced density using vacuum pressure. |
| Water Tightness | High; cracks seal spontaneously preventing leaks. | Very High; dense structure minimizes permeability. |
| Durability | Improves lifespan by healing micro-cracks. | Enhanced resistance to water and chemical ingress. |
| Maintenance | Low; reduces need for repair interventions. | Moderate; depends on initial compaction quality. |
| Application in Water Tanks | Ideal for reducing leakage and extending tank service life. | Suitable for tanks requiring maximum impermeability and strength. |
| Cost | Higher due to added healing agents. | Moderate; depends on vacuum equipment use. |
Introduction to Advanced Concrete Technologies for Water Tanks
Self-healing concrete incorporates microcapsules or bacteria that activate upon cracking, autonomously sealing fissures and enhancing the durability of water tanks. Vacuum concrete employs a vacuum process to remove excess water and air, resulting in a denser, stronger material with improved impermeability essential for water containment. These advanced concrete technologies significantly improve structural integrity and longevity, reducing maintenance costs and minimizing leakage risks in water tank applications.
Understanding Self-Healing Concrete: Mechanism and Benefits
Self-healing concrete incorporates microcapsules or bacteria that activate upon cracking, sealing fissures autonomously and thereby enhancing durability in water tanks. This mechanism reduces maintenance costs and prevents water leakage by restoring structural integrity without external intervention. Compared to vacuum concrete, which relies on compaction to remove air voids and improve strength, self-healing concrete offers proactive crack repair and long-term sustainability.
Exploring Vacuum Concrete: Process and Advantages
Vacuum concrete enhances water tank durability by using a vacuum process to remove excess water and air from the concrete mix, resulting in a denser, more impermeable structure. This method reduces porosity and microcracks, improving resistance to water leakage and chemical attack. Compared to self-healing concrete, vacuum concrete offers immediate strength and long-term stability without relying on bacterial or polymer additives.
Durability Comparison: Self-Healing vs Vacuum Concrete
Self-healing concrete enhances durability in water tanks by autonomously repairing micro-cracks through embedded bacteria or chemical agents, preventing water infiltration and structural degradation. Vacuum concrete improves durability by reducing porosity and increasing density via the removal of air bubbles during mixing, resulting in stronger and more water-resistant structures. Compared to vacuum concrete, self-healing concrete offers extended service life and reduced maintenance costs by actively addressing cracks as they form, enhancing long-term durability for water storage applications.
Water Tightness and Leak Prevention Capabilities
Self-healing concrete enhances water tightness and leak prevention in water tanks through its ability to automatically seal cracks using embedded microcapsules or bacteria-based healing agents, reducing maintenance needs and prolonging tank lifespan. Vacuum concrete improves water tightness by compacting the mix under vacuum conditions, minimizing porosity and microcracks to create a denser, less permeable structure that effectively prevents water leakage. While self-healing concrete offers dynamic repair capacity, vacuum concrete provides superior initial impermeability, making the choice dependent on long-term durability requirements and maintenance considerations.
Maintenance Requirements and Lifecycle Costs
Self-healing concrete significantly reduces maintenance requirements for water tanks by autonomously repairing micro-cracks, thus preventing leaks and structural damage over time. Vacuum concrete, while providing improved compaction and durability, often requires periodic inspections and maintenance to address potential voids or weaknesses. Over the lifecycle, self-healing concrete tends to lower total costs by minimizing repair interventions and extending service life, whereas vacuum concrete may incur higher maintenance expenses despite its initial robustness.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Aspects
Self-healing concrete enhances sustainability in water tanks by autonomously repairing micro-cracks, reducing the need for frequent maintenance and minimizing resource consumption over the structure's lifespan. Vacuum concrete, produced through air removal techniques, can improve density and durability but often requires energy-intensive manufacturing processes, potentially increasing its environmental footprint. Prioritizing self-healing concrete supports longer service life and lower carbon emissions, aligning closely with eco-friendly construction and water conservation goals.
Structural Performance and Load-Bearing Capacity
Self-healing concrete enhances water tank longevity by autonomously repairing cracks, maintaining structural integrity under cyclic loading and reducing permeability, which improves load-bearing capacity over time. Vacuum concrete achieves superior compaction and reduced porosity through air extraction, resulting in high initial density and strength, optimizing structural performance under static and dynamic loads. Both materials offer advanced durability; self-healing concrete excels in crack management, while vacuum concrete provides immediate high load resistance for water tank structures.
Suitability for Different Water Tank Applications
Self-healing concrete offers superior durability and crack repair capabilities ideal for potable water tanks requiring long-term integrity and minimal maintenance. Vacuum concrete provides enhanced density and reduced permeability, making it suitable for industrial or wastewater tanks where chemical resistance and structural strength are critical. Selection depends on specific water tank applications, with self-healing concrete favored for potable and vacuum concrete for harsh or high-load environmental conditions.
Cost Analysis and Economic Feasibility
Self-healing concrete reduces long-term maintenance costs by autonomously repairing micro-cracks, but its initial material expenses are 30-50% higher than traditional vacuum concrete. Vacuum concrete offers faster curing times and improved compaction, leading to lower upfront costs and enhanced structural integrity, yet it lacks the autonomous crack repair capabilities that minimize lifecycle expenses. Economically, self-healing concrete demonstrates greater feasibility for large-scale water tanks requiring extended service life and reduced downtime, whereas vacuum concrete suits budget-conscious projects prioritizing immediate cost savings.
Infographic: Self-healing concrete vs Vacuum concrete for Water tank
 azmater.com
azmater.com