Polymer-modified concrete enhances durability and flexibility, making it ideal for road construction in harsh environments. Roller-compacted concrete offers rapid placement and high compressive strength, optimizing efficiency and load-bearing capacity on highways.
Table of Comparison
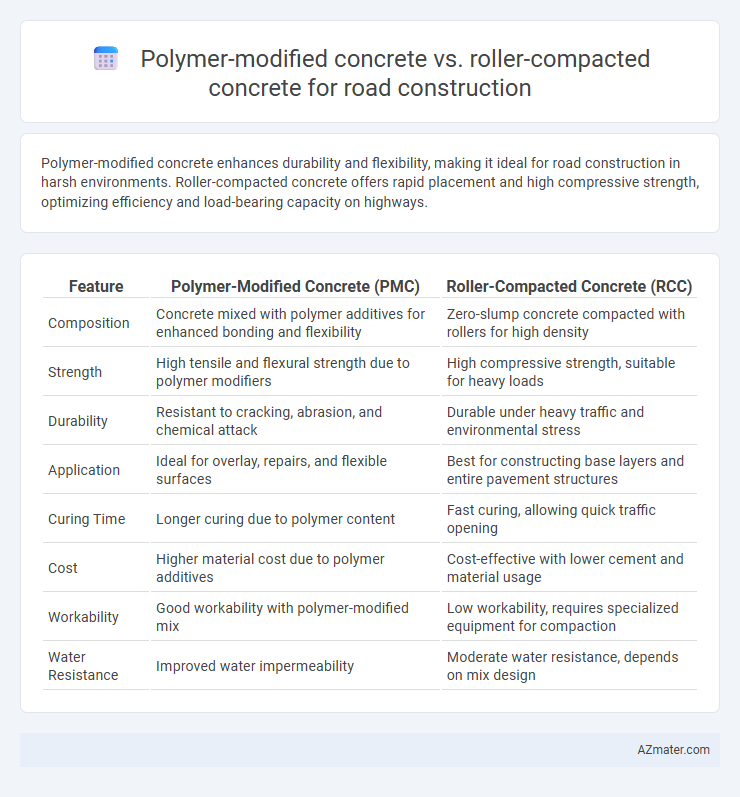
| Feature | Polymer-Modified Concrete (PMC) | Roller-Compacted Concrete (RCC) |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Concrete mixed with polymer additives for enhanced bonding and flexibility | Zero-slump concrete compacted with rollers for high density |
| Strength | High tensile and flexural strength due to polymer modifiers | High compressive strength, suitable for heavy loads |
| Durability | Resistant to cracking, abrasion, and chemical attack | Durable under heavy traffic and environmental stress |
| Application | Ideal for overlay, repairs, and flexible surfaces | Best for constructing base layers and entire pavement structures |
| Curing Time | Longer curing due to polymer content | Fast curing, allowing quick traffic opening |
| Cost | Higher material cost due to polymer additives | Cost-effective with lower cement and material usage |
| Workability | Good workability with polymer-modified mix | Low workability, requires specialized equipment for compaction |
| Water Resistance | Improved water impermeability | Moderate water resistance, depends on mix design |
Introduction to Modern Road Construction Materials
Polymer-modified concrete enhances traditional concrete by incorporating polymers that improve flexibility, adhesion, and durability, making it ideal for high-stress road surfaces prone to cracking and deformation. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) offers a cost-effective, rapid construction solution with its low-slump mix compacted by rollers, providing high compressive strength and resistance to heavy traffic loads. Both materials address modern road construction demands, with polymer-modified concrete suited for rehabilitation and overlays, while RCC excels in new pavements requiring fast placement and long-term performance.
Overview of Polymer-Modified Concrete
Polymer-modified concrete (PMC) incorporates polymers to enhance traditional concrete properties, improving flexibility, adhesion, and durability in road construction. This modification increases resistance to cracking, chemical attack, and freeze-thaw cycles, making PMC ideal for high-traffic and harsh environmental conditions. Compared to conventional concrete types, PMC offers superior performance in terms of longevity and maintenance requirements on road surfaces.
Understanding Roller-Compacted Concrete
Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) is a stiff, low-slump concrete widely used in road construction for its high durability and rapid placement capabilities. Its dry consistency allows placement with earth-moving equipment and compaction by vibratory rollers, enabling faster construction and reduced costs compared to traditional polymer-modified concrete (PMC). RCC's dense, interlocked aggregate matrix provides excellent load-bearing capacity and resistance to rutting, making it ideal for heavy traffic roadways and industrial pavements.
Key Material Properties: PMC vs RCC
Polymer-modified concrete (PMC) exhibits enhanced flexural strength and superior chemical resistance compared to conventional roller-compacted concrete (RCC), making it ideal for high-stress road applications exposed to aggressive environments. RCC offers higher compressive strength and rapid placement capabilities with lower cement content, promoting economic efficiency and faster construction timelines. The improved bonding properties and reduced permeability of PMC contribute to increased durability, while RCC's dense matrix provides excellent load distribution under heavy traffic loads.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Polymer-modified concrete exhibits higher tensile and flexural strength compared to roller-compacted concrete due to the enhanced bonding properties of polymers, making it more resistant to crack propagation in road construction. Roller-compacted concrete provides excellent compressive strength and rapid setting time, which suits heavy traffic applications but may have lower durability under freeze-thaw cycles and chemical exposure. Both materials offer robust structural performance, with polymer-modified concrete delivering superior long-term durability and resistance to environmental stressors.
Construction Techniques and Equipment
Polymer-modified concrete (PMC) utilizes specialized admixtures and requires standard concrete mixers and traditional paver equipment for placement, often demanding precise temperature and curing control to enhance bonding and durability. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) relies on asphalt-type paving machines and vibratory rollers for rapid, layer-wise compaction, enabling faster construction with minimal formwork. Equipment choice directly influences project timelines and structural performance, with PMC suited for high-strength overlay applications and RCC favored for cost-effective, large-scale pavement construction.
Cost Analysis: PMC vs RCC
Polymer-modified concrete (PMC) generally incurs higher material costs due to the addition of polymers that enhance durability and bonding, which can lead to long-term savings by reducing maintenance expenses. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) offers lower initial costs with faster placement and reduced labor requirements, making it cost-effective for large-scale road construction projects. However, PMC's improved resistance to cracking and chemical attacks may justify its premium price in environments requiring enhanced performance and extended service life.
Performance in Harsh Environments
Polymer-modified concrete exhibits superior durability and resistance to chemical attacks, freeze-thaw cycles, and abrasion, making it highly effective in harsh environments for road construction. Roller-compacted concrete offers excellent strength and rapid construction but may have lower resistance to extreme weathering and chemical exposure compared to polymer-modified variants. Selecting polymer-modified concrete improves longevity and reduces maintenance costs in aggressive climates where roads face severe environmental stresses.
Maintenance and Longevity Considerations
Polymer-modified concrete significantly enhances road durability by improving resistance to cracking, abrasion, and chemical attack, reducing maintenance frequency and extending service life compared to traditional concretes. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) offers rapid construction benefits and high load-bearing capacity but may require more frequent surface maintenance due to its porous texture and potential for surface wear. Choosing polymer-modified concrete often results in lower long-term maintenance costs and greater longevity, while RCC provides cost-effective initial construction with moderate upkeep demands.
Best Applications for PMC and RCC in Road Projects
Polymer-modified concrete (PMC) excels in road construction projects requiring enhanced durability, chemical resistance, and flexibility, making it ideal for bridge decks, highways with heavy traffic, and areas prone to extreme weather conditions. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) is best suited for large-scale pavement applications, such as airport runways, industrial roads, and highway surfaces where rapid construction and high compressive strength are priorities. PMC's superior adhesion and crack resistance optimize longevity in demanding environments, while RCC offers cost-effective, fast-setting solutions for extensive surface coverage under heavy loading.
Infographic: Polymer-modified concrete vs Roller-compacted concrete for Road construction
 azmater.com
azmater.com