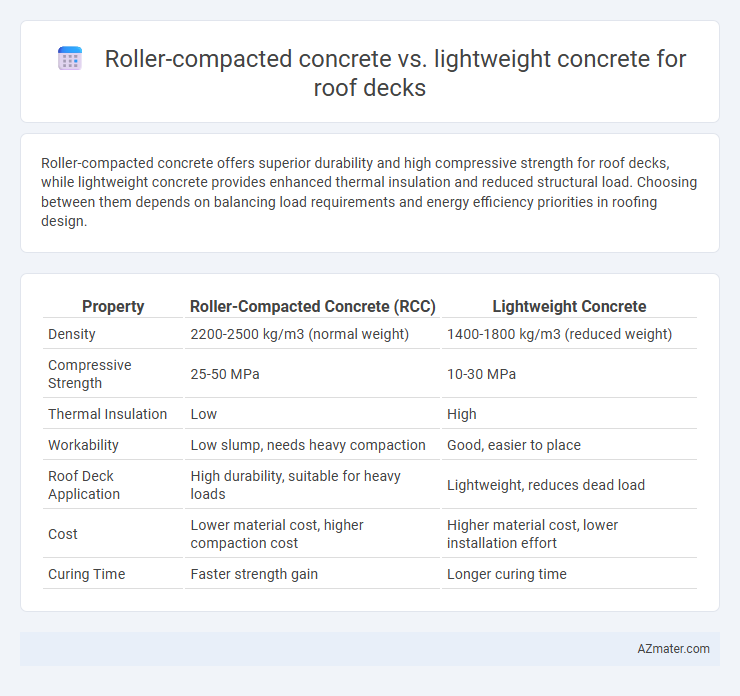
Roller-compacted concrete offers superior durability and high compressive strength for roof decks, while lightweight concrete provides enhanced thermal insulation and reduced structural load. Choosing between them depends on balancing load requirements and energy efficiency priorities in roofing design.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Roller-Compacted Concrete (RCC) | Lightweight Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 2200-2500 kg/m3 (normal weight) | 1400-1800 kg/m3 (reduced weight) |
| Compressive Strength | 25-50 MPa | 10-30 MPa |
| Thermal Insulation | Low | High |
| Workability | Low slump, needs heavy compaction | Good, easier to place |
| Roof Deck Application | High durability, suitable for heavy loads | Lightweight, reduces dead load |
| Cost | Lower material cost, higher compaction cost | Higher material cost, lower installation effort |
| Curing Time | Faster strength gain | Longer curing time |
Introduction to Roof Deck Materials
Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) for roof decks offers high compressive strength, durability, and rapid construction due to its low cement content and minimal water usage. Lightweight concrete, often incorporating expanded clay or shale aggregates, provides superior thermal insulation and reduces the overall dead load on structures. Selecting between RCC and lightweight concrete depends on factors such as structural load capacity, thermal performance, and installation speed in roof deck applications.
What is Roller-Compacted Concrete (RCC)?
Roller-Compacted Concrete (RCC) is a dry mix concrete with no-slump consistency, allowing it to be compacted by heavy rollers, making it highly durable and suitable for roof decks requiring strong load-bearing capacity. RCC offers excellent resistance to wear, erosion, and heavy traffic, contrasting with lightweight concrete, which provides better thermal insulation but lower structural strength. Its high density and rapid construction time make RCC ideal for robust roofing systems in industrial and commercial buildings.
What is Lightweight Concrete?
Lightweight concrete is a type of concrete that incorporates lightweight aggregates such as expanded clay, shale, or pumice to reduce density while maintaining structural strength, making it ideal for roof decks due to its reduced dead load. Its lower thermal conductivity enhances insulation, contributing to energy efficiency and comfort in building design. Compared to roller-compacted concrete, lightweight concrete provides improved workability and better load distribution for roofing applications.
Key Properties Comparison: RCC vs Lightweight Concrete
Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) for roof decks offers high compressive strength ranging from 20 to 40 MPa and excellent durability, making it suitable for heavy load-bearing structures, while lightweight concrete provides densities between 1200 to 1850 kg/m3 and superior thermal insulation properties, reducing roof dead load significantly. RCC exhibits low permeability and high abrasion resistance, ensuring lifespan extension in harsh weather conditions, whereas lightweight concrete enhances energy efficiency due to its thermal conductivity values as low as 0.1 to 0.4 W/m*K. The choice depends on structural load requirements and insulation needs, with RCC favoring robustness and lightweight concrete prioritizing weight reduction and insulation performance.
Structural Performance and Load-Bearing Capacity
Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) exhibits higher compressive strength and superior load-bearing capacity compared to lightweight concrete, making it ideal for roof decks requiring robust structural performance. Lightweight concrete offers reduced dead load due to lower density, which can enhance seismic performance but typically provides lower strength and stiffness. For applications demanding heavy load resistance and durability, RCC is preferred, while lightweight concrete suits designs prioritizing weight reduction over ultimate load capacity.
Insulation and Thermal Efficiency
Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) offers superior structural strength but has lower insulation properties compared to lightweight concrete, which contains air-entrained aggregates enhancing thermal resistance. Lightweight concrete's reduced density and higher porosity result in better thermal efficiency, reducing heat transfer and improving energy savings for roof decks. Choosing lightweight concrete for roof decks optimizes insulation performance, while RCC prioritizes load-bearing capacity and durability.
Installation Methods and Construction Speed
Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) for roof decks utilizes heavy rollers for compaction, enabling rapid placement and swift curing, which significantly accelerates construction speed compared to traditional methods. Lightweight concrete, applied using conventional formwork and often requiring longer curing times, slows down the installation process due to its delicate handling and finishing requirements. RCC's mechanized installation promotes efficiency in large-scale projects, while lightweight concrete offers advantages in reducing dead load but at the expense of faster construction timelines.
Cost Analysis and Material Availability
Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) offers cost advantages for roof decks due to its use of less cement and lower labor requirements compared to conventional concrete, making it more economical in large-scale projects. Lightweight concrete, while typically more expensive per cubic meter because of specialized aggregates like expanded clay or shale, provides savings by reducing roof dead loads and enabling smaller supporting structures. Material availability for RCC is generally better due to reliance on standard aggregates and cement, whereas lightweight concrete depends on region-specific lightweight aggregates, which can limit sourcing and increase costs in some areas.
Durability and Maintenance Requirements
Roller-compacted concrete offers high durability and compressive strength, making it resistant to cracking and wear on roof decks, with low maintenance requirements due to its dense and impermeable surface. Lightweight concrete, while providing excellent thermal insulation and reduced structural load, generally has lower durability and may require more frequent maintenance to address potential issues like surface spalling or moisture penetration. Choosing between the two depends on balancing the need for long-term durability with thermal performance and maintenance capacity for the specific roof deck application.
Best Applications for RCC and Lightweight Concrete in Roof Decks
Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) is best suited for roof decks requiring high structural strength and durability, such as industrial or commercial buildings with heavy load demands. Lightweight concrete excels in applications where reducing dead load is critical, improving thermal insulation and seismic performance in residential or low-rise buildings. Selecting RCC offers superior wear resistance and rapid construction, while lightweight concrete provides enhanced energy efficiency and ease of installation for roof deck systems.
Infographic: Roller-compacted concrete vs Lightweight concrete for Roof deck
 azmater.com
azmater.com