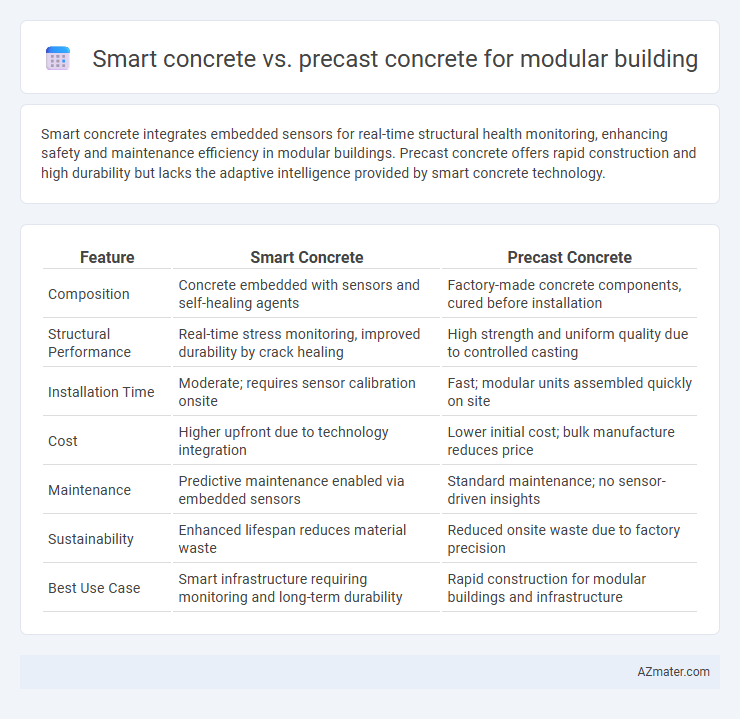
Smart concrete integrates embedded sensors for real-time structural health monitoring, enhancing safety and maintenance efficiency in modular buildings. Precast concrete offers rapid construction and high durability but lacks the adaptive intelligence provided by smart concrete technology.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Smart Concrete | Precast Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Concrete embedded with sensors and self-healing agents | Factory-made concrete components, cured before installation |
| Structural Performance | Real-time stress monitoring, improved durability by crack healing | High strength and uniform quality due to controlled casting |
| Installation Time | Moderate; requires sensor calibration onsite | Fast; modular units assembled quickly on site |
| Cost | Higher upfront due to technology integration | Lower initial cost; bulk manufacture reduces price |
| Maintenance | Predictive maintenance enabled via embedded sensors | Standard maintenance; no sensor-driven insights |
| Sustainability | Enhanced lifespan reduces material waste | Reduced onsite waste due to factory precision |
| Best Use Case | Smart infrastructure requiring monitoring and long-term durability | Rapid construction for modular buildings and infrastructure |
Introduction to Modular Building Materials
Smart concrete integrates sensors and self-healing properties, enhancing durability and structural health monitoring in modular building applications. Precast concrete offers controlled factory production, ensuring consistent quality and rapid on-site assembly for modular structures. Both materials optimize construction efficiency and sustainability but differ in technology implementation and performance benefits.
What is Smart Concrete?
Smart concrete integrates advanced materials such as sensors and self-healing agents to monitor structural health and automatically repair minor damages, enhancing durability and safety in modular buildings. It offers real-time data on stress, strain, and environmental conditions, enabling proactive maintenance and reducing long-term costs. This innovative material contrasts with traditional precast concrete, which is manufactured off-site and emphasizes rapid assembly but lacks embedded monitoring capabilities.
Understanding Precast Concrete
Precast concrete, manufactured in controlled factory environments, offers consistent quality and rapid installation for modular buildings, reducing onsite labor and construction time. Its precise casting process enables integration of complex shapes and embedded components, enhancing structural performance and design flexibility. Compared to smart concrete with embedded sensors and adaptive properties, precast concrete excels in scalability and uniformity, making it a preferred choice for large-scale modular construction projects.
Key Differences: Smart Concrete vs Precast Concrete
Smart concrete integrates advanced materials like sensors and self-healing agents to enhance durability and monitor structural health in real-time, whereas precast concrete consists of factory-produced, standardized components designed for quick assembly on-site. Smart concrete offers adaptive performance with capabilities such as crack detection and stress response, while precast concrete emphasizes uniformity, controlled quality, and reduced construction time. The key differences lie in smart concrete's technological adaptability and real-time data integration compared to precast concrete's modular, production-efficient approach for building assembly.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Smart concrete incorporates advanced materials like graphene and self-healing agents to significantly enhance strength and durability, outperforming traditional precast concrete by reducing microcrack formation and improving load-bearing capacity. Precast concrete offers uniform quality and controlled curing conditions, resulting in reliable compressive strength typically ranging from 30 to 60 MPa, but lacks the adaptive resilience provided by smart concrete technologies. The integration of smart concrete in modular buildings extends service life and reduces maintenance costs through autonomous crack repair and superior resistance to environmental degradation compared to conventional precast elements.
Installation Process and Speed
Smart concrete in modular building offers a rapid installation process due to its self-healing properties and adaptability, reducing downtime and labor costs. Precast concrete panels are manufactured off-site, enabling quick on-site assembly but often requiring heavy lifting equipment and precise alignment, which can extend setup time. Choosing smart concrete enhances speed by minimizing repairs and adjustments during installation, whereas precast concrete relies on efficient logistics and crew coordination for timely construction.
Cost Analysis and Efficiency
Smart concrete integrates sensors and self-healing properties, reducing long-term maintenance costs and improving structural longevity in modular buildings, while its initial installation may be higher. Precast concrete offers cost advantages through mass production, faster onsite assembly, and consistent quality control, significantly lowering labor and construction time expenses. Evaluating both, smart concrete optimizes operational efficiency and lifecycle costs, whereas precast concrete excels in upfront cost savings and streamlined construction processes.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Smart concrete incorporates self-healing properties that significantly extend the lifespan of modular buildings, reducing waste and the need for frequent repairs. Precast concrete allows for precise manufacturing in controlled environments, minimizing material wastage and lowering energy consumption during construction. Both materials enhance sustainability by promoting energy efficiency and reducing carbon footprints, with smart concrete providing added benefits through advanced durability and reduced maintenance requirements.
Applications in Modular Construction
Smart concrete offers adaptive strength monitoring and real-time data feedback, enhancing structural safety and performance in modular building projects. Precast concrete provides uniform quality and rapid assembly, making it ideal for repetitive modular components with precise dimensional control. Combining smart technology with precast elements optimizes modular construction efficiency and long-term durability.
Future Trends in Concrete Technologies for Modular Building
Smart concrete integrates self-sensing and self-healing properties through embedded nanomaterials and sensors, enhancing durability and reducing maintenance costs in modular buildings. Precast concrete offers rapid construction and high-quality control due to factory fabrication, yet lacks the adaptive responsiveness of smart concrete technologies. Future trends emphasize hybrid approaches combining precast methods with smart concrete innovations to optimize structural performance, sustainability, and lifecycle efficiency in modular construction.
Infographic: Smart concrete vs Precast concrete for Modular building
 azmater.com
azmater.com