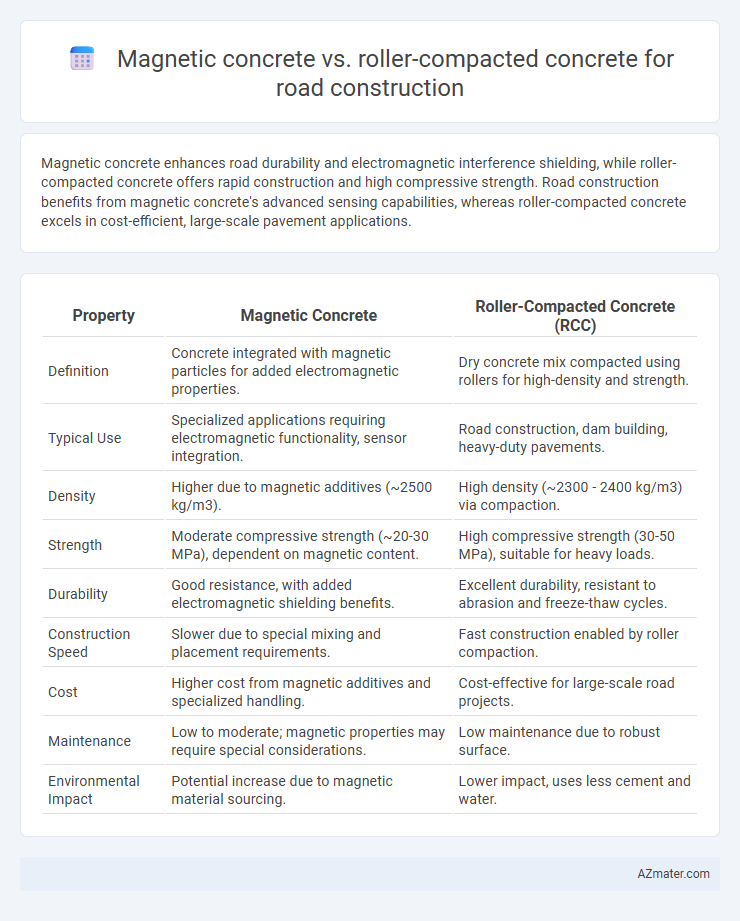
Magnetic concrete enhances road durability and electromagnetic interference shielding, while roller-compacted concrete offers rapid construction and high compressive strength. Road construction benefits from magnetic concrete's advanced sensing capabilities, whereas roller-compacted concrete excels in cost-efficient, large-scale pavement applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Magnetic Concrete | Roller-Compacted Concrete (RCC) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Concrete integrated with magnetic particles for added electromagnetic properties. | Dry concrete mix compacted using rollers for high-density and strength. |
| Typical Use | Specialized applications requiring electromagnetic functionality, sensor integration. | Road construction, dam building, heavy-duty pavements. |
| Density | Higher due to magnetic additives (~2500 kg/m3). | High density (~2300 - 2400 kg/m3) via compaction. |
| Strength | Moderate compressive strength (~20-30 MPa), dependent on magnetic content. | High compressive strength (30-50 MPa), suitable for heavy loads. |
| Durability | Good resistance, with added electromagnetic shielding benefits. | Excellent durability, resistant to abrasion and freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Construction Speed | Slower due to special mixing and placement requirements. | Fast construction enabled by roller compaction. |
| Cost | Higher cost from magnetic additives and specialized handling. | Cost-effective for large-scale road projects. |
| Maintenance | Low to moderate; magnetic properties may require special considerations. | Low maintenance due to robust surface. |
| Environmental Impact | Potential increase due to magnetic material sourcing. | Lower impact, uses less cement and water. |
Introduction to Magnetic Concrete and Roller-Compacted Concrete
Magnetic concrete incorporates ferromagnetic materials like iron particles to enhance electromagnetic properties, enabling functionalities such as structural health monitoring and deicing in road construction. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) is a zero-slump concrete blend characterized by its dry consistency, placed and compacted with heavy rollers to provide high strength and durability for pavements and heavy-duty roads. Comparing these materials reveals that magnetic concrete offers smart infrastructure capabilities, whereas RCC emphasizes rapid construction and cost-effectiveness for large-scale road projects.
Composition and Material Properties
Magnetic concrete incorporates ferromagnetic materials such as iron filings or magnetic powders, enhancing electromagnetic properties and potential for structural health monitoring, whereas roller-compacted concrete (RCC) consists primarily of a low-water content mix with Portland cement, aggregates, and minimal additives, designed for high compaction and rapid curing. Magnetic concrete exhibits unique magnetic permeability and electrical conductivity, enabling sensors integration, while RCC emphasizes high strength, durability, and wear resistance suitable for heavy-traffic road surfaces. The material properties of RCC ensure excellent load distribution and reduced permeability, contrasting with magnetic concrete's specialized application potential driven by its composite's magnetic responsiveness.
Construction Methods and Processes
Magnetic concrete incorporates ferromagnetic materials within the mix, requiring specialized casting and curing processes that enhance structural magnetic properties and allow for innovative monitoring techniques during road construction. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) utilizes a dry mix compacted by heavy rollers, emphasizing rapid on-site placement and minimal curing time, which facilitates faster construction and reduced labor costs for road projects. The distinct construction methods of magnetic concrete involve advanced material handling and precision alignment, whereas RCC relies on conventional earth-moving equipment and compaction technology for efficient pavement installation.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Magnetic concrete incorporates iron particles, enhancing internal microstructure and improving load-bearing capacity, which can increase compressive strength by up to 25% compared to traditional mixes. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) offers exceptional density and low permeability due to its dry consistency and compaction method, resulting in superior durability against abrasion and freeze-thaw cycles. While magnetic concrete excels in strength augmentation, RCC's durability benefits make it highly suitable for heavy-traffic road construction demanding long-term resistance to environmental stresses.
Performance in Various Climates
Magnetic concrete incorporates iron particles enhancing thermal conductivity, which improves heat dissipation and reduces freeze-thaw damage in cold climates, whereas roller-compacted concrete (RCC) offers superior density and strength, making it highly durable under heavy traffic and extreme temperature fluctuations. RCC's rapid construction and low permeability contribute to excellent performance in both hot, arid and wet, humid environments. Magnetic concrete's ability to integrate electromagnetic sensing systems supports proactive maintenance in diverse climatic conditions, while RCC's proven resilience ensures long-term structural integrity.
Cost Analysis and Economic Feasibility
Magnetic concrete incorporates ferromagnetic materials, increasing initial costs by 20-30% compared to conventional roller-compacted concrete (RCC), which remains favored for its lower cost and ease of application in large-scale road construction. While magnetic concrete offers potential long-term benefits like enhanced structural health monitoring and durability, the high material and technology investment currently limits its economic feasibility for widespread use. RCC provides a cost-effective alternative with established performance and lower maintenance expenses, making it the more economically viable choice for most road infrastructure projects.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Magnetic concrete incorporates iron oxide particles, enhancing electromagnetic properties and potentially enabling energy-efficient infrastructure monitoring, while offering recycling advantages through magnetic separation techniques. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) consumes less water and cement compared to traditional concrete, reducing carbon emissions and promoting rapid construction with minimal disturbance to the environment. Both materials contribute to sustainable road construction by lowering resource consumption and enhancing durability, but RCC's established eco-friendly credentials currently surpass magnetic concrete's emerging green benefits.
Maintenance and Lifecycle Considerations
Magnetic concrete incorporates ferromagnetic particles enhancing self-healing properties and early crack detection, potentially reducing maintenance frequency and extending lifecycle durability in road construction. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) offers rapid construction with high compressive strength and low permeability, minimizing long-term maintenance needs due to improved resistance against wear and environmental factors. Lifecycle cost analysis often favors RCC for its lower overall maintenance expenditure despite magnetic concrete's innovative monitoring capabilities.
Suitability for Different Road Types
Magnetic concrete offers enhanced durability and self-sensing capabilities, making it suitable for smart urban roads requiring real-time condition monitoring. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) provides high compressive strength and rapid construction efficiency, ideal for heavy-duty highways and industrial pavements. Selection depends on traffic load, environmental conditions, and maintenance needs, with magnetic concrete favored for intelligent infrastructure and RCC for cost-effective, robust surface layers.
Future Prospects and Technological Innovations
Magnetic concrete integrates ferromagnetic nanoparticles to enhance self-healing properties and electromagnetic shielding, promising improved durability and reduced maintenance costs in road construction. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) utilizes a dry mix and heavy compaction, offering rapid construction and high load-bearing capacity suitable for large infrastructure projects. Future prospects for road construction hinge on combining magnetic concrete's smart functionalities with RCC's mechanical strength, driven by advances in nanotechnology and automated compaction machinery.
Infographic: Magnetic concrete vs Roller-compacted concrete for Road construction
 azmater.com
azmater.com