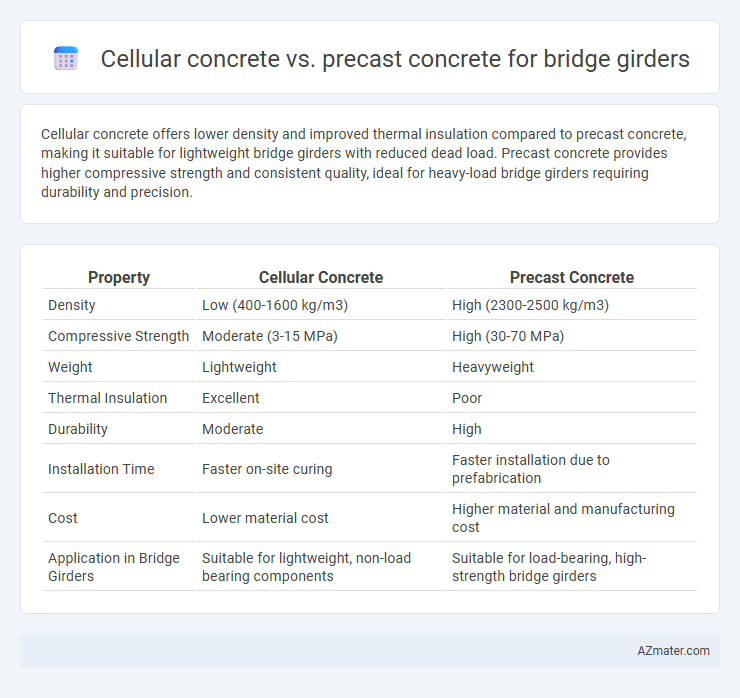
Cellular concrete offers lower density and improved thermal insulation compared to precast concrete, making it suitable for lightweight bridge girders with reduced dead load. Precast concrete provides higher compressive strength and consistent quality, ideal for heavy-load bridge girders requiring durability and precision.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Cellular Concrete | Precast Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Density | Low (400-1600 kg/m3) | High (2300-2500 kg/m3) |
| Compressive Strength | Moderate (3-15 MPa) | High (30-70 MPa) |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavyweight |
| Thermal Insulation | Excellent | Poor |
| Durability | Moderate | High |
| Installation Time | Faster on-site curing | Faster installation due to prefabrication |
| Cost | Lower material cost | Higher material and manufacturing cost |
| Application in Bridge Girders | Suitable for lightweight, non-load bearing components | Suitable for load-bearing, high-strength bridge girders |
Introduction to Bridge Girder Construction Materials
Cellular concrete and precast concrete represent two prominent materials for bridge girder construction, each offering distinct structural and performance advantages. Cellular concrete, characterized by its lightweight and enhanced thermal insulation properties, provides reduced dead load on bridge superstructures and improved energy efficiency. Precast concrete exhibits high compressive strength and quality control benefits due to factory fabrication, enabling rapid onsite installation and consistent durability in bridge girder applications.
What is Cellular Concrete?
Cellular concrete is a lightweight, low-density material composed of cement, water, and a pre-formed foam that creates numerous small air bubbles, resulting in reduced weight and improved thermal insulation. This material provides excellent workability and can be easily poured or pumped into complex forms, making it suitable for applications requiring reduced dead load on bridge girders. Compared to precast concrete, cellular concrete offers advantages in weight reduction and better impact absorption, which can enhance the overall durability and performance of bridge structures.
Understanding Precast Concrete
Precast concrete for bridge girders offers high strength, durability, and quality control due to factory fabrication under controlled conditions, resulting in consistent structural performance. It enables faster construction timelines and reduced on-site labor compared to cellular concrete, which is lighter but less robust for heavy load applications. Understanding precast concrete's modular nature helps optimize bridge design by facilitating complex shapes and ensuring precise dimensional tolerances critical for long-span girders.
Strength and Load-Bearing Comparison
Cellular concrete exhibits lower compressive strength, typically ranging between 3 to 12 MPa, compared to precast concrete's high strength values of 30 to 70 MPa, making precast concrete more suitable for bridge girders requiring significant load-bearing capacity. Precast concrete girders offer superior durability and structural performance under heavy traffic loads and dynamic forces, ensuring longer service life in bridge applications. The lightweight property of cellular concrete reduces dead load but limits its use to non-primary load-bearing elements, whereas precast concrete's higher density and strength provide the necessary support for main structural components like bridge girders.
Weight and Density Differences
Cellular concrete offers significantly lower density, typically ranging from 400 to 1600 kg/m3, compared to precast concrete's density of around 2400 kg/m3, resulting in reduced dead load on bridge girders. The lightweight nature of cellular concrete enhances ease of handling and transportation, while maintaining sufficient compressive strength for non-structural or secondary structural applications in bridge construction. Precast concrete's higher density provides superior load-bearing capacity and durability, making it ideal for primary structural elements where weight is less critical.
Durability and Longevity
Cellular concrete offers enhanced durability for bridge girders due to its lightweight structure and superior resistance to freeze-thaw cycles, reducing the risk of cracking and structural damage over time. Precast concrete provides exceptional longevity through controlled manufacturing processes that ensure consistent density and strength, leading to high resistance against weathering, chemical exposure, and corrosion. Both materials contribute to extended bridge service life, but precast concrete generally outperforms cellular concrete in load-bearing capacity and long-term durability under heavy traffic conditions.
Installation and Construction Time
Cellular concrete offers faster installation for bridge girders due to its lightweight nature and ease of casting on-site, reducing the need for heavy lifting equipment compared to precast concrete. Precast concrete girders require transportation and crane placement, which can extend construction time, especially in remote or congested areas. The reduced curing time and adaptability of cellular concrete contribute to quicker project turnaround and lower labor costs during bridge girder construction.
Cost Analysis: Cellular vs Precast Concrete
Cellular concrete offers significant cost savings in bridge girder construction due to its reduced material density, lowering transportation and handling expenses compared to precast concrete. Precast concrete requires extensive formwork and curing facilities, increasing initial costs, whereas cellular concrete can be cast in place, minimizing labor and site preparation expenditures. Maintenance and longevity costs favor precast concrete, but the upfront cost efficiency of cellular concrete makes it a competitive option for budget-sensitive bridge projects.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Cellular concrete offers superior sustainability for bridge girders due to its lightweight composition, reducing material consumption and lowering carbon emissions during transportation and installation. Precast concrete, while durable and strong, generally involves higher energy use and raw material extraction, leading to a larger environmental footprint. The porous structure of cellular concrete enhances thermal insulation and reduces the urban heat island effect, promoting eco-friendly construction practices in bridge infrastructure.
Suitability for Bridge Girder Applications
Cellular concrete offers lightweight properties and excellent thermal insulation, making it suitable for reducing overall bridge girder weight and easing transportation and installation. Precast concrete provides superior structural strength, durability, and consistent quality, ideal for bearing heavy loads and ensuring long-term performance in bridge girders. The choice between cellular and precast concrete hinges on project-specific requirements, including load capacity, durability, and construction efficiency.
Infographic: Cellular concrete vs Precast concrete for Bridge girder
 azmater.com
azmater.com