Acid-resistant concrete offers superior chemical durability in foundation applications exposed to aggressive acidic environments, preventing structural degradation. Blast-furnace slag concrete enhances foundation longevity through improved sulfate resistance and reduced permeability, contributing to durability in corrosive soil conditions.
Table of Comparison
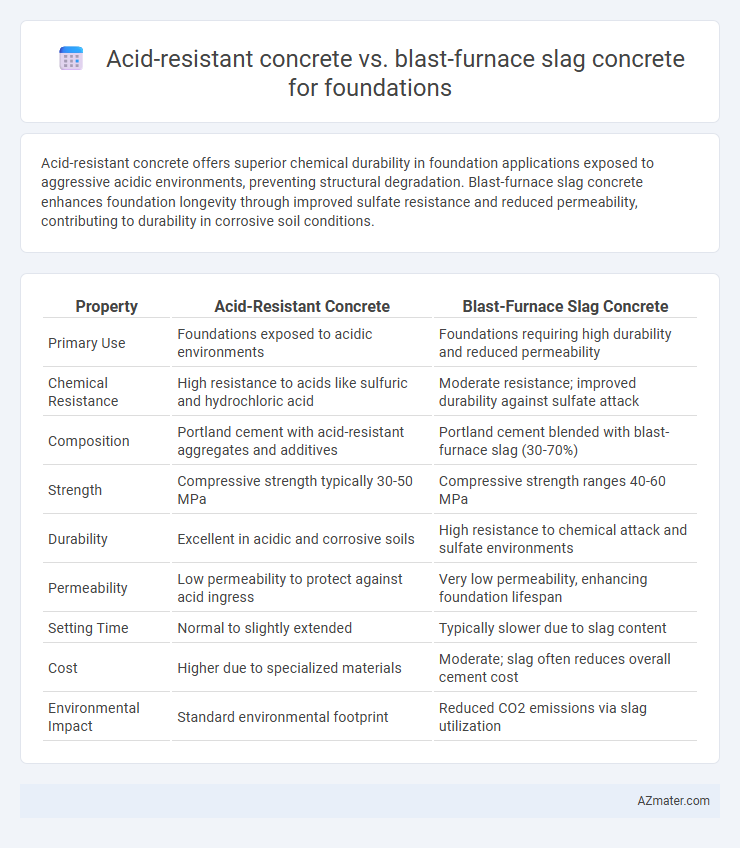
| Property | Acid-Resistant Concrete | Blast-Furnace Slag Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Foundations exposed to acidic environments | Foundations requiring high durability and reduced permeability |
| Chemical Resistance | High resistance to acids like sulfuric and hydrochloric acid | Moderate resistance; improved durability against sulfate attack |
| Composition | Portland cement with acid-resistant aggregates and additives | Portland cement blended with blast-furnace slag (30-70%) |
| Strength | Compressive strength typically 30-50 MPa | Compressive strength ranges 40-60 MPa |
| Durability | Excellent in acidic and corrosive soils | High resistance to chemical attack and sulfate environments |
| Permeability | Low permeability to protect against acid ingress | Very low permeability, enhancing foundation lifespan |
| Setting Time | Normal to slightly extended | Typically slower due to slag content |
| Cost | Higher due to specialized materials | Moderate; slag often reduces overall cement cost |
| Environmental Impact | Standard environmental footprint | Reduced CO2 emissions via slag utilization |
Introduction to Specialized Concrete Types for Foundations
Acid-resistant concrete offers exceptional durability in highly acidic environments, making it ideal for foundations exposed to aggressive chemical conditions, while blast-furnace slag concrete enhances structural strength and sustainability by incorporating industrial by-products that improve resistance to sulfate attacks. Both specialized concretes optimize foundational integrity by addressing specific environmental challenges: acid-resistant concrete prevents degradation from corrosive substances, and blast-furnace slag concrete reduces permeability and increases long-term durability in harsh soil conditions. Selecting the appropriate type depends on site-specific chemical exposures and load-bearing requirements crucial for foundation longevity and performance.
Understanding Acid-Resistant Concrete: Composition and Properties
Acid-resistant concrete is specifically formulated with chemical-resistant aggregates and binders such as silica fume and high alumina cement to withstand highly acidic environments, providing superior durability against chemical corrosion compared to blast-furnace slag concrete. Blast-furnace slag concrete primarily enhances strength and sulfate resistance through ground granulated blast-furnace slag (GGBFS), but it offers limited protection in strong acid conditions. Understanding these compositional differences is critical for foundation applications exposed to acidic soils or industrial waste, where acid-resistant concrete ensures long-term structural integrity and mitigates degradation.
Blast-Furnace Slag Concrete: Key Features and Benefits
Blast-furnace slag concrete incorporates ground granulated blast-furnace slag (GGBFS) as a supplementary cementitious material, enhancing durability and resistance to chemical attacks, including acids. It offers superior sulfate and chloride resistance compared to traditional acid-resistant concrete, making it ideal for foundations exposed to aggressive environments. The use of blast-furnace slag reduces permeability, increases long-term strength, and lowers carbon footprint, promoting sustainable construction practices.
Comparative Chemical Resistance: Acid-Attack Scenarios
Acid-resistant concrete outperforms blast-furnace slag concrete in environments exposed to strong acids such as sulfuric or hydrochloric acid, effectively preventing degradation through specialized acid-resistant aggregates and cementitious materials. Blast-furnace slag concrete provides moderate resistance by reducing permeability and chemical ingress but may suffer deterioration under prolonged acid attack due to its calcium-rich matrix. Chemical resistance in foundation applications depends heavily on the specific acid concentration, exposure duration, and pH levels, with acid-resistant concrete offering superior durability in aggressive acid-attack scenarios.
Mechanical Performance in Aggressive Environments
Acid-resistant concrete exhibits superior chemical durability and compressive strength when exposed to highly acidic environments, making it ideal for foundations in industries handling corrosive substances. Blast-furnace slag concrete demonstrates enhanced resistance to sulfate attack and improved long-term strength due to its dense microstructure and reduced permeability in aggressive soil conditions. Mechanical performance in aggressive environments favors acid-resistant concrete for acid exposure, while blast-furnace slag concrete offers balanced strength and durability against sulfate-rich or marine environments.
Durability and Longevity of Foundation Structures
Acid-resistant concrete incorporates specialized aggregates and chemical additives to withstand corrosive environments, significantly enhancing the durability of foundation structures exposed to acidic soils or industrial waste. Blast-furnace slag concrete leverages ground granulated blast-furnace slag (GGBFS) as a supplementary cementitious material, improving resistance to chemical attacks and reducing permeability, which contributes to the longevity of foundations in sulfate-rich or aggressive environments. Both concrete types extend foundation lifespan by mitigating degradation mechanisms, but acid-resistant concrete is preferable for highly acidic conditions, while blast-furnace slag concrete offers cost-effective durability improvements in sulfate-prone soils.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Acid-resistant concrete provides enhanced durability in chemically aggressive environments, reducing maintenance frequency and resource consumption over the foundation's lifespan. Blast-furnace slag concrete offers significant sustainability benefits by utilizing industrial by-products, lowering CO2 emissions, and decreasing reliance on traditional Portland cement. Incorporating blast-furnace slag in foundation concrete promotes circular economy principles and reduces environmental impact while maintaining adequate resistance to environmental stressors.
Installation and Curing Considerations
Acid-resistant concrete requires meticulous installation with specialized admixtures to ensure chemical stability and typically demands extended curing periods to achieve its full strength and resistance properties. Blast-furnace slag concrete, known for its enhanced durability and reduced permeability, benefits from moderate curing temperatures and can often be cured using standard water curing methods, which accelerates strength development. Both types require careful moisture control during curing to optimize performance in foundation applications, but acid-resistant mixtures may necessitate additional protective measures against aggressive chemical environments.
Cost Analysis: Initial and Lifecycle Expenses
Acid-resistant concrete typically incurs higher initial costs due to specialized materials like epoxy resins and chemical-resistant aggregates, which enhance durability in acidic environments. Blast-furnace slag concrete offers a more economical upfront price by incorporating industrial by-products that improve strength and sulfate resistance while reducing cement usage and carbon footprint. Lifecycle expenses favor blast-furnace slag concrete through reduced maintenance and repair costs caused by acid degradation, making it a cost-effective choice for foundations exposed to moderate chemical attacks.
Recommended Applications: Selecting the Right Concrete for Foundations
Acid-resistant concrete is ideal for industrial foundations exposed to aggressive chemical environments, ensuring durability against acidic corrosion. Blast-furnace slag concrete offers enhanced strength and improved resistance to sulfate attack, making it suitable for foundations in harsh soil conditions and marine settings. Choosing between these concretes depends on the specific environmental challenges and chemical exposure expected at the foundation site.
Infographic: Acid-resistant concrete vs Blast-furnace slag concrete for Foundation
 azmater.com
azmater.com