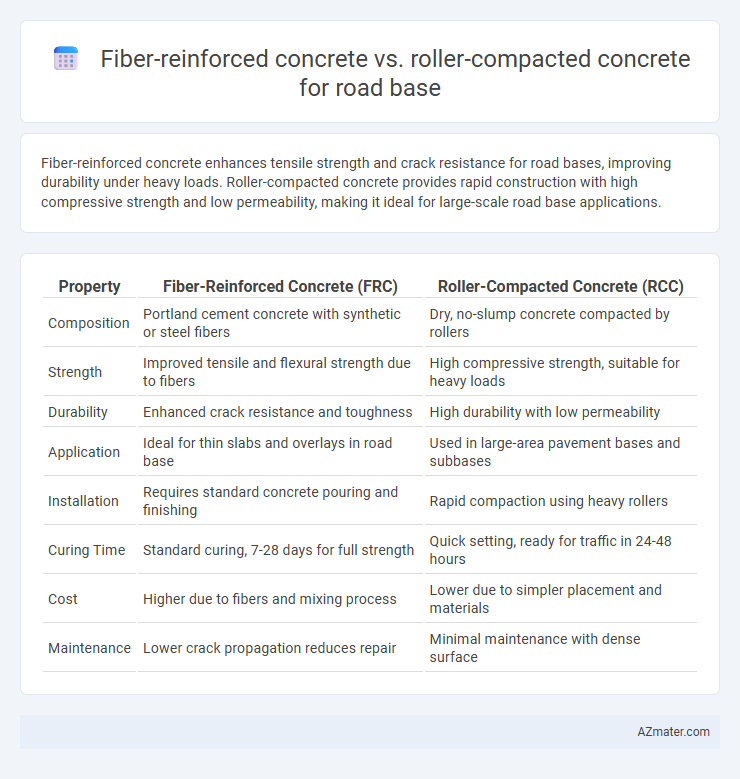
Fiber-reinforced concrete enhances tensile strength and crack resistance for road bases, improving durability under heavy loads. Roller-compacted concrete provides rapid construction with high compressive strength and low permeability, making it ideal for large-scale road base applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Fiber-Reinforced Concrete (FRC) | Roller-Compacted Concrete (RCC) |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Portland cement concrete with synthetic or steel fibers | Dry, no-slump concrete compacted by rollers |
| Strength | Improved tensile and flexural strength due to fibers | High compressive strength, suitable for heavy loads |
| Durability | Enhanced crack resistance and toughness | High durability with low permeability |
| Application | Ideal for thin slabs and overlays in road base | Used in large-area pavement bases and subbases |
| Installation | Requires standard concrete pouring and finishing | Rapid compaction using heavy rollers |
| Curing Time | Standard curing, 7-28 days for full strength | Quick setting, ready for traffic in 24-48 hours |
| Cost | Higher due to fibers and mixing process | Lower due to simpler placement and materials |
| Maintenance | Lower crack propagation reduces repair | Minimal maintenance with dense surface |
Introduction to Modern Road Base Materials
Fiber-reinforced concrete enhances road base durability by integrating synthetic or steel fibers that improve tensile strength and crack resistance, making it suitable for heavy traffic conditions. Roller-compacted concrete, a dry-mix concrete placed with rollers, offers rapid construction and high compressive strength, optimizing the road base for large-scale infrastructure projects. Both materials represent advancements in modern road base engineering, prioritizing longevity and performance under dynamic loads.
Understanding Fiber-Reinforced Concrete
Fiber-reinforced concrete (FRC) incorporates discrete fibers such as steel, glass, or synthetic materials to enhance tensile strength, impact resistance, and crack control in road base applications. Compared to roller-compacted concrete (RCC), FRC offers improved durability and flexibility under dynamic loads, reducing maintenance costs over time. Its microstructural reinforcement makes FRC particularly effective in mitigating shrinkage and fatigue-related damages in pavement bases.
Overview of Roller-Compacted Concrete
Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) for road base offers a high-density, low-slump mixture compacted by vibratory rollers, resulting in exceptional strength and durability ideal for heavy traffic conditions. RCC demonstrates rapid curing times and reduced construction costs compared to traditional concrete due to its in-place compaction and minimal formwork requirements. Its rigid pavement characteristics provide superior load distribution and long-term performance, making it a preferred choice for highways, industrial pavements, and airport runways.
Key Material Properties Comparison
Fiber-reinforced concrete (FRC) offers enhanced tensile strength and crack resistance due to the integration of synthetic or steel fibers, improving durability under dynamic loading conditions in road base applications. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) is characterized by its lower water content and high-density compaction, resulting in superior compressive strength and rapid construction speed, making it ideal for large-scale road base projects. Both materials exhibit distinct performance benefits: FRC excels in crack control and toughness, while RCC provides robust load-bearing capacity and economical placement efficiency.
Construction Techniques and Equipment
Fiber-reinforced concrete for road bases requires precise mixing equipment to evenly distribute synthetic or steel fibers within the concrete matrix, enhancing tensile strength and crack resistance during placement using standard slipform pavers or conventional finishing tools. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) employs heavy vibratory rollers during compaction, eliminating the need for conventional finishing; construction crews rely on high-capacity mixers and spreaders tailored for low-slump concrete, accelerating pavement installation with robust mechanical compaction methods. Equipment selection directly influences the material performance and installation speed, with fiber reinforcement demanding meticulous blending, whereas RCC benefits from efficient, large-scale rolling techniques ideal for high-volume road base applications.
Durability and Longevity Analysis
Fiber-reinforced concrete (FRC) enhances road base durability by improving crack resistance and tensile strength through the integration of synthetic or steel fibers, leading to extended service life under dynamic loads. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) offers superior compressive strength and abrasion resistance due to its dense, low-slump mix, making it highly durable for heavy traffic applications but more susceptible to shrinkage cracks without fiber reinforcement. Long-term performance analysis indicates that FRC provides enhanced toughness and fatigue resistance, while RCC's cost-effectiveness and rapid placement favor large-scale projects, with optimal durability achieved when combined with fiber reinforcement technologies.
Performance Under Heavy Traffic Loads
Fiber-reinforced concrete exhibits enhanced tensile strength and crack resistance, significantly improving durability under heavy traffic loads compared to traditional mixes. Roller-compacted concrete offers excellent compressive strength and rapid construction benefits, but may exhibit lower flexural performance without fiber reinforcement. Evaluating their load-bearing capacity and fatigue resistance is crucial in optimizing road base performance for high-traffic conditions.
Cost Considerations and Economic Efficiency
Fiber-reinforced concrete (FRC) offers enhanced durability and crack resistance but typically incurs higher initial costs due to fiber materials and mixing complexity. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) provides a more cost-effective solution for road bases with faster placement and reduced labor costs, making it economically efficient for large-scale projects. Evaluating project scale, material availability, and long-term maintenance costs is crucial for selecting the optimal concrete type for road base applications.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Fiber-reinforced concrete enhances durability and reduces maintenance frequency, lowering resource consumption and environmental footprint over the road base lifecycle. Roller-compacted concrete requires less water and energy during production, contributing to a smaller carbon footprint and rapid construction with minimal site disturbance. Both materials support sustainable road construction, with fiber reinforcement optimizing long-term performance and roller-compacted concrete enabling efficient, eco-friendly installation.
Choosing the Right Concrete for Your Road Base
Fiber-reinforced concrete offers enhanced tensile strength and crack resistance, making it ideal for road bases subjected to heavy loads and dynamic stresses. Roller-compacted concrete provides rapid construction with high durability and cost-effectiveness, suitable for large-scale projects with tight timelines. Selecting the right concrete depends on factors such as traffic intensity, budget constraints, and specific site conditions to optimize long-term performance and maintenance costs.
Infographic: Fiber-reinforced concrete vs Roller-compacted concrete for Road base
 azmater.com
azmater.com