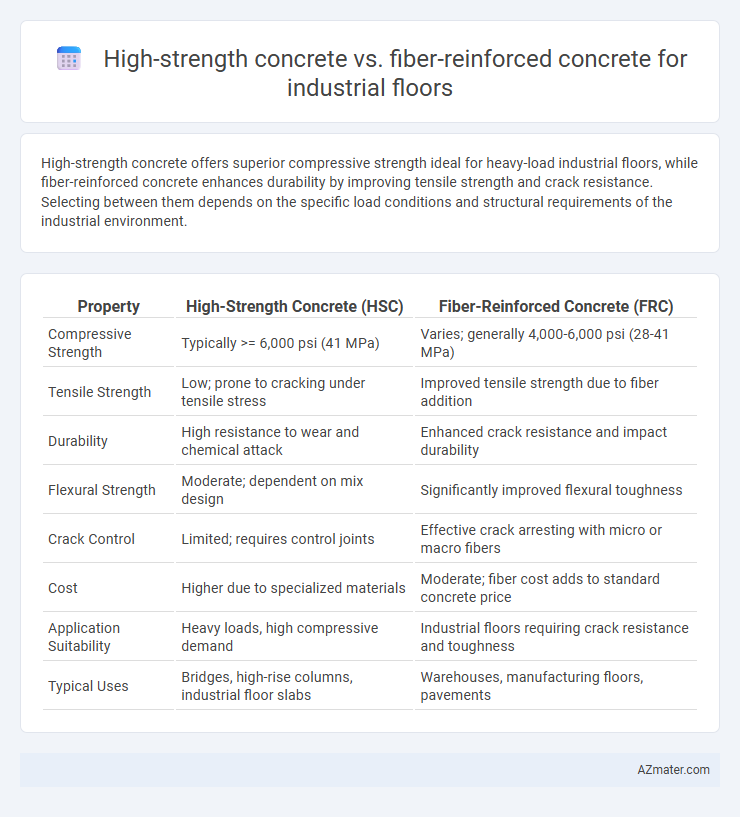
High-strength concrete offers superior compressive strength ideal for heavy-load industrial floors, while fiber-reinforced concrete enhances durability by improving tensile strength and crack resistance. Selecting between them depends on the specific load conditions and structural requirements of the industrial environment.
Table of Comparison
| Property | High-Strength Concrete (HSC) | Fiber-Reinforced Concrete (FRC) |
|---|---|---|
| Compressive Strength | Typically >= 6,000 psi (41 MPa) | Varies; generally 4,000-6,000 psi (28-41 MPa) |
| Tensile Strength | Low; prone to cracking under tensile stress | Improved tensile strength due to fiber addition |
| Durability | High resistance to wear and chemical attack | Enhanced crack resistance and impact durability |
| Flexural Strength | Moderate; dependent on mix design | Significantly improved flexural toughness |
| Crack Control | Limited; requires control joints | Effective crack arresting with micro or macro fibers |
| Cost | Higher due to specialized materials | Moderate; fiber cost adds to standard concrete price |
| Application Suitability | Heavy loads, high compressive demand | Industrial floors requiring crack resistance and toughness |
| Typical Uses | Bridges, high-rise columns, industrial floor slabs | Warehouses, manufacturing floors, pavements |
Introduction to Industrial Flooring Requirements
Industrial flooring demands exceptional durability, abrasion resistance, and load-bearing capacity to withstand heavy machinery and constant traffic. High-strength concrete offers superior compressive strength, making it ideal for supporting heavy loads, while fiber-reinforced concrete enhances tensile strength and crack resistance, improving overall durability in dynamic industrial environments. Selecting the appropriate concrete type depends on specific industrial requirements such as load intensity, impact resistance, and maintenance considerations.
Overview of High-strength Concrete
High-strength concrete for industrial floors boasts a compressive strength exceeding 6000 psi, providing exceptional load-bearing capacity and durability for heavy machinery and high traffic. It offers superior resistance to abrasion and chemical attacks, making it ideal for harsh industrial environments. Its dense microstructure minimizes permeability, enhancing long-term performance and reducing maintenance costs.
Overview of Fiber-reinforced Concrete
Fiber-reinforced concrete (FRC) incorporates synthetic, steel, or natural fibers to improve tensile strength, durability, and crack resistance, making it ideal for industrial floors subjected to heavy loads and impact. Unlike high-strength concrete, which primarily increases compressive strength, FRC enhances toughness and reduces shrinkage-induced cracking, resulting in longer service life and reduced maintenance. The integration of fibers also mitigates the risk of sudden structural failures, promoting safety and resilience in industrial flooring applications.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
High-strength concrete typically offers compressive strengths exceeding 6000 psi, providing excellent load-bearing capacity for industrial floors, while fiber-reinforced concrete enhances tensile strength and toughness through the inclusion of steel, glass, or synthetic fibers. Fiber reinforcement improves crack resistance and impact durability, which is critical in industrial environments subject to dynamic loads and heavy machinery. Mechanical properties such as flexural strength and fracture toughness are significantly enhanced in fiber-reinforced concrete compared to standard high-strength mixes, making it a preferred choice for floors requiring superior toughness and reduced maintenance.
Durability and Crack Resistance
High-strength concrete offers exceptional compressive strength essential for industrial floors subjected to heavy loads, but it can be prone to brittle failure and micro-cracking under stress. Fiber-reinforced concrete significantly enhances crack resistance and ductility by distributing tensile stresses through embedded fibers, reducing the risk of shrinkage cracks and improving overall durability in dynamic industrial environments. Combining fibers with high-strength concrete optimizes both load-bearing capacity and crack control, extending floor lifespan under rigorous operational conditions.
Load-Bearing Capacity
High-strength concrete achieves superior load-bearing capacity through its dense matrix and higher compressive strength, making it ideal for supporting heavy industrial machinery and static loads. Fiber-reinforced concrete enhances load-bearing performance by distributing stresses more evenly and improving tensile strength, which reduces the risk of cracking under dynamic or impact loads. Combining both materials can optimize floor durability and resilience in demanding industrial environments.
Installation and Workability
High-strength concrete offers greater compressive strength for industrial floors but requires precise water-cement ratios and careful handling to avoid shrinkage and cracking during installation. Fiber-reinforced concrete improves workability by enhancing toughness and reducing surface defects, allowing easier finishing and faster placement with less risk of segregation. Both types demand skilled labor, yet fiber-reinforced mixes often provide better durability and simplified installation for heavy-duty industrial flooring applications.
Cost Analysis and Lifecycle Value
High-strength concrete offers superior compressive strength, reducing thickness and material for industrial floors, which lowers upfront costs but may require more expensive admixtures and curing processes. Fiber-reinforced concrete enhances tensile strength and crack resistance, leading to reduced maintenance and repair costs over the floor's lifecycle. Evaluating cost analysis and lifecycle value, fiber-reinforced concrete often provides better long-term savings through durability and extended service intervals despite higher initial investment compared to high-strength concrete.
Maintenance and Repair Considerations
High-strength concrete offers superior durability and load-bearing capacity for industrial floors but may exhibit brittleness leading to cracks that require prompt repair to maintain structural integrity. Fiber-reinforced concrete significantly reduces crack propagation and enhances impact resistance, minimizing maintenance interventions and extending service life. The choice between the two depends on balancing initial repair costs and long-term durability needs in industrial environments.
Best Applications and Recommendations
High-strength concrete excels in industrial floors requiring exceptional load-bearing capacity and durability, making it ideal for heavy machinery areas and warehousing where compressive strength exceeds 6000 psi. Fiber-reinforced concrete enhances toughness, crack resistance, and impact durability, best suited for dynamic loading conditions, such as forklift traffic and thermal cycling in manufacturing plants. For optimal performance, use high-strength concrete in structurally critical zones and fiber-reinforced mixes in areas prone to abrasion and localized stress to maximize floor lifespan and reduce maintenance.
Infographic: High-strength concrete vs Fiber-reinforced concrete for Industrial floor
 azmater.com
azmater.com