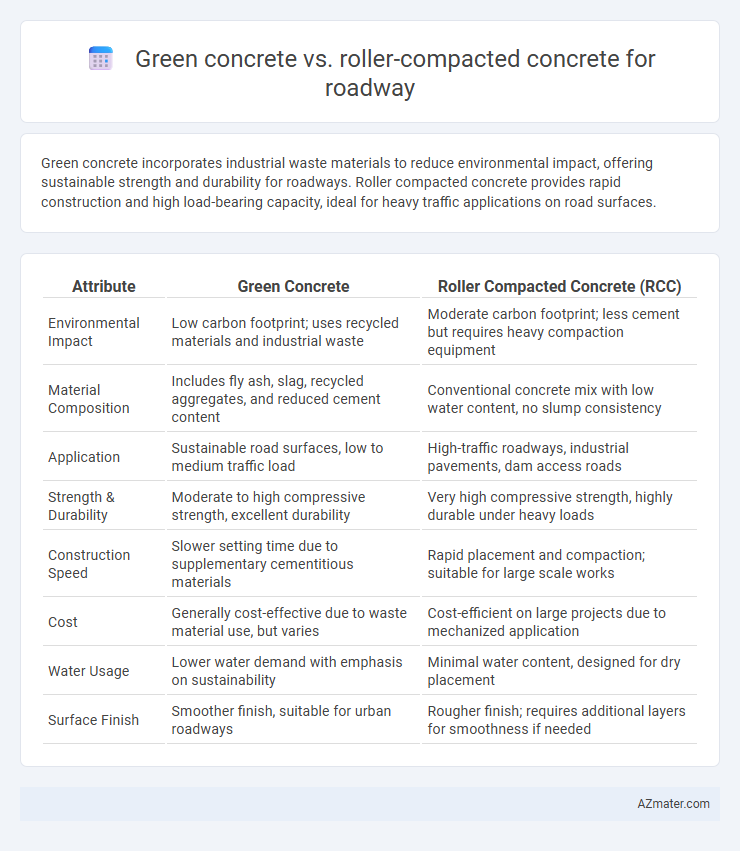
Green concrete incorporates industrial waste materials to reduce environmental impact, offering sustainable strength and durability for roadways. Roller compacted concrete provides rapid construction and high load-bearing capacity, ideal for heavy traffic applications on road surfaces.
Table of Comparison
| Attribute | Green Concrete | Roller Compacted Concrete (RCC) |
|---|---|---|
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint; uses recycled materials and industrial waste | Moderate carbon footprint; less cement but requires heavy compaction equipment |
| Material Composition | Includes fly ash, slag, recycled aggregates, and reduced cement content | Conventional concrete mix with low water content, no slump consistency |
| Application | Sustainable road surfaces, low to medium traffic load | High-traffic roadways, industrial pavements, dam access roads |
| Strength & Durability | Moderate to high compressive strength, excellent durability | Very high compressive strength, highly durable under heavy loads |
| Construction Speed | Slower setting time due to supplementary cementitious materials | Rapid placement and compaction; suitable for large scale works |
| Cost | Generally cost-effective due to waste material use, but varies | Cost-efficient on large projects due to mechanized application |
| Water Usage | Lower water demand with emphasis on sustainability | Minimal water content, designed for dry placement |
| Surface Finish | Smoother finish, suitable for urban roadways | Rougher finish; requires additional layers for smoothness if needed |
Introduction to Green Concrete and Roller Compacted Concrete
Green concrete incorporates industrial waste materials like fly ash and slag to reduce carbon emissions, offering enhanced sustainability compared to traditional mixtures. Roller Compacted Concrete (RCC) is a zero-slump concrete mix that is spread and compacted using heavy rollers, providing rapid construction speed and high durability for roadway applications. Both materials present eco-friendly alternatives with distinct advantages in strength, workability, and environmental impact for modern pavement engineering.
Composition and Material Differences
Green concrete incorporates recycled industrial by-products such as fly ash, slag, and silica fume, reducing cement content and lowering carbon emissions. Roller compacted concrete (RCC) uses a drier mix with zero-slump consistency, containing a higher aggregate to cement ratio for enhanced compaction and strength. The material differences between green concrete and RCC significantly affect their environmental impact, workability, and suitability for roadway applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Green concrete incorporates industrial byproducts like fly ash or slag, significantly reducing CO2 emissions and promoting the recycling of waste materials, making it highly sustainable. Roller compacted concrete (RCC) offers durability and fast construction with lower water usage compared to traditional concrete, contributing to environmental conservation in roadway projects. Both materials support sustainable infrastructure but green concrete excels in minimizing carbon footprint, while RCC prioritizes resource efficiency and rapid deployment.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Green concrete utilizes industrial by-products like fly ash and slag, enhancing environmental sustainability while providing compressive strengths typically ranging from 20 to 40 MPa, suitable for low to moderate traffic roadways. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) achieves higher strength levels, often exceeding 35 MPa within days, attributed to its dense, compacted structure, making it ideal for heavy-duty pavements and high-traffic roadways. In terms of durability, RCC demonstrates superior resistance to abrasion, freeze-thaw cycles, and fatigue, whereas green concrete's durability depends heavily on the mix design and curing conditions, showing varied performance under harsh environments.
Construction Methods and Equipment Requirements
Green concrete for roadways requires conventional mixing and curing processes, leveraging eco-friendly materials such as fly ash or slag, and typically uses standard batching plants and transit mixers. Roller compacted concrete (RCC) involves a dry mix design compacted with high-density vibratory rollers immediately after placement, utilizing specialized paving equipment like high-capacity spreaders and rollers to achieve rapid strength gain. Construction of RCC roads benefits from shorter curing times and faster placement, reducing project duration and heavy equipment needs compared to traditional green concrete methods.
Performance Under Traffic Loads
Green concrete exhibits enhanced durability and reduced carbon footprint while maintaining adequate strength for moderate traffic loads, making it suitable for sustainable roadway applications. Roller compacted concrete (RCC) offers superior load-bearing capacity and skid resistance under heavy traffic conditions due to its dense and robust structure. The choice depends on traffic intensity, with RCC preferred for high-traffic highways demanding long-term performance and green concrete favored in eco-sensitive areas prioritizing environmental sustainability.
Cost Analysis: Initial and Lifecycle
Green concrete for roadways typically offers a lower initial cost due to the use of recycled materials and industrial by-products like fly ash and slag, reducing cement consumption. Roller compacted concrete (RCC) demands higher upfront investment driven by specialized equipment and rapid placement techniques but provides superior durability and reduced maintenance expenses over its lifecycle. Evaluating total cost of ownership reveals RCC's potential for lower lifecycle costs despite higher initial outlay, while green concrete is more cost-effective for projects prioritizing environmental sustainability and immediate budget constraints.
Maintenance and Longevity
Green concrete, composed of recycled materials and industrial byproducts, offers enhanced durability and reduced maintenance needs due to its improved resistance to cracking and environmental degradation. Roller compacted concrete (RCC) provides high compressive strength and rapid construction benefits, but may require more frequent surface maintenance to address wear from heavy traffic. Both materials extend roadway longevity compared to traditional asphalt, with green concrete excelling in sustainability and maintenance cost reduction, while RCC delivers superior load-bearing capacity and structural stability.
Suitability for Different Roadway Applications
Green concrete offers enhanced sustainability and strength, making it ideal for urban roadways where environmental impact and durability are critical. Roller Compacted Concrete (RCC) provides rapid construction and high load-bearing capacity, suitable for heavy traffic highways and industrial pavements. RCC's low permeability and quick curing time make it preferable for large-scale infrastructure projects requiring efficient construction and long-term performance.
Future Trends and Innovations in Roadway Concrete
Green concrete, incorporating recycled materials and industrial by-products, drives sustainable roadway construction by reducing carbon footprints and enhancing durability. Roller compacted concrete (RCC) innovations focus on improved mix designs and automated compaction techniques to accelerate construction while maintaining high strength and skid resistance. Future trends include integrating nanomaterials and smart sensors in both green concrete and RCC to enable real-time monitoring and adaptive maintenance, promoting longer-lasting and eco-friendly roadways.
Infographic: Green concrete vs Roller compacted concrete for Roadway
 azmater.com
azmater.com