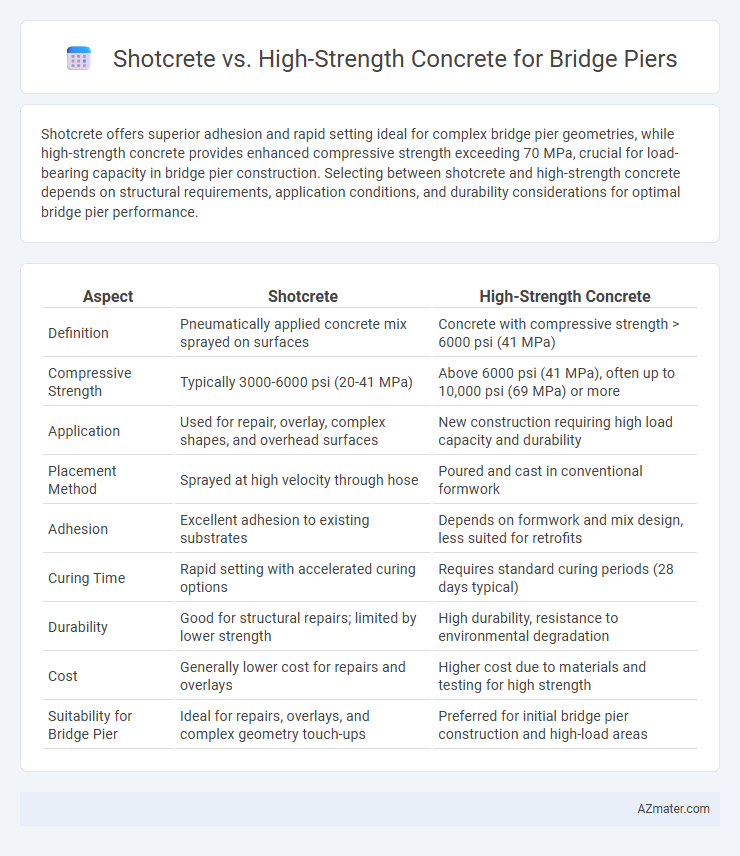
Shotcrete offers superior adhesion and rapid setting ideal for complex bridge pier geometries, while high-strength concrete provides enhanced compressive strength exceeding 70 MPa, crucial for load-bearing capacity in bridge pier construction. Selecting between shotcrete and high-strength concrete depends on structural requirements, application conditions, and durability considerations for optimal bridge pier performance.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Shotcrete | High-Strength Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pneumatically applied concrete mix sprayed on surfaces | Concrete with compressive strength > 6000 psi (41 MPa) |
| Compressive Strength | Typically 3000-6000 psi (20-41 MPa) | Above 6000 psi (41 MPa), often up to 10,000 psi (69 MPa) or more |
| Application | Used for repair, overlay, complex shapes, and overhead surfaces | New construction requiring high load capacity and durability |
| Placement Method | Sprayed at high velocity through hose | Poured and cast in conventional formwork |
| Adhesion | Excellent adhesion to existing substrates | Depends on formwork and mix design, less suited for retrofits |
| Curing Time | Rapid setting with accelerated curing options | Requires standard curing periods (28 days typical) |
| Durability | Good for structural repairs; limited by lower strength | High durability, resistance to environmental degradation |
| Cost | Generally lower cost for repairs and overlays | Higher cost due to materials and testing for high strength |
| Suitability for Bridge Pier | Ideal for repairs, overlays, and complex geometry touch-ups | Preferred for initial bridge pier construction and high-load areas |
Introduction to Bridge Pier Construction Materials
Bridge pier construction demands materials with exceptional load-bearing capacity and durability, where shotcrete offers rapid application and superior adhesion for complex shapes. High-strength concrete, characterized by compressive strengths exceeding 6,000 psi, provides enhanced structural performance and resistance to environmental stresses in bridge piers. Selecting between shotcrete and high-strength concrete depends on project-specific requirements such as structural load, exposure conditions, and construction timeline.
Overview of Shotcrete and High-Strength Concrete
Shotcrete is a pneumatically applied concrete that offers rapid placement and excellent adhesion, ideal for complex bridge pier geometries and repair work. High-strength concrete, characterized by compressive strengths typically above 40 MPa, provides superior load-bearing capacity and durability for bridge piers subjected to heavy traffic and environmental stress. Both materials enhance structural integrity, but shotcrete excels in versatile application scenarios while high-strength concrete delivers optimal performance in traditional cast-in-place construction.
Key Properties and Composition Comparison
Shotcrete offers superior adhesion and rapid application on complex bridge pier geometries, utilizing a mixture of cement, fine aggregates, and accelerators that enhance early strength gain. High-strength concrete, characterized by its low water-cement ratio and inclusion of supplementary cementitious materials like silica fume, provides exceptional compressive strength and durability for critical load-bearing components. The key properties distinguishing shotcrete include its shot application method and fast setting time, while high-strength concrete is optimized for maximum structural performance through controlled composition and curing processes.
Application Methods: Shotcrete vs High-Strength Concrete
Shotcrete application involves pneumatically spraying concrete onto surfaces, allowing for rapid placement and excellent adhesion on irregular or vertical bridge piers. High-strength concrete, typically cast using formwork, offers superior compressive strength but requires longer curing times and more labor-intensive form installation. Shotcrete excels in retrofit and repair operations due to its ease of application, while high-strength concrete is preferred for new construction demanding enhanced structural capacity.
Structural Performance for Bridge Piers
Shotcrete offers superior adhesion and compaction in irregular formwork, enhancing the structural integrity of bridge piers through improved bond strength and reduced porosity. High-strength concrete provides increased compressive strength and durability, essential for withstanding heavy loads and environmental stressors on bridge piers. Comparative studies indicate shotcrete's ability to reduce microcracking and improve energy absorption, contributing to enhanced seismic performance in bridge pier structures.
Durability and Longevity Considerations
Shotcrete offers superior adhesion and rapid application benefits for bridge piers, enhancing initial durability through dense, uniform layers. High-strength concrete provides increased compressive strength and resistance to environmental stresses, contributing significantly to the long-term longevity of bridge structures. Combining shotcrete's protective coating with high-strength concrete cores optimizes durability against freeze-thaw cycles, chemical attacks, and abrasion.
Cost Analysis and Economic Factors
Shotcrete offers cost advantages in bridge pier construction due to faster application and reduced formwork expenses compared to high-strength concrete, minimizing labor and time on site. High-strength concrete, while more expensive per cubic meter, provides long-term economic benefits through enhanced durability and reduced maintenance costs over the bridge's lifespan. Analyzing the total cost of ownership, shotcrete can lower initial expenditures, whereas high-strength concrete may optimize lifecycle costs through superior performance and longevity.
Installation Speed and Construction Efficiency
Shotcrete offers faster installation speeds for bridge piers due to its spray application method, reducing formwork requirements and enabling quicker setting times compared to traditional high-strength concrete. High-strength concrete provides superior compressive strength but often requires longer curing periods and more extensive formwork, impacting overall construction efficiency. Opting for shotcrete can significantly accelerate construction schedules and minimize labor costs while maintaining adequate structural performance for bridge pier applications.
Maintenance Requirements and Life-Cycle Costs
Shotcrete offers faster application and better adaptability to complex geometries, reducing initial repair labor compared to high-strength concrete. While high-strength concrete provides superior compressive strength and durability, it demands less frequent maintenance over the bridge pier's lifespan, potentially lowering life-cycle costs. Evaluating long-term performance data, shotcrete may incur higher maintenance expenditures due to vulnerability to environmental degradation, whereas high-strength concrete supports extended service intervals and optimized cost-efficiency.
Choosing the Right Material for Bridge Pier Projects
Selecting the right material for bridge pier construction requires evaluating factors such as load-bearing capacity, durability, and environmental conditions. Shotcrete offers rapid application and excellent adhesion for complex shapes, making it ideal for retrofit and repair projects, while high-strength concrete provides superior compressive strength and long-term durability for new constructions subjected to heavy loads. Engineers must analyze project-specific demands, including structural requirements and exposure to aggressive environments, to determine whether shotcrete or high-strength concrete best meets performance and sustainability goals.
Infographic: Shotcrete vs High-strength Concrete for Bridge Pier
 azmater.com
azmater.com