Mass concrete offers superior compressive strength and durability for floor slabs, ideal for heavy load-bearing applications. Lightweight concrete reduces structural load and improves thermal insulation, enhancing energy efficiency in floor slabs.
Table of Comparison
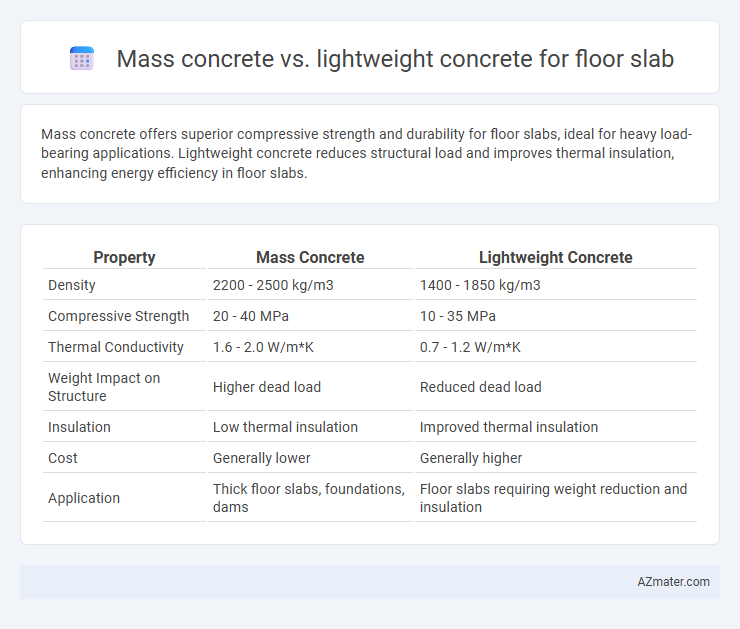
| Property | Mass Concrete | Lightweight Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 2200 - 2500 kg/m3 | 1400 - 1850 kg/m3 |
| Compressive Strength | 20 - 40 MPa | 10 - 35 MPa |
| Thermal Conductivity | 1.6 - 2.0 W/m*K | 0.7 - 1.2 W/m*K |
| Weight Impact on Structure | Higher dead load | Reduced dead load |
| Insulation | Low thermal insulation | Improved thermal insulation |
| Cost | Generally lower | Generally higher |
| Application | Thick floor slabs, foundations, dams | Floor slabs requiring weight reduction and insulation |
Introduction to Mass Concrete and Lightweight Concrete
Mass concrete refers to large-volume concrete structures characterized by thick sections, typically used for foundational slabs or heavy-duty floor slabs requiring exceptional strength and thermal mass. Lightweight concrete incorporates lightweight aggregates, reducing density and improving insulation qualities, making it suitable for floor slabs where weight reduction and thermal efficiency are priorities. The choice between mass concrete and lightweight concrete affects load-bearing capacity, thermal performance, and construction costs in floor slab applications.
Key Properties of Mass Concrete
Mass concrete for floor slabs is characterized by its high density, typically ranging from 2200 to 2500 kg/m3, providing excellent thermal mass and structural stability. Its low thermal conductivity helps in minimizing temperature gradients, reducing thermal cracking risks in large floor slabs. The material's significant compressive strength, often exceeding 30 MPa, ensures robust load-bearing capacity essential for heavy-duty applications.
Key Properties of Lightweight Concrete
Lightweight concrete for floor slabs offers reduced density, typically ranging from 1600 to 1920 kg/m3, which significantly decreases the overall structure weight, enhancing load-bearing efficiency. Its key properties include high thermal insulation, improved fire resistance due to the presence of lightweight aggregates like expanded clay or shale, and lower thermal conductivity compared to mass concrete. This type of concrete also exhibits adequate compressive strength, generally between 17 to 35 MPa, making it suitable for structural floor applications where weight reduction and energy efficiency are critical.
Structural Performance Comparison
Mass concrete for floor slabs offers high compressive strength and durability, making it ideal for heavy load-bearing applications and reducing deflection under significant weight. Lightweight concrete provides superior thermal insulation and reduces structural dead load, which enhances seismic performance but may have lower compressive strength compared to mass concrete. The choice between mass and lightweight concrete depends on balancing load requirements, thermal properties, and structural performance criteria specific to the floor slab design.
Thermal Insulation and Energy Efficiency
Mass concrete floor slabs provide substantial thermal mass, which helps regulate indoor temperatures by absorbing and slowly releasing heat, enhancing energy efficiency in moderate climates. Lightweight concrete, with its lower density and higher air content, offers superior thermal insulation properties, reducing heat transfer and lowering heating and cooling costs. Choosing between mass and lightweight concrete depends on the specific energy efficiency goals and thermal insulation requirements of the building design.
Load-Bearing Capacity and Thickness
Mass concrete floor slabs offer higher load-bearing capacity due to their dense composition and greater thickness, making them suitable for heavy structural loads and industrial applications. Lightweight concrete slabs, with lower density and reduced thickness, provide sufficient strength for residential and commercial floors while minimizing dead load and improving thermal insulation. The choice between mass and lightweight concrete depends on structural requirements, with mass concrete providing robust support and lightweight concrete enhancing efficiency and ease of handling.
Construction Methods and Applications
Mass concrete for floor slabs involves using dense, heavy materials like normal-weight aggregates, providing high structural strength and durability ideal for industrial and heavy-load applications. Lightweight concrete incorporates materials such as expanded clay or pumice, reducing overall slab weight, improving thermal insulation, and making it suitable for multi-story buildings and areas with strict load restrictions. Construction methods for mass concrete typically require careful temperature control and curing to prevent cracking, whereas lightweight concrete often demands specialized mixing and handling techniques to maintain consistency and bonding strength.
Cost Analysis: Mass vs Lightweight Concrete
Mass concrete typically incurs lower initial material costs due to the use of dense natural aggregates, whereas lightweight concrete involves higher expenses because of specialized lightweight aggregates such as expanded clay or shale. Lightweight concrete offers reduced transportation and handling costs, as its lower density decreases the overall dead load, potentially allowing for thinner slabs and less structural reinforcement. While mass concrete may require more extensive foundation support and increased labor, lightweight concrete can offer long-term savings through energy efficiency and reduced structural demands, offsetting the higher upfront investment.
Durability and Maintenance Considerations
Mass concrete floor slabs exhibit superior durability due to their high density and low permeability, which resist water ingress and reduce the risk of cracking and spalling over time. Lightweight concrete, while offering thermal insulation and reduced structural load, may require more frequent maintenance to address potential surface wear and vulnerability to impact damage. Choosing between mass and lightweight concrete for floor slabs depends on balancing the long-term durability demands with maintenance efforts and performance expectations in the intended application environment.
Best Use Cases for Floor Slab Selection
Mass concrete offers high compressive strength and durability, making it ideal for floor slabs in heavy load-bearing structures such as industrial buildings and warehouses. Lightweight concrete provides excellent thermal insulation and reduces dead load, which is beneficial for multi-story residential buildings and structures with seismic considerations. Selecting between mass and lightweight concrete depends on whether structural strength or weight reduction and energy efficiency are the primary project requirements.
Infographic: Mass concrete vs Lightweight concrete for Floor slab
 azmater.com
azmater.com