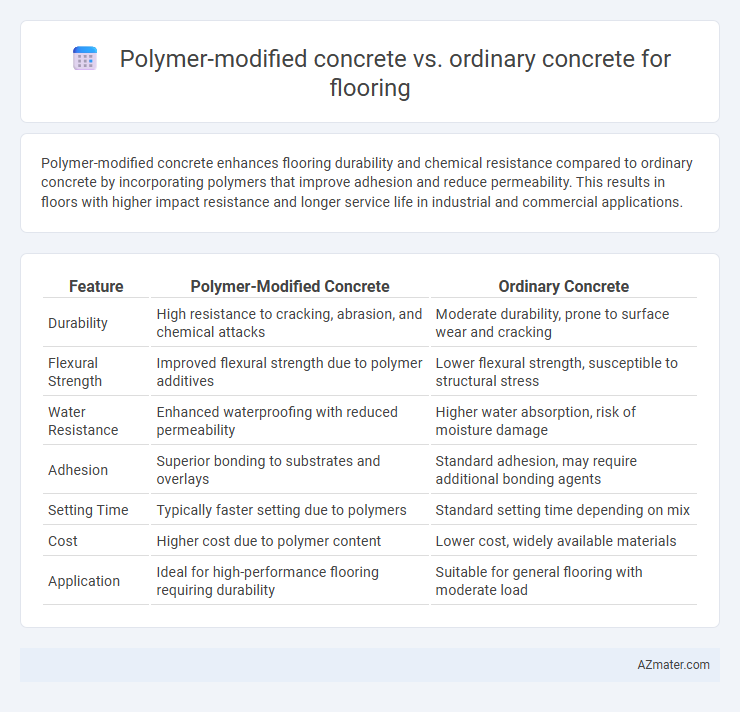
Polymer-modified concrete enhances flooring durability and chemical resistance compared to ordinary concrete by incorporating polymers that improve adhesion and reduce permeability. This results in floors with higher impact resistance and longer service life in industrial and commercial applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Polymer-Modified Concrete | Ordinary Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | High resistance to cracking, abrasion, and chemical attacks | Moderate durability, prone to surface wear and cracking |
| Flexural Strength | Improved flexural strength due to polymer additives | Lower flexural strength, susceptible to structural stress |
| Water Resistance | Enhanced waterproofing with reduced permeability | Higher water absorption, risk of moisture damage |
| Adhesion | Superior bonding to substrates and overlays | Standard adhesion, may require additional bonding agents |
| Setting Time | Typically faster setting due to polymers | Standard setting time depending on mix |
| Cost | Higher cost due to polymer content | Lower cost, widely available materials |
| Application | Ideal for high-performance flooring requiring durability | Suitable for general flooring with moderate load |
Introduction to Polymer-Modified Concrete and Ordinary Concrete
Polymer-modified concrete incorporates polymers such as latex or epoxy to enhance strength, durability, and adhesion compared to ordinary concrete, which consists of cement, water, and aggregates without additives. This modification improves resistance to cracking, chemical attacks, and abrasion, making it suitable for high-performance flooring applications. Ordinary concrete, while cost-effective and widely used, often lacks the flexibility and longevity provided by polymer modifications in demanding environments.
Composition Differences: Polymer-Modified vs Ordinary Concrete
Polymer-modified concrete incorporates synthetic polymers such as latex, acrylics, or styrene-butadiene to enhance bonding, flexibility, and durability, while ordinary concrete relies solely on cement, water, and aggregates. The addition of polymers reduces porosity and improves resistance to cracking, abrasion, and chemical attacks, making it ideal for high-performance flooring applications. Ordinary concrete's composition limits its flexibility and resistance properties, often resulting in lower longevity and increased maintenance needs in flooring environments.
Key Properties and Performance of Each Concrete Type
Polymer-modified concrete exhibits superior durability, enhanced flexural strength, and improved resistance to chemical attacks compared to ordinary concrete, making it ideal for high-performance flooring applications. Ordinary concrete, while cost-effective and commonly used, lacks the elasticity and adhesion properties that polymers provide, resulting in higher susceptibility to cracking and wear under heavy traffic. The inclusion of polymers in concrete enhances waterproofing capabilities and reduces permeability, significantly extending the lifespan and maintenance intervals for flooring surfaces.
Durability and Longevity in Flooring Applications
Polymer-modified concrete (PMC) significantly enhances durability and longevity in flooring applications compared to ordinary concrete by improving resistance to abrasion, chemical attacks, and moisture penetration. The incorporation of polymers reduces micro-cracking and increases tensile strength, resulting in floors that maintain structural integrity and surface quality under heavy traffic conditions. Consequently, PMC floors exhibit superior performance and extended service life, making them ideal for industrial and commercial environments.
Adhesion and Bonding Capabilities
Polymer-modified concrete exhibits superior adhesion and bonding capabilities compared to ordinary concrete, resulting from the inclusion of polymers that enhance the interfacial bond between the cement matrix and aggregate particles. This improved bond strength reduces the likelihood of cracking and delamination, making polymer-modified concrete ideal for high-traffic flooring applications. Enhanced adhesion also leads to greater durability and resistance to moisture ingress, which are critical factors in flooring performance and longevity.
Resistance to Chemicals, Stains, and Abrasion
Polymer-modified concrete exhibits significantly enhanced resistance to chemicals, stains, and abrasion compared to ordinary concrete, making it ideal for heavy-duty flooring applications in industrial and commercial settings. The incorporation of polymers improves the concrete's density and reduces porosity, preventing chemical penetration and surface degradation from oils, acids, and alkalis. This advanced durability results in longer-lasting flooring with minimal maintenance requirements, outperforming standard concrete in environments exposed to harsh substances and frequent wear.
Installation Process and Curing Time
Polymer-modified concrete for flooring offers a faster installation process compared to ordinary concrete due to its enhanced workability and reduced water absorption. The curing time for polymer-modified concrete typically ranges from 24 to 48 hours, significantly shorter than the 7 to 28 days required for ordinary concrete, enabling quicker project turnaround. This accelerated curing is achieved through the integration of polymers that improve bonding and reduce permeability, resulting in a durable, high-performance flooring solution.
Cost Analysis: Initial and Long-term Investment
Polymer-modified concrete typically incurs a higher initial cost compared to ordinary concrete due to the use of specialized polymers and additives that enhance durability and bonding strength. Long-term investment favors polymer-modified concrete as it provides superior resistance to cracking, abrasion, and chemical attacks, reducing maintenance and repair expenses over the lifespan of flooring. Ordinary concrete requires more frequent upkeep, resulting in increased life-cycle costs despite its lower upfront price.
Ideal Use Cases for Polymer-Modified and Ordinary Concrete
Polymer-modified concrete excels in flooring applications requiring enhanced durability, chemical resistance, and adhesion, making it ideal for industrial environments, commercial kitchens, and areas with heavy traffic or moisture exposure. Ordinary concrete suits residential flooring and outdoor pavements where cost-efficiency and standard wear resistance are sufficient without the need for specialized performance characteristics. Selecting polymer-modified concrete improves floor longevity and reduces maintenance in demanding conditions, while ordinary concrete offers a cost-effective solution for less rigorous flooring needs.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Concrete for Flooring
Polymer-modified concrete offers enhanced durability, superior adhesion, and increased resistance to chemicals and abrasions compared to ordinary concrete, making it ideal for high-traffic flooring applications. Ordinary concrete remains cost-effective and suitable for less demanding environments where heavy wear and chemical exposure are minimal. Selecting the right concrete depends on balancing budget constraints with performance requirements such as longevity, maintenance, and environmental conditions of the flooring area.
Infographic: Polymer-modified concrete vs Ordinary concrete for Flooring
 azmater.com
azmater.com