Recycled aggregate concrete reduces environmental impact by utilizing construction waste, while high-performance concrete offers superior strength and durability essential for high-rise building stability. Selecting between them depends on balancing sustainability goals with structural performance requirements.
Table of Comparison
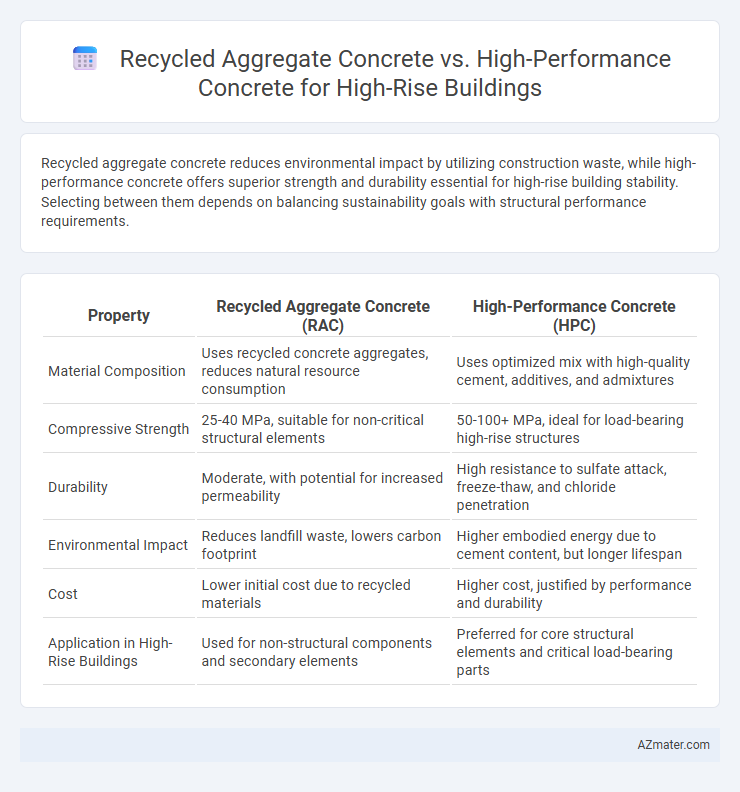
| Property | Recycled Aggregate Concrete (RAC) | High-Performance Concrete (HPC) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Uses recycled concrete aggregates, reduces natural resource consumption | Uses optimized mix with high-quality cement, additives, and admixtures |
| Compressive Strength | 25-40 MPa, suitable for non-critical structural elements | 50-100+ MPa, ideal for load-bearing high-rise structures |
| Durability | Moderate, with potential for increased permeability | High resistance to sulfate attack, freeze-thaw, and chloride penetration |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces landfill waste, lowers carbon footprint | Higher embodied energy due to cement content, but longer lifespan |
| Cost | Lower initial cost due to recycled materials | Higher cost, justified by performance and durability |
| Application in High-Rise Buildings | Used for non-structural components and secondary elements | Preferred for core structural elements and critical load-bearing parts |
Introduction to Concrete Types in High-Rise Construction
Recycled aggregate concrete (RAC) utilizes processed construction waste, promoting sustainability and reducing environmental impact in high-rise buildings, while high-performance concrete (HPC) offers superior strength, durability, and workability essential for structural integrity and long service life. RAC typically exhibits lower density and compressive strength compared to HPC, which is engineered for high load-bearing capacity and resistance to harsh environmental conditions commonly faced by skyscrapers. Selection between RAC and HPC depends on specific project requirements, balancing ecological benefits of recycled materials with the advanced mechanical properties provided by high-performance formulations.
Defining Recycled Aggregate Concrete (RAC)
Recycled Aggregate Concrete (RAC) incorporates crushed concrete debris as aggregates, offering a sustainable alternative to natural resources in high-rise building construction. RAC demonstrates comparable mechanical properties and durability to conventional concrete when appropriately processed and mixed, making it suitable for structural applications in tall buildings. Its environmental benefits include reduced landfill waste and lower carbon footprint, aligning with green building objectives.
Key Features of High-Performance Concrete (HPC)
High-performance concrete (HPC) is characterized by superior strength, enhanced durability, and improved workability compared to recycled aggregate concrete, making it ideal for high-rise buildings requiring load-bearing capacity and long-term resilience. HPC incorporates optimized mix designs with chemical admixtures and low water-cement ratios, which reduce permeability and increase resistance to environmental deterioration such as freeze-thaw cycles and chloride penetration. The combination of high compressive strength, reduced shrinkage, and excellent bonding properties ensures structural integrity and safety in skyscraper construction, outperforming recycled aggregate concrete in critical performance metrics.
Sustainability Benefits of Recycled Aggregate Concrete
Recycled aggregate concrete (RAC) significantly reduces environmental impact by repurposing construction and demolition waste, minimizing the demand for natural aggregates and decreasing landfill disposal. Its lower embodied energy and reduced carbon footprint contribute to sustainable urban development in high-rise buildings compared to high-performance concrete (HPC). Utilizing RAC supports circular economy principles, enhancing resource efficiency while maintaining adequate structural performance for vertical construction.
Strength and Durability Comparison: RAC vs HPC
Recycled aggregate concrete (RAC) often exhibits lower compressive strength and higher water absorption compared to high-performance concrete (HPC), impacting long-term durability in high-rise buildings. HPC demonstrates superior mechanical properties, including compressive strengths exceeding 70 MPa, enhanced impermeability, and resistance to environmental degradation, making it preferable for structural elements requiring high durability. While RAC promotes sustainability by utilizing construction waste, its variable quality necessitates careful mix design and treatment to achieve performance levels close to HPC for critical high-rise applications.
Workability and Mix Design Considerations
Recycled aggregate concrete (RAC) requires careful adjustment of mix design to compensate for the variability and higher water absorption of recycled aggregates, often necessitating increased binder content and admixtures to maintain workability suitable for high-rise construction. High-performance concrete (HPC) incorporates optimized particle packing, supplementary cementitious materials, and chemical admixtures to achieve superior workability, strength, and durability, essential for the demands of tall structures. Both concrete types demand precise control of water-cement ratio and admixture dosage to ensure consistent flowability and cohesive mix properties under the complex stress conditions of high-rise building applications.
Structural Performance in High-Rise Applications
Recycled aggregate concrete (RAC) demonstrates competitive compressive strength and modulus of elasticity, making it a sustainable alternative for non-critical high-rise structural elements, although its variable quality can affect durability and long-term performance. High-performance concrete (HPC) offers superior strength, enhanced durability, and improved resistance to environmental stresses, critical for load-bearing and seismic zones in high-rise buildings. Structural performance in high-rise applications favors HPC for its consistent mechanical properties and longevity, while RAC can be strategically used to reduce environmental impact without compromising essential structural integrity.
Cost Analysis: RAC vs HPC for Tall Buildings
Recycled Aggregate Concrete (RAC) offers significant cost savings in material procurement by utilizing waste aggregates, reducing overall expense by up to 20% compared to traditional aggregates used in High-Performance Concrete (HPC). While HPC incurs higher initial costs due to advanced admixtures and strict quality control, its superior compressive strength and durability contribute to long-term savings through reduced maintenance and longer service life, often justifying the premium in tall building applications. Cost analysis for tall structures must balance RAC's lower upfront investment against HPC's enhanced performance, where structural demands and lifecycle expenses become critical factors in decision-making.
Challenges and Limitations in Practical Use
Recycled aggregate concrete (RAC) poses challenges in high-rise building applications due to its lower strength variability, increased porosity, and reduced durability compared to high-performance concrete (HPC), affecting long-term structural reliability and load-bearing capacity. HPC offers superior mechanical properties and enhanced durability but faces limitations such as higher material costs, complex mix designs, and stringent quality control requirements that complicate large-scale implementation in skyscraper construction. The integration of RAC in high-rise structures requires advanced treatment methods and precise quality assessments to mitigate performance risks, whereas HPC demands specialized technical expertise to optimize performance within budgetary constraints.
Future Trends in Concrete Technology for High-Rise Construction
Recycled aggregate concrete (RAC) is increasingly integrated into high-rise construction due to its sustainability benefits and reduction of construction waste, offering comparable strength and durability with advancements in mix design and treatment technologies. High-performance concrete (HPC) continues to dominate with superior mechanical properties, enhanced durability, and faster curing times, essential for the demanding structural and environmental conditions of skyscrapers. Future trends indicate hybrid approaches combining RAC and HPC elements, alongside innovations in nano-materials and self-healing concrete, aiming to optimize resource efficiency, structural resilience, and environmental impact in high-rise building projects.
Infographic: Recycled aggregate concrete vs High-performance concrete for High-rise Building
 azmater.com
azmater.com