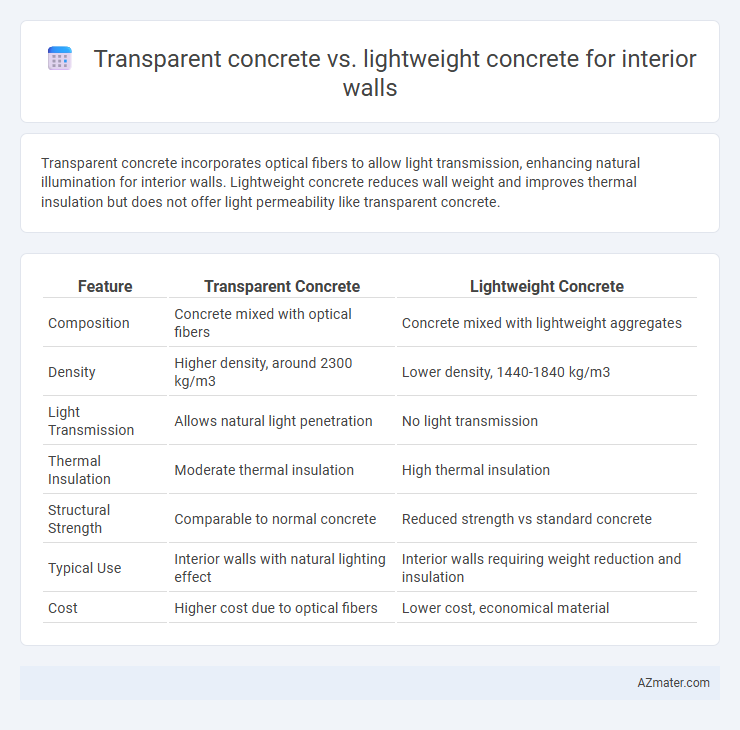
Transparent concrete incorporates optical fibers to allow light transmission, enhancing natural illumination for interior walls. Lightweight concrete reduces wall weight and improves thermal insulation but does not offer light permeability like transparent concrete.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Transparent Concrete | Lightweight Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Concrete mixed with optical fibers | Concrete mixed with lightweight aggregates |
| Density | Higher density, around 2300 kg/m3 | Lower density, 1440-1840 kg/m3 |
| Light Transmission | Allows natural light penetration | No light transmission |
| Thermal Insulation | Moderate thermal insulation | High thermal insulation |
| Structural Strength | Comparable to normal concrete | Reduced strength vs standard concrete |
| Typical Use | Interior walls with natural lighting effect | Interior walls requiring weight reduction and insulation |
| Cost | Higher cost due to optical fibers | Lower cost, economical material |
Introduction to Transparent vs Lightweight Concrete
Transparent concrete integrates optical fibers within a cement matrix, allowing natural or artificial light to pass through, enhancing aesthetic appeal and energy efficiency in interior walls. Lightweight concrete utilizes lightweight aggregates such as expanded clay or perlite, significantly reducing wall weight while improving thermal insulation and ease of installation. Both materials offer distinct functional advantages: transparent concrete emphasizes light transmission and modern design, whereas lightweight concrete focuses on structural efficiency and insulation performance.
Composition and Material Differences
Transparent concrete incorporates optical fibers embedded within a cementitious matrix, allowing light transmission while maintaining structural integrity, primarily using fine aggregates and high-quality cement. Lightweight concrete, by contrast, utilizes low-density aggregates such as expanded clay, perlite, or aerated materials to reduce weight and improve thermal insulation, often featuring a higher porosity and lower compressive strength. The fundamental difference lies in transparent concrete's optical fiber integration for light permeability versus lightweight concrete's aggregate selection aimed at weight reduction and enhanced insulation properties.
Structural Properties and Strength Comparison
Transparent concrete, incorporating optical fibers, offers moderate compressive strength typically ranging between 30-50 MPa, suitable for decorative interior walls with the added benefit of natural light transmission. Lightweight concrete, composed of expanded aggregates, exhibits lower density (approximately 1600-2000 kg/m3) and compressive strength varying from 10-40 MPa, providing enhanced thermal insulation but generally less structural capacity than transparent concrete. Structural properties favor transparent concrete for applications requiring higher strength and translucency, while lightweight concrete excels where weight reduction and insulation are prioritized.
Aesthetic Advantages for Interior Walls
Transparent concrete enhances interior wall aesthetics by introducing natural light transmission while maintaining structural integrity, creating visually striking and luminous spaces. Lightweight concrete offers design flexibility with its ease of shaping and texturing, allowing for diverse finishes that complement modern interior styles. Combining both materials can optimize aesthetic appeal by balancing translucency and versatile textures in interior wall applications.
Daylighting and Energy Efficiency
Transparent concrete enhances daylighting in interior walls by allowing natural light to penetrate, reducing the need for artificial lighting and lowering energy consumption. Lightweight concrete, while offering good thermal insulation, does not provide light transmission but improves energy efficiency by reducing heat transfer. Combining transparent concrete's light diffusion with lightweight concrete's insulation optimizes interior illumination and energy savings in building design.
Acoustic Performance and Sound Insulation
Transparent concrete incorporates optical fibers or resin, providing unique translucency while offering moderate sound insulation, making it suitable for modern interiors where light transmission and aesthetics are prioritized but acoustic isolation is secondary. Lightweight concrete, composed of expanded clay, shale, or pumice aggregates, excels in acoustic performance by absorbing and dampening sound waves, resulting in superior sound insulation properties ideal for minimizing noise transmission in interior walls. For applications demanding high acoustic insulation, lightweight concrete outperforms transparent concrete due to its denser matrix and enhanced sound absorption capabilities.
Installation Challenges and Techniques
Transparent concrete installation requires precise alignment of optical fibers within the cement matrix, demanding specialized techniques to ensure light transmission and structural integrity. Lightweight concrete offers easier handling due to reduced weight but necessitates careful mix design to prevent segregation and maintain strength. Both materials require skilled labor; transparent concrete demands meticulous embedding and curing methods, while lightweight concrete installation often involves tailored curing processes to optimize durability and minimize shrinkage.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Transparent concrete integrates optical fibers, enhancing natural light transmission and reducing energy consumption for interior spaces, leading to lower carbon emissions over its lifecycle. Lightweight concrete's reduced density decreases material usage and structural load, contributing to resource efficiency and less environmental impact during transportation and construction. Both materials improve sustainability but transparent concrete excels in energy savings, while lightweight concrete offers advantages in material conservation and insulation.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Transparent concrete generally incurs higher initial costs than lightweight concrete due to specialized materials such as optical fibers and complex manufacturing processes. Lightweight concrete offers economic advantages through reduced material and transportation expenses, as well as enhanced thermal insulation that can lower long-term energy costs. When selecting materials for interior walls, budget constraints and lifecycle cost savings play crucial roles in determining the more feasible option between transparent and lightweight concrete.
Best Use Cases: Which Concrete for Which Interior Wall?
Transparent concrete is ideal for interior walls requiring natural light diffusion without compromising structural integrity, such as feature walls in modern offices or galleries. Lightweight concrete suits interior partitions and non-load-bearing walls where fire resistance and thermal insulation are priorities, like residential and commercial buildings. Choosing between them depends on balancing aesthetic needs and functional requirements like light transmission versus insulation performance.
Infographic: Transparent concrete vs Lightweight concrete for Interior wall
 azmater.com
azmater.com