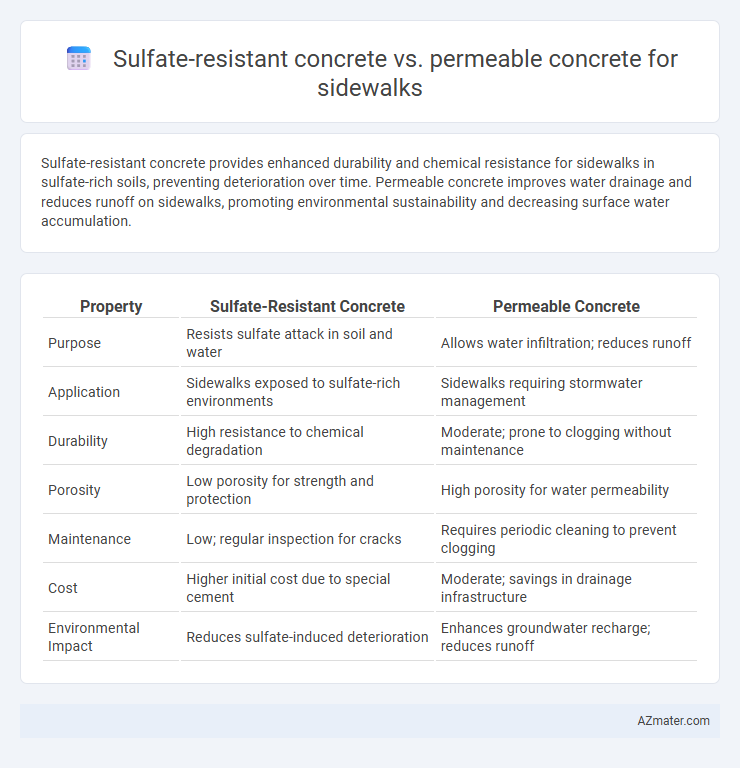
Sulfate-resistant concrete provides enhanced durability and chemical resistance for sidewalks in sulfate-rich soils, preventing deterioration over time. Permeable concrete improves water drainage and reduces runoff on sidewalks, promoting environmental sustainability and decreasing surface water accumulation.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Sulfate-Resistant Concrete | Permeable Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Resists sulfate attack in soil and water | Allows water infiltration; reduces runoff |
| Application | Sidewalks exposed to sulfate-rich environments | Sidewalks requiring stormwater management |
| Durability | High resistance to chemical degradation | Moderate; prone to clogging without maintenance |
| Porosity | Low porosity for strength and protection | High porosity for water permeability |
| Maintenance | Low; regular inspection for cracks | Requires periodic cleaning to prevent clogging |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to special cement | Moderate; savings in drainage infrastructure |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces sulfate-induced deterioration | Enhances groundwater recharge; reduces runoff |
Understanding Sulfate-Resistant Concrete
Sulfate-resistant concrete is specifically designed to withstand chemical attacks from sulfate-rich soils, preventing deterioration in sidewalk structures exposed to aggressive environments. This type of concrete incorporates low C3A cement content and supplementary cementitious materials like fly ash or slag to enhance durability against sulfate ions. Compared to permeable concrete, which prioritizes water permeability and stormwater management, sulfate-resistant concrete ensures long-term stability and strength in sulfate-prone areas, making it ideal for sidewalks in industrial zones or regions with high sulfate groundwater.
Key Properties of Permeable Concrete
Permeable concrete features high porosity and excellent water permeability, allowing rainwater to pass through its interconnected voids, which significantly reduces surface runoff and improves groundwater recharge. Unlike sulfate-resistant concrete that is specifically formulated to withstand chemical attack from sulfates in soil or water, permeable concrete prioritizes drainage and environmental benefits, making it ideal for sidewalks in urban areas prone to flooding. The material's compressive strength and freeze-thaw durability are optimized to balance structural integrity with permeability requirements.
Sulfate Attack: Risks and Solutions for Sidewalks
Sulfate-resistant concrete is engineered with low-permeability cement and supplementary cementitious materials like fly ash or slag to mitigate damage from sulfate attack, making it highly suitable for sidewalks exposed to sulfate-rich soils or groundwater. Permeable concrete, designed to allow water infiltration, can reduce surface runoff but may increase sulfate ingress if used in environments with high sulfate concentrations, potentially compromising durability. Selecting sulfate-resistant concrete for sidewalks in sulfate-prone areas significantly lowers risks of expansion, cracking, and spalling, ensuring long-term structural integrity and minimizing maintenance costs.
Water Drainage Benefits of Permeable Concrete
Permeable concrete enhances water drainage by allowing rainwater to infiltrate through its porous structure, reducing runoff and the risk of surface flooding on sidewalks. Sulfate-resistant concrete primarily focuses on durability in sulfate-rich soils but does not provide significant drainage benefits. Effective water management is achieved with permeable concrete, promoting groundwater recharge and minimizing pavement deterioration caused by trapped moisture.
Durability Comparison: Sulfate-Resistant vs Permeable Concrete
Sulfate-resistant concrete offers superior durability in environments exposed to sulfate-rich soils or water, effectively preventing chemical attack and structural degradation over time. Permeable concrete enhances drainage and reduces surface water accumulation but generally has lower resistance to aggressive sulfate exposure, leading to potential deterioration in such conditions. Selecting sulfate-resistant concrete for sidewalks in sulfate-prone areas ensures longer-lasting strength and minimizes maintenance compared to permeable concrete.
Climate and Environmental Considerations
Sulfate-resistant concrete is ideal for sidewalks in regions with high sulfate soil or groundwater levels, preventing chemical degradation and ensuring long-term durability in wet or coastal climates. Permeable concrete enhances stormwater management by allowing water infiltration, reducing runoff and heat island effects, which is crucial for urban areas prone to heavy rainfall and flooding. Selecting between these materials involves balancing sulfate resistance for chemical durability with permeability for environmental sustainability, tailored to specific local climate conditions.
Maintenance Requirements for Both Concrete Types
Sulfate-resistant concrete requires minimal maintenance due to its enhanced durability against sulfate attack, reducing the risk of cracking and spalling in aggressive soil conditions commonly found near sidewalks. Permeable concrete, designed to allow water infiltration, necessitates regular cleaning to prevent clogging from debris and sediments that can impair its drainage function and cause surface deterioration. Proper maintenance routines for both types ensure long-term sidewalk performance, with sulfate-resistant concrete focusing on structural integrity and permeable concrete emphasizing hydraulic functionality.
Cost Analysis: Initial and Long-Term Expenses
Sulfate-resistant concrete generally incurs higher initial costs due to specialized cement and admixtures designed to withstand sulfate attack, making it suitable for chemically aggressive environments. Permeable concrete often features lower upfront expenses but may require more frequent maintenance and repairs because of its porous structure, impacting long-term costs. Evaluating total lifecycle expenses reveals sulfate-resistant concrete can be more cost-effective in sulfate-rich soils, while permeable concrete offers savings in drainage-related applications with lower chemical exposure.
Best Use Cases for Sidewalk Applications
Sulfate-resistant concrete is ideal for sidewalks exposed to sulfate-rich soils or groundwater, providing enhanced durability against chemical attacks and minimizing deterioration. Permeable concrete best suits high-traffic urban sidewalks where effective stormwater management is crucial, allowing water infiltration to reduce runoff and enhance safety. Choosing between these materials depends on environmental conditions and required hydraulic performance for optimal sidewalk longevity.
Recommendations for Choosing the Right Concrete
Sulfate-resistant concrete is ideal for sidewalks exposed to aggressive sulfate soils or groundwater, preventing chemical deterioration and extending structural longevity. Permeable concrete is recommended in areas requiring enhanced stormwater management and reduced runoff, promoting groundwater recharge and mitigating flooding risks. Selecting the right concrete depends on environmental exposure, site drainage requirements, and long-term durability goals for sidewalk applications.
Infographic: Sulfate-resistant concrete vs Permeable concrete for Sidewalk
 azmater.com
azmater.com