Recycled aggregate concrete offers sustainable road construction by reusing waste materials while maintaining adequate strength and durability. Roller-compacted concrete provides rapid placement and high load-bearing capacity, making it ideal for heavy-traffic roads.
Table of Comparison
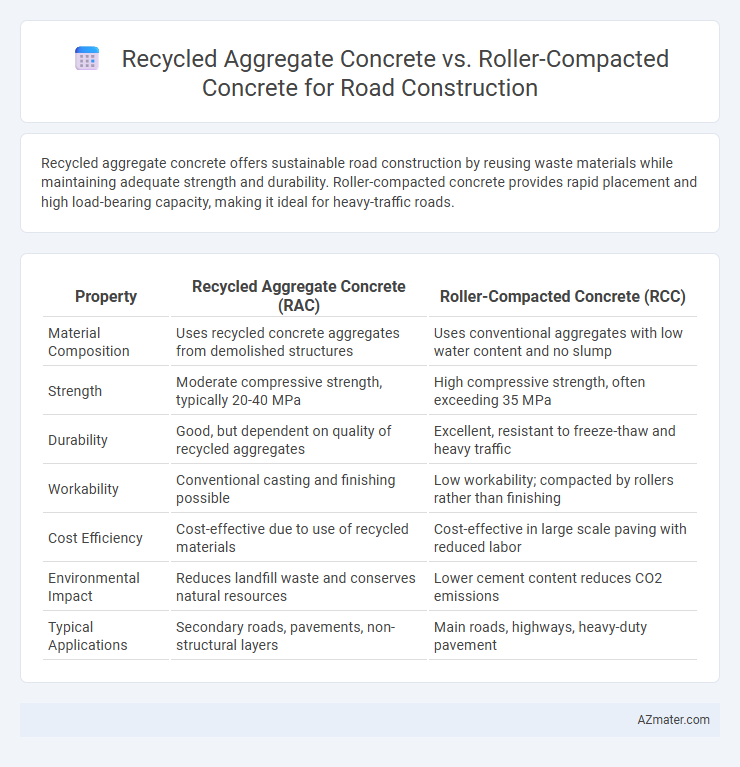
| Property | Recycled Aggregate Concrete (RAC) | Roller-Compacted Concrete (RCC) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Uses recycled concrete aggregates from demolished structures | Uses conventional aggregates with low water content and no slump |
| Strength | Moderate compressive strength, typically 20-40 MPa | High compressive strength, often exceeding 35 MPa |
| Durability | Good, but dependent on quality of recycled aggregates | Excellent, resistant to freeze-thaw and heavy traffic |
| Workability | Conventional casting and finishing possible | Low workability; compacted by rollers rather than finishing |
| Cost Efficiency | Cost-effective due to use of recycled materials | Cost-effective in large scale paving with reduced labor |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces landfill waste and conserves natural resources | Lower cement content reduces CO2 emissions |
| Typical Applications | Secondary roads, pavements, non-structural layers | Main roads, highways, heavy-duty pavement |
Introduction to Sustainable Road Construction Materials
Recycled aggregate concrete (RAC) and roller-compacted concrete (RCC) are pivotal in sustainable road construction due to their environmental benefits and structural performance. RAC utilizes crushed recycled concrete waste, reducing landfill use and conserving natural aggregates, while RCC employs a dry, low-slump mix that offers rapid placement and early strength gain, minimizing construction time and resource consumption. Both materials contribute to sustainable infrastructure by enhancing durability, lowering carbon footprints, and promoting resource efficiency in roadway projects.
Overview of Recycled Aggregate Concrete (RAC)
Recycled Aggregate Concrete (RAC) incorporates crushed concrete and demolition waste as replacement for natural aggregates, promoting sustainability in road construction. This eco-friendly material offers comparable compressive strength and durability to conventional concrete while reducing landfill waste and lowering carbon emissions. RAC's adaptability to various mixture designs allows effective use in pavement base and surface layers, making it a viable alternative for environmentally conscious infrastructure projects.
Understanding Roller-Compacted Concrete (RCC)
Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) is a densely compacted, low-slump concrete often used in road construction due to its high strength and durability combined with rapid placement and compaction through heavy rollers. RCC's composition typically includes conventional concrete ingredients mixed with lower water content and no slump, enhancing load-bearing capacity and resistance to abrasion and weathering. Compared to recycled aggregate concrete, RCC offers faster construction times and superior performance under heavy traffic loads, making it ideal for highways and industrial pavements.
Material Properties: RAC vs RCC
Recycled Aggregate Concrete (RAC) incorporates crushed concrete and masonry as aggregates, resulting in variable strength and durability due to the heterogeneity of recycled materials, often showing lower compressive strength and increased water absorption compared to natural aggregates. Roller-Compacted Concrete (RCC) uses a drier mix with well-graded aggregates and minimal cement paste, producing high-density, low-permeability pavements with high early strength and excellent resistance to abrasion and freeze-thaw cycles. Material properties of RCC make it suitable for heavy-load road construction, while RAC offers sustainable alternatives but may require quality control measures to achieve comparable performance in terms of strength and durability.
Structural Performance Comparison
Recycled aggregate concrete (RAC) exhibits enhanced sustainability with slightly reduced compressive strength and durability compared to traditional materials, impacting long-term structural integrity in road construction. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) offers superior load-bearing capacity and rapid strength gain, making it optimal for heavy traffic and high-stress applications. Comparative studies indicate RCC provides better rutting resistance and fatigue performance, while RAC contributes to environmental benefits with moderate structural trade-offs.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Recycled aggregate concrete (RAC) reduces landfill waste and consumption of natural resources by incorporating crushed demolition materials, significantly lowering the carbon footprint compared to traditional concrete. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) offers high durability and rapid construction, but typically relies on virgin materials, which can increase environmental impact through resource extraction and energy use. Utilizing RAC in road construction enhances sustainability by minimizing waste and promoting circular economy principles, whereas RCC optimizes resource efficiency in terms of energy and time but requires complementary eco-friendly practices to achieve similar environmental benefits.
Construction Techniques and Equipment Requirements
Recycled aggregate concrete (RAC) for road construction requires standard mixing equipment adapted to handle variable aggregate quality, demanding thorough preprocessing to remove contaminants and ensure consistent strength. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) utilizes specialized high-capacity mixers and heavy vibratory rollers to achieve rapid compaction and high density, enabling faster paving without traditional formwork. Equipment for RCC includes motor graders and vibratory steel wheels, while RAC relies more on conventional concrete batching plants and standard pavers, influencing overall construction speed and equipment investments.
Cost Analysis: RAC vs RCC
Recycled aggregate concrete (RAC) offers significant cost savings by utilizing waste materials, reducing the need for virgin aggregates and lowering landfill expenses, making it an economical choice for sustainable road construction. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) typically demands lower construction costs due to faster placement and minimal finishing requirements, which reduces labor and equipment usage. While RAC reduces material costs, RCC outperforms in total project cost efficiency by minimizing construction time and operational disruption on highways.
Durability and Maintenance Considerations
Recycled aggregate concrete offers enhanced sustainability in road construction but may exhibit slightly higher permeability affecting long-term durability compared to traditional materials. Roller-compacted concrete provides superior density and resistance to abrasion, resulting in lower maintenance requirements due to its high compressive strength and reduced porosity. Selecting between the two depends on balancing environmental benefits with performance demands, where roller-compacted concrete typically ensures extended service life with minimal upkeep.
Case Studies and Practical Applications
Recycled aggregate concrete (RAC) demonstrates significant environmental benefits and cost savings in road construction through numerous case studies, highlighting its successful use in urban infrastructure projects where sustainability is prioritized. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) offers superior compaction, rapid construction timelines, and enhanced load-bearing capacity, as evidenced by highway and airport runway applications documented globally. Practical applications of RAC focus on reducing landfill waste and material costs, while RCC's strength and durability make it optimal for high-traffic roadways, showcasing their respective advantages in modern pavement engineering.
Infographic: Recycled aggregate concrete vs Roller-compacted concrete for Road construction
 azmater.com
azmater.com