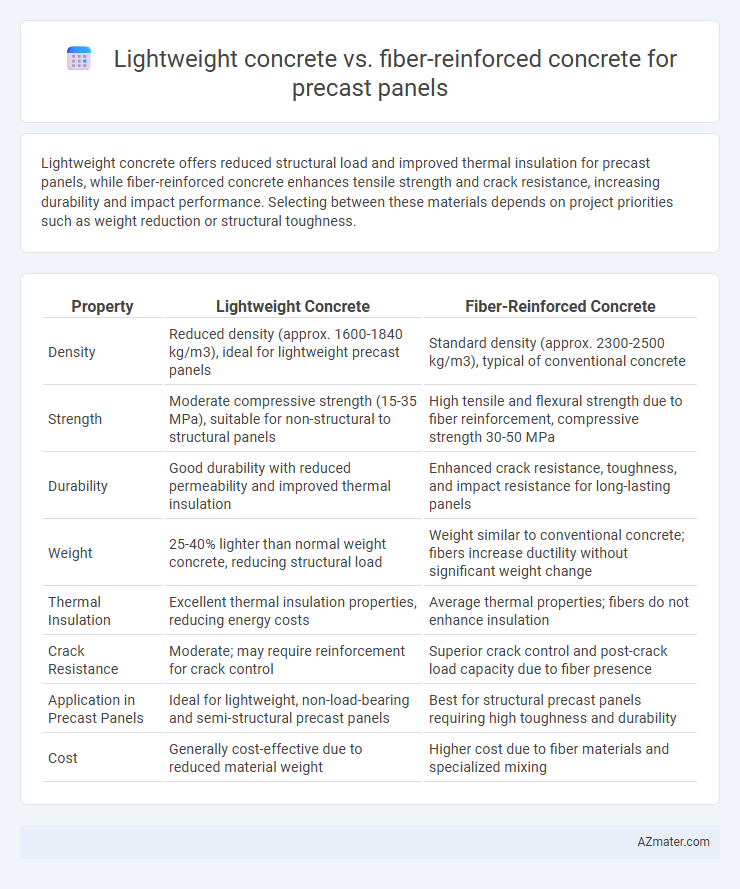
Lightweight concrete offers reduced structural load and improved thermal insulation for precast panels, while fiber-reinforced concrete enhances tensile strength and crack resistance, increasing durability and impact performance. Selecting between these materials depends on project priorities such as weight reduction or structural toughness.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Lightweight Concrete | Fiber-Reinforced Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Density | Reduced density (approx. 1600-1840 kg/m3), ideal for lightweight precast panels | Standard density (approx. 2300-2500 kg/m3), typical of conventional concrete |
| Strength | Moderate compressive strength (15-35 MPa), suitable for non-structural to structural panels | High tensile and flexural strength due to fiber reinforcement, compressive strength 30-50 MPa |
| Durability | Good durability with reduced permeability and improved thermal insulation | Enhanced crack resistance, toughness, and impact resistance for long-lasting panels |
| Weight | 25-40% lighter than normal weight concrete, reducing structural load | Weight similar to conventional concrete; fibers increase ductility without significant weight change |
| Thermal Insulation | Excellent thermal insulation properties, reducing energy costs | Average thermal properties; fibers do not enhance insulation |
| Crack Resistance | Moderate; may require reinforcement for crack control | Superior crack control and post-crack load capacity due to fiber presence |
| Application in Precast Panels | Ideal for lightweight, non-load-bearing and semi-structural precast panels | Best for structural precast panels requiring high toughness and durability |
| Cost | Generally cost-effective due to reduced material weight | Higher cost due to fiber materials and specialized mixing |
Introduction to Precast Panels
Precast panels are essential components in modern construction, offering rapid installation and high quality control by being manufactured off-site. Lightweight concrete enhances precast panels by reducing dead load and improving thermal insulation, making it ideal for multi-story buildings. Fiber-reinforced concrete increases the panels' tensile strength and crack resistance, ensuring durability and enhanced structural performance under dynamic loads.
Overview of Lightweight Concrete
Lightweight concrete for precast panels is characterized by its reduced density, achieved through the incorporation of lightweight aggregates such as expanded clay, shale, or pumice, resulting in improved thermal insulation and lower structural load. This type of concrete offers significant benefits in construction by enhancing energy efficiency while maintaining adequate compressive strength for panels. Compared to fiber-reinforced concrete, lightweight concrete primarily emphasizes weight reduction and insulation rather than tensile strength or crack resistance.
Overview of Fiber-Reinforced Concrete
Fiber-reinforced concrete (FRC) incorporates discrete fibers such as steel, glass, or synthetic materials to enhance tensile strength, toughness, and crack resistance in precast panels. Its improved durability and reduced shrinkage make FRC ideal for high-performance precast elements exposed to dynamic loads and harsh environments. Compared to lightweight concrete, FRC offers superior impact resistance and structural integrity, optimizing the longevity and safety of precast panels.
Material Composition Differences
Lightweight concrete for precast panels primarily incorporates lightweight aggregates such as expanded clay, shale, or pumice to reduce density and improve thermal insulation. Fiber-reinforced concrete, in contrast, integrates materials like steel, glass, or synthetic fibers dispersed throughout the matrix to enhance tensile strength and crack resistance. The distinct material compositions directly influence performance characteristics, where lightweight concrete emphasizes reduced weight while fiber-reinforced concrete focuses on improving durability and structural integrity.
Structural Performance Comparison
Lightweight concrete offers reduced self-weight, enhancing ease of handling and reducing foundation loads in precast panels, though it may exhibit lower tensile strength and crack resistance. Fiber-reinforced concrete significantly improves tensile strength, toughness, and crack control due to dispersed fibers, resulting in enhanced durability and structural integrity for precast panels. Comparative studies show fiber-reinforced concrete panels outperform lightweight concrete in flexural strength and impact resistance, making them preferable for load-bearing applications in precast construction.
Durability and Longevity
Lightweight concrete for precast panels offers improved thermal insulation and reduced structural load but may exhibit lower durability under aggressive environmental conditions compared to fiber-reinforced concrete, which enhances tensile strength and crack resistance through embedded fibers like steel, glass, or synthetic materials. Fiber-reinforced concrete demonstrates superior longevity by minimizing shrinkage cracks and resisting impact, freeze-thaw cycles, and corrosive agents, crucial for maintaining structural integrity in precast panels over time. Selecting fiber-reinforced concrete optimizes panel durability, reducing maintenance frequency and extending service life in infrastructure exposed to dynamic loads and harsh climates.
Thermal and Acoustic Properties
Lightweight concrete offers superior thermal insulation due to its lower density and high air content, reducing heat transfer in precast panels. Fiber-reinforced concrete enhances acoustic performance by absorbing and dampening sound vibrations through distributed fibers, making it ideal for noise reduction applications. Combining both materials can optimize thermal resistance and acoustic insulation, improving energy efficiency and sound control in building envelopes.
Installation and Handling Benefits
Lightweight concrete offers ease of installation for precast panels due to its reduced weight, which lowers transportation costs and simplifies lifting equipment requirements. Fiber-reinforced concrete enhances handling by improving toughness and crack resistance, reducing the risk of damage during transport and installation. Both materials contribute to improved efficiency on-site, but fiber-reinforced concrete provides superior durability and impact resistance in handling scenarios.
Cost Considerations
Lightweight concrete generally offers lower material costs and reduced transportation expenses due to its lower density compared to fiber-reinforced concrete, making it an economical choice for large precast panels. Fiber-reinforced concrete involves higher initial costs because of the added synthetic or steel fibers, but it provides enhanced durability and reduced maintenance costs over the panel's lifespan. Budget planning for precast panels should balance the upfront material savings of lightweight concrete against the long-term performance advantages and potential repair cost reductions associated with fiber-reinforced concrete.
Best Applications for Each Concrete Type
Lightweight concrete is ideal for precast panels requiring reduced structural load and improved thermal insulation, making it suitable for building facades and non-load-bearing walls. Fiber-reinforced concrete offers enhanced tensile strength and crack resistance, best applied in precast panels subject to high impact, bending stresses, or heavy load-bearing requirements, such as industrial floors and bridge components. Selecting between these concretes depends on specific project demands for durability, load capacity, and insulation performance.
Infographic: Lightweight concrete vs Fiber-reinforced concrete for Precast panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com