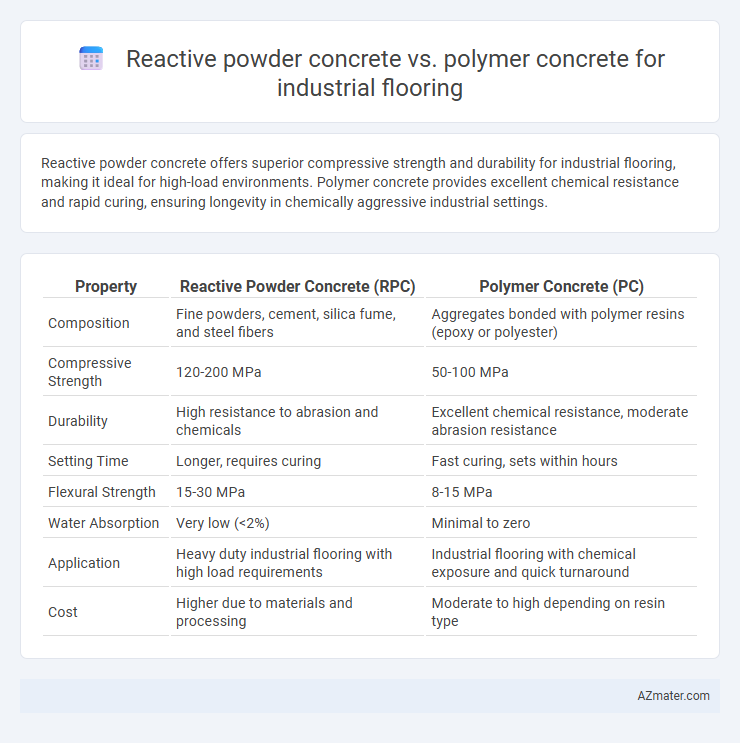
Reactive powder concrete offers superior compressive strength and durability for industrial flooring, making it ideal for high-load environments. Polymer concrete provides excellent chemical resistance and rapid curing, ensuring longevity in chemically aggressive industrial settings.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Reactive Powder Concrete (RPC) | Polymer Concrete (PC) |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Fine powders, cement, silica fume, and steel fibers | Aggregates bonded with polymer resins (epoxy or polyester) |
| Compressive Strength | 120-200 MPa | 50-100 MPa |
| Durability | High resistance to abrasion and chemicals | Excellent chemical resistance, moderate abrasion resistance |
| Setting Time | Longer, requires curing | Fast curing, sets within hours |
| Flexural Strength | 15-30 MPa | 8-15 MPa |
| Water Absorption | Very low (<2%) | Minimal to zero |
| Application | Heavy duty industrial flooring with high load requirements | Industrial flooring with chemical exposure and quick turnaround |
| Cost | Higher due to materials and processing | Moderate to high depending on resin type |
Introduction to Industrial Flooring Solutions
Reactive powder concrete offers exceptional compressive strength and durability ideal for heavy industrial flooring, providing resistance against abrasion and impact. Polymer concrete enhances chemical resistance and adhesion, making it suitable for environments exposed to corrosive substances or frequent thermal cycling. Selecting between reactive powder and polymer concrete depends on specific load requirements, exposure conditions, and maintenance considerations in industrial flooring applications.
Overview of Reactive Powder Concrete (RPC)
Reactive Powder Concrete (RPC) is an ultra-high-performance material known for its exceptional strength, durability, and resistance to chemical attack, making it ideal for industrial flooring applications. It is composed of fine powders, including silica fume, quartz, and cement, combined with steel fibers to enhance tensile strength and toughness. RPC outperforms traditional polymer concrete in load-bearing capacity and longevity, providing superior wear resistance essential for heavy industrial environments.
Overview of Polymer Concrete
Polymer concrete is a composite material composed of aggregates bonded together with a polymer binder, typically polyester, epoxy, or vinyl ester resins, offering superior chemical resistance and high compressive strength. It provides excellent durability and rapid curing, making it ideal for industrial flooring applications requiring resistance to heavy mechanical loads, chemical spills, and thermal fluctuations. Compared to reactive powder concrete, polymer concrete exhibits enhanced adhesion to substrates and improved resistance to abrasion and corrosion, ensuring longer service life in aggressive industrial environments.
Material Composition Comparison
Reactive powder concrete (RPC) consists primarily of cement, fine quartz sand, silica fume, superplasticizers, and steel fibers, resulting in a highly dense and ultra-high strength composite with minimal porosity. Polymer concrete incorporates a thermosetting resin binder, such as epoxy or polyester, combined with inorganic aggregates like sand or crushed stone, offering superior chemical resistance and flexibility. The key material distinction is RPC's cementitious matrix with micro-reinforcement versus polymer concrete's resin-based matrix, affecting performance criteria such as durability, bonding, and resistance to industrial wear conditions.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Reactive powder concrete (RPC) offers exceptional mechanical strength with compressive strengths typically exceeding 200 MPa, making it highly suitable for heavy-duty industrial flooring. Polymer concrete, reinforced with resins such as epoxy or polyester, provides superior chemical resistance and excellent durability against abrasion and impact, enhancing longevity in aggressive industrial environments. While RPC excels in load-bearing capacity, polymer concrete delivers enhanced toughness and resistance to environmental degradation, allowing tailored flooring solutions based on specific industrial demands.
Chemical and Abrasion Resistance
Reactive powder concrete (RPC) exhibits superior chemical resistance due to its ultra-dense microstructure, making it ideal for industrial flooring exposed to aggressive chemicals and acids. Polymer concrete offers excellent abrasion resistance because of its resin binder, which enhances toughness and durability against mechanical wear. Both materials provide high performance, but RPC stands out in chemical environments, whereas polymer concrete excels in applications with intense abrasion demands.
Installation Process and Curing Time
Reactive powder concrete (RPC) offers a complex installation process requiring precise mixing and controlled placement techniques, with a curing time spanning 7 to 28 days to achieve optimal strength. Polymer concrete simplifies installation by utilizing pre-mixed resins and aggregates, enabling faster application and significantly reduced curing periods, often within 24 to 48 hours. These differences make polymer concrete favorable for rapid turnaround projects, while RPC is preferred for its superior mechanical properties in high-load industrial flooring.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Reactive powder concrete (RPC) generally exhibits higher initial costs due to advanced materials like quartz powder and steel fibers, but offers superior durability and lower maintenance expenses in industrial flooring applications. Polymer concrete, while typically more cost-effective upfront because of resin binders, may incur increased long-term costs from potential chemical degradation and reduced wear resistance in heavy-duty environments. Economic considerations prioritize lifecycle cost analysis, where RPC often delivers better return on investment by minimizing downtime and repair costs in industrial settings.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Reactive powder concrete (RPC) offers superior durability and strength with significantly lower cement content, reducing CO2 emissions compared to conventional concrete, which enhances sustainability for industrial flooring applications. Polymer concrete incorporates resins derived from petrochemicals, leading to higher embodied energy and potential environmental concerns, but it provides excellent chemical resistance and longevity that can minimize maintenance-related waste. Selecting RPC over polymer concrete can contribute to lower overall environmental impact by combining reduced carbon footprint and extended service life in industrial flooring solutions.
Choosing the Right Concrete for Industrial Flooring
Reactive powder concrete offers superior compressive strength and durability, making it ideal for heavy-duty industrial flooring subject to high mechanical stress and frequent traffic. Polymer concrete provides excellent chemical resistance and rapid curing times, suitable for environments exposed to aggressive chemicals and requiring minimal downtime. Selecting the right concrete depends on balancing load-bearing capacity, chemical exposure, and installation speed for optimal industrial flooring performance.
Infographic: Reactive powder concrete vs Polymer concrete for Industrial flooring
 azmater.com
azmater.com