Vinyl ester offers lightweight corrosion resistance for racing car bodies but lacks the superior strength and stiffness of carbon fiber. Carbon fiber provides exceptional tensile strength and rigidity, enhancing performance and durability under extreme racing conditions.
Table of Comparison
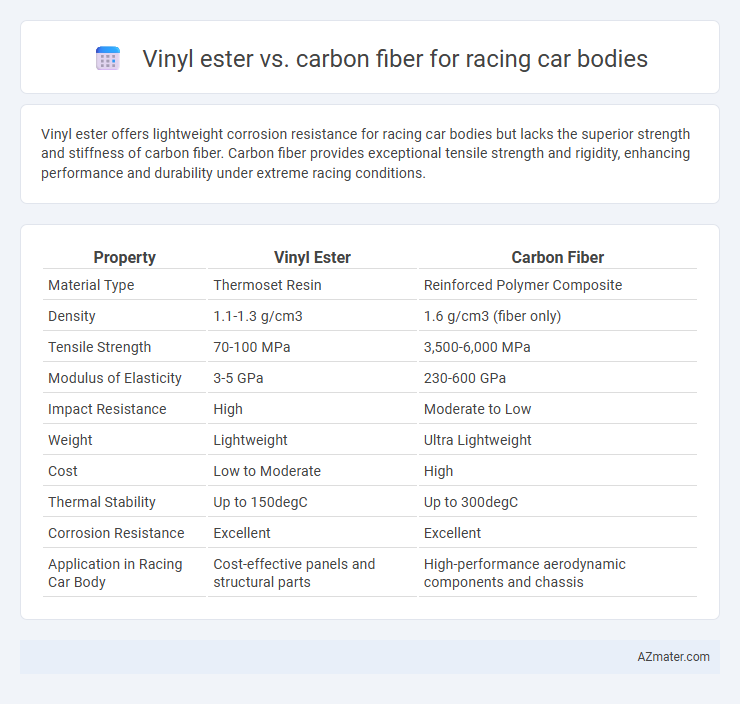
| Property | Vinyl Ester | Carbon Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoset Resin | Reinforced Polymer Composite |
| Density | 1.1-1.3 g/cm3 | 1.6 g/cm3 (fiber only) |
| Tensile Strength | 70-100 MPa | 3,500-6,000 MPa |
| Modulus of Elasticity | 3-5 GPa | 230-600 GPa |
| Impact Resistance | High | Moderate to Low |
| Weight | Lightweight | Ultra Lightweight |
| Cost | Low to Moderate | High |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 150degC | Up to 300degC |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent | Excellent |
| Application in Racing Car Body | Cost-effective panels and structural parts | High-performance aerodynamic components and chassis |
Introduction to Racing Car Body Materials
Vinyl ester and carbon fiber are prominent materials used in racing car body construction due to their distinct properties and performance benefits. Vinyl ester offers excellent resistance to corrosion and impact, providing durability at a lower cost. Carbon fiber is preferred for its superior strength-to-weight ratio and stiffness, enhancing aerodynamic efficiency and speed in high-performance racing applications.
Overview of Vinyl Ester
Vinyl ester resin is a popular choice for racing car bodies due to its excellent resistance to corrosion and superior mechanical strength compared to standard polyester resins. It offers enhanced toughness and durability, making it suitable for high-performance applications where lightweight and impact resistance are critical. While carbon fiber composites provide higher stiffness and strength-to-weight ratios, vinyl ester remains a cost-effective and resilient option for racing vehicle exteriors.
Overview of Carbon Fiber
Carbon fiber is a composite material renowned for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, stiffness, and durability, making it a preferred choice for high-performance racing car bodies. Unlike vinyl ester, carbon fiber offers superior impact resistance and fatigue life, enhancing both safety and vehicle longevity on the track. Its ability to be precisely molded into aerodynamic shapes contributes significantly to improved speed and handling in competitive racing environments.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Vinyl ester composites offer good corrosion resistance and moderate strength, making them cost-effective for racing car bodies, but they generally fall short in stiffness and impact resistance compared to carbon fiber. Carbon fiber composites provide superior tensile strength, stiffness, and fatigue resistance, crucial for high-performance racing applications where lightweight durability is essential. The enhanced mechanical properties of carbon fiber translate to better energy absorption and structural integrity under extreme racing conditions, outperforming vinyl ester in strength and long-term durability.
Weight Considerations for Racing Performance
Vinyl ester composites offer a lightweight yet durable option, but carbon fiber significantly outperforms them with a lower density and higher strength-to-weight ratio, crucial for enhancing racing car acceleration and handling. The reduced weight of carbon fiber results in improved fuel efficiency and quicker lap times due to superior stiffness and impact resistance. Selecting carbon fiber for racing car bodies optimizes weight savings without compromising structural integrity, directly benefiting overall performance on the track.
Cost Analysis: Vinyl Ester vs Carbon Fiber
Vinyl ester resin offers a significantly lower cost compared to carbon fiber composites, making it an economical choice for racing car bodies where budget constraints are critical. While carbon fiber provides superior strength-to-weight ratio and enhanced performance benefits, its manufacturing and material expenses can be up to three times higher than vinyl ester-based composites. Teams prioritizing cost efficiency without extreme performance demands often prefer vinyl ester due to reduced material cost, easier processing, and lower production complexity.
Manufacturing and Repair Processes
Vinyl ester composites offer simpler manufacturing processes with faster curing times and lower costs compared to carbon fiber, making them suitable for rapid prototyping in racing car bodies. Carbon fiber requires more complex layup procedures, precision in fiber alignment, and longer curing cycles, but provides superior strength-to-weight ratios essential for high-performance racing. Repairing vinyl ester components is generally more straightforward and less expensive, while carbon fiber repairs demand specialized skills and materials to restore structural integrity without compromising performance.
Resistance to Environmental Factors
Vinyl ester resins exhibit excellent resistance to water, chemicals, and corrosion, making them highly suitable for environments with exposure to moisture and harsh chemicals. Carbon fiber composites, while offering superior strength-to-weight ratios, rely on the resin matrix for environmental protection, with epoxy resins typically providing better UV and chemical resistance compared to vinyl ester when properly formulated. For racing car bodies, the choice depends on balancing vinyl ester's chemical resistance with carbon fiber's structural benefits, often enhanced by protective coatings to improve durability against environmental factors.
Applications in Professional Motorsports
Vinyl ester composites, valued for their excellent corrosion resistance and cost-effectiveness, are typically used in less structurally critical body panels or aerodynamic components in professional motorsports. Carbon fiber, distinguished by its superior strength-to-weight ratio and stiffness, is the preferred material for high-performance racing car bodies, offering enhanced rigidity and weight savings essential for competitive track performance. In professional racing, the application of carbon fiber allows for precision engineering in chassis and aerodynamic components, directly impacting speed, handling, and safety.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Racing Car
Vinyl ester offers a balance of excellent corrosion resistance and good mechanical properties, making it a cost-effective choice for racing car bodies facing harsh environmental conditions. Carbon fiber provides superior strength-to-weight ratio and rigidity, significantly enhancing performance and handling in high-speed racing but comes at a higher price point. Selecting the right material depends on factors such as budget constraints, performance requirements, and the specific stress loads experienced by the car body during races.
Infographic: Vinyl ester vs Carbon fiber for Racing car body
 azmater.com
azmater.com