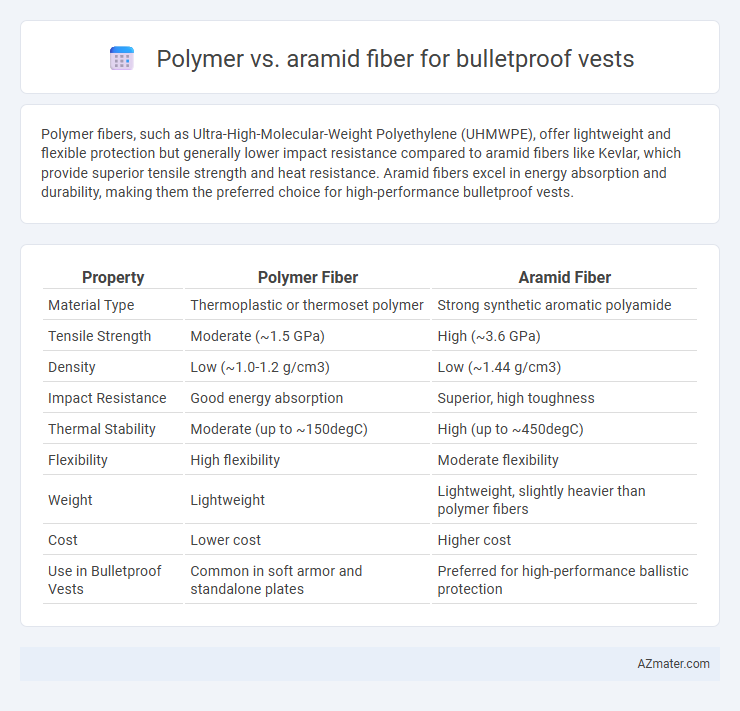
Polymer fibers, such as Ultra-High-Molecular-Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE), offer lightweight and flexible protection but generally lower impact resistance compared to aramid fibers like Kevlar, which provide superior tensile strength and heat resistance. Aramid fibers excel in energy absorption and durability, making them the preferred choice for high-performance bulletproof vests.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polymer Fiber | Aramid Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic or thermoset polymer | Strong synthetic aromatic polyamide |
| Tensile Strength | Moderate (~1.5 GPa) | High (~3.6 GPa) |
| Density | Low (~1.0-1.2 g/cm3) | Low (~1.44 g/cm3) |
| Impact Resistance | Good energy absorption | Superior, high toughness |
| Thermal Stability | Moderate (up to ~150degC) | High (up to ~450degC) |
| Flexibility | High flexibility | Moderate flexibility |
| Weight | Lightweight | Lightweight, slightly heavier than polymer fibers |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
| Use in Bulletproof Vests | Common in soft armor and standalone plates | Preferred for high-performance ballistic protection |
Introduction to Bulletproof Vest Materials
Bulletproof vests primarily utilize two advanced materials: polymer fibers like Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE) and aramid fibers such as Kevlar. UHMWPE offers exceptional tensile strength and lightweight properties, enhancing mobility and comfort, while aramid fibers provide high heat resistance and effective ballistic protection through their durable, woven structure. Both materials are engineered for optimal energy absorption and impact dispersion, making them crucial for modern ballistic armor performance.
Overview of Polymer Fibers in Ballistic Protection
Polymer fibers such as ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) are widely used in bulletproof vests due to their high strength-to-weight ratio and excellent energy absorption capabilities. These fibers offer superior flexibility and lighter weight compared to aramid fibers like Kevlar, enhancing wearer comfort while maintaining ballistic resistance. UHMWPE fibers also exhibit outstanding resistance to moisture and chemicals, improving durability in various operational environments.
Introduction to Aramid Fibers (Kevlar, Twaron)
Aramid fibers, including Kevlar and Twaron, are renowned for their exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and high impact resistance, making them ideal materials for bulletproof vests. These synthetic fibers exhibit excellent heat resistance and durability, enabling effective energy absorption and distribution upon ballistic impact. Compared to conventional polymers, aramid fibers provide superior tensile strength and stab resistance, enhancing personal protection in ballistic armor applications.
Mechanical Properties: Strength and Flexibility
Polymer fibers like ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) exhibit exceptional tensile strength combined with lightweight flexibility, making them ideal for bulletproof vests requiring high mobility. Aramid fibers such as Kevlar offer superior impact resistance and stiffness, providing enhanced durability under ballistic stress but with less flexibility compared to polymers. The choice between polymer and aramid fibers in protective gear hinges on balancing tensile strength and flexibility to optimize both wearability and ballistic performance.
Weight and Comfort Comparison
Polymer fibers like ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) offer significantly lighter bulletproof vests compared to aramid fibers such as Kevlar, enhancing wearer mobility and reducing fatigue. Aramid fibers provide high tensile strength and heat resistance but tend to be heavier and less breathable, impacting overall comfort during extended use. The weight advantage of polymer fibers directly correlates to increased comfort, making them preferable for lightweight, flexible ballistic protection in various tactical scenarios.
Ballistic Performance: Stopping Power
Aramid fibers like Kevlar offer superior ballistic performance due to their high tensile strength and energy absorption capacity, effectively dispersing the impact of bullets and reducing penetration. Polymer fibers such as UHMWPE provide excellent stopping power with lighter weight and increased flexibility, enhancing wearer comfort without compromising protection. Both materials are widely used in bulletproof vests, but aramid fibers excel in multi-hit resistance while polymers typically perform better against blunt force trauma.
Durability and Resistance to Environmental Factors
Polymer fibers, such as ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE), offer excellent durability with strong resistance to moisture, UV exposure, and chemical degradation, making them ideal for varied environmental conditions. Aramid fibers like Kevlar provide high tensile strength and thermal stability but can degrade when exposed to prolonged UV radiation and moisture, affecting long-term durability. The choice between polymer and aramid fibers depends on the specific environmental factors and operational lifespan requirements of the bulletproof vest.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Polymer fibers such as ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) typically offer lower production costs and simpler manufacturing processes compared to aramid fibers like Kevlar. UHMWPE fibers allow for efficient weaving and molding, resulting in lightweight vests with reduced labor and energy expenses. In contrast, aramid fiber production involves more complex chemical synthesis and curing steps, increasing overall manufacturing time and material costs for bulletproof vest applications.
Applications in Law Enforcement and Military
Polymer fibers such as Ultra-High-Molecular-Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE) provide lightweight, high-strength protection ideal for law enforcement officers requiring mobility during patrols and tactical operations. Aramid fibers like Kevlar offer exceptional heat resistance and ballistic performance, making them the preferred choice for military personnel facing diverse combat scenarios, including high-velocity projectile threats. Both materials enhance bulletproof vests by balancing protection, flexibility, and weight, optimizing safety for frontline users across public safety and defense sectors.
Future Trends in Bulletproof Vest Materials
Emerging trends in bulletproof vest materials highlight the increasing integration of high-performance polymers such as ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) and advanced aramid fibers like Twaron and Kevlar. Innovations focus on enhancing lightweight properties, improved tensile strength, and superior energy dispersion to increase wearer comfort and protection efficiency. Research into hybrid composite materials and nanotechnology promises next-generation vests with greater flexibility, durability, and multi-threat resistance.
Infographic: Polymer vs Aramid fiber for Bulletproof vest
 azmater.com
azmater.com