Geopolymer composites offer superior durability, fire resistance, and low maintenance compared to wood-plastic composites, which tend to degrade under UV exposure and moisture in outdoor decking applications. Enhanced compressive strength and environmental sustainability make geopolymer composites a more resilient and eco-friendly choice for long-term outdoor decking solutions.
Table of Comparison
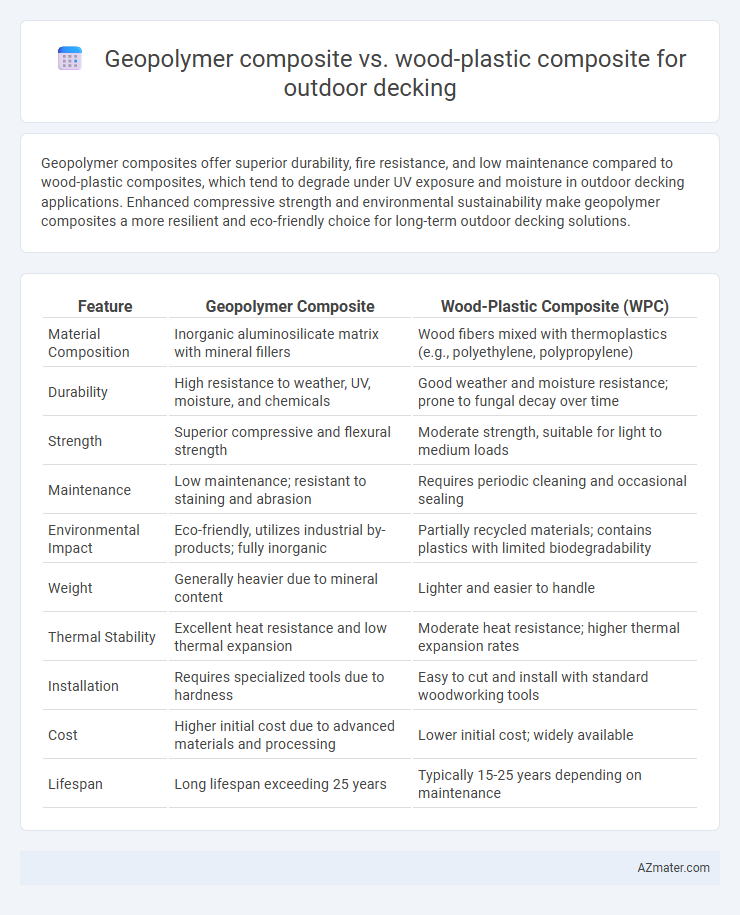
| Feature | Geopolymer Composite | Wood-Plastic Composite (WPC) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Inorganic aluminosilicate matrix with mineral fillers | Wood fibers mixed with thermoplastics (e.g., polyethylene, polypropylene) |
| Durability | High resistance to weather, UV, moisture, and chemicals | Good weather and moisture resistance; prone to fungal decay over time |
| Strength | Superior compressive and flexural strength | Moderate strength, suitable for light to medium loads |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; resistant to staining and abrasion | Requires periodic cleaning and occasional sealing |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, utilizes industrial by-products; fully inorganic | Partially recycled materials; contains plastics with limited biodegradability |
| Weight | Generally heavier due to mineral content | Lighter and easier to handle |
| Thermal Stability | Excellent heat resistance and low thermal expansion | Moderate heat resistance; higher thermal expansion rates |
| Installation | Requires specialized tools due to hardness | Easy to cut and install with standard woodworking tools |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to advanced materials and processing | Lower initial cost; widely available |
| Lifespan | Long lifespan exceeding 25 years | Typically 15-25 years depending on maintenance |
Introduction to Outdoor Decking Materials
Geopolymer composites offer superior durability and resistance to weathering compared to traditional wood-plastic composites, making them ideal for outdoor decking applications. These materials exhibit enhanced fire resistance, low maintenance requirements, and greater environmental sustainability due to the use of industrial byproducts like fly ash or slag. Wood-plastic composites, while popular for their ease of installation and aesthetic similarity to natural wood, often face issues with moisture absorption and UV degradation over time.
Overview of Geopolymer Composites
Geopolymer composites are inorganic materials synthesized from aluminosilicate precursors, offering exceptional durability, fire resistance, and low environmental impact, making them ideal for outdoor decking. Their high compressive strength, resistance to UV radiation, and minimal water absorption outperform traditional wood-plastic composites, which often suffer from moisture-induced degradation and limited fire resistance. These characteristics position geopolymer composites as a sustainable, long-lasting alternative in outdoor construction applications.
Overview of Wood-Plastic Composites
Wood-plastic composites (WPCs) for outdoor decking combine natural wood fibers with thermoplastics, offering enhanced resistance to moisture, decay, and insect damage compared to traditional wood. WPCs provide a low-maintenance, durable surface with improved dimensional stability and reduced splintering, making them popular for outdoor applications. Their blend of wood aesthetics and plastic durability positions them as a versatile choice, though they may exhibit lower heat tolerance and UV resistance than alternative materials like geopolymer composites.
Material Composition and Manufacturing
Geopolymer composites for outdoor decking consist primarily of inorganic aluminosilicate materials combined with industrial by-products like fly ash or slag, which are cured through a chemical activation process enhancing durability and resistance to weathering. Wood-plastic composites (WPC) combine thermoplastics such as polyethylene or polypropylene with wood fibers or flour, produced via extrusion or injection molding that blends organic and synthetic components to improve dimensional stability and reduce maintenance. The manufacturing of geopolymer composites involves alkali activation and curing at ambient or elevated temperatures, whereas WPC relies on melting and mixing processes that facilitate the integration of wood particles into a polymer matrix.
Durability and Weather Resistance Comparison
Geopolymer composites exhibit superior durability and weather resistance compared to wood-plastic composites (WPC) for outdoor decking applications, as they are highly resistant to UV radiation, moisture, and temperature fluctuations without degrading or warping. The inorganic matrix of geopolymer composites prevents microbial growth, rot, and insect damage, while WPCs tend to absorb water over time, leading to fungal decay and dimensional instability. Long-term exposure tests demonstrate geopolymer composites maintain structural integrity and aesthetic appeal far longer than WPCs, making them a more reliable choice for harsh outdoor environments.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Geopolymer composites for outdoor decking exhibit superior environmental benefits compared to wood-plastic composites due to their low carbon footprint and use of industrial by-products such as fly ash or slag, reducing waste and greenhouse gas emissions. Wood-plastic composites rely heavily on non-renewable petroleum-based plastics and often involve energy-intensive recycling processes that contribute to microplastic pollution. Geopolymer materials offer enhanced durability and require less maintenance, prolonging lifecycle and minimizing resource consumption, making them a more sustainable choice for eco-friendly decking solutions.
Mechanical Strength and Load-Bearing Capacity
Geopolymer composites exhibit superior mechanical strength and load-bearing capacity compared to wood-plastic composites, making them more suitable for outdoor decking applications exposed to heavy loads and harsh environmental conditions. The inorganic matrix of geopolymer composites provides enhanced rigidity and durability, resisting deformation and structural fatigue over time. In contrast, wood-plastic composites, while offering good flexibility and moderate strength, tend to exhibit lower load-bearing performance and higher susceptibility to environmental degradation.
Maintenance Requirements and Lifespan
Geopolymer composites for outdoor decking offer superior durability with minimal maintenance, resisting moisture, UV rays, and biological decay better than wood-plastic composites (WPC). WPC decks typically require regular sealing, cleaning, and repairs due to vulnerability to fading, cracking, and mold growth over 10 to 20 years, whereas geopolymer composites can last 30+ years with simple cleaning. The inorganic matrix of geopolymer composites ensures enhanced structural integrity and longevity, making them a low-maintenance alternative compared to the organic-polymer nature of WPC materials.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Geopolymer composites for outdoor decking offer enhanced durability and fire resistance but typically come with higher initial costs compared to wood-plastic composites due to raw material and processing expenses. Wood-plastic composites are widely available in the market, benefiting from established manufacturing processes and economies of scale, making them a more cost-effective choice for budget-conscious consumers. Market availability favors wood-plastic composites with extensive distribution networks and diverse product options, whereas geopolymer composites remain niche, limiting accessibility and driving higher prices.
Conclusion: Choosing the Best Composite for Outdoor Decking
Geopolymer composites offer superior durability, fire resistance, and low maintenance compared to wood-plastic composites (WPC), making them ideal for long-term outdoor decking applications in harsh environments. Wood-plastic composites provide better aesthetics and a more natural wood feel but require more upkeep and are less resistant to moisture and UV degradation. Selecting the best composite depends on prioritizing durability and sustainability with geopolymer composites or opting for cost-effective and visually appealing wood-plastic composites.
Infographic: Geopolymer composite vs Wood-plastic composite for Outdoor decking
 azmater.com
azmater.com