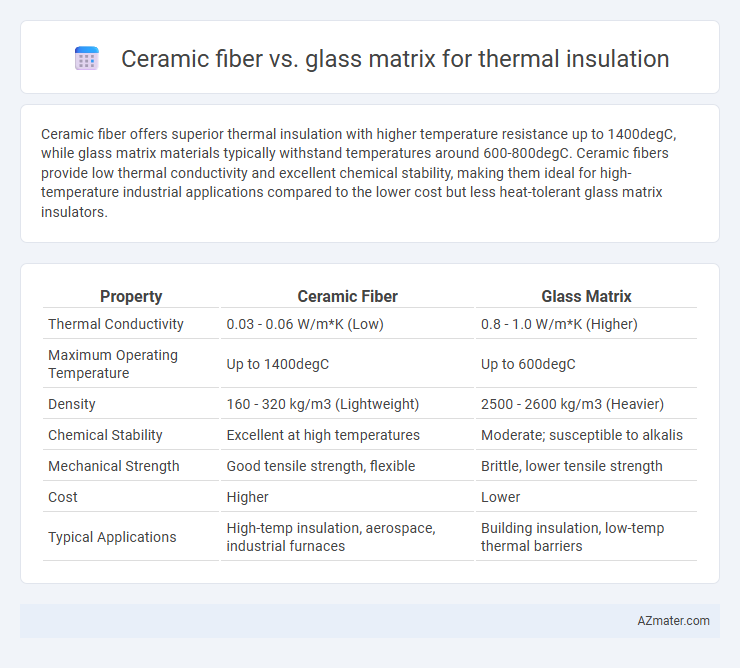
Ceramic fiber offers superior thermal insulation with higher temperature resistance up to 1400degC, while glass matrix materials typically withstand temperatures around 600-800degC. Ceramic fibers provide low thermal conductivity and excellent chemical stability, making them ideal for high-temperature industrial applications compared to the lower cost but less heat-tolerant glass matrix insulators.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ceramic Fiber | Glass Matrix |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | 0.03 - 0.06 W/m*K (Low) | 0.8 - 1.0 W/m*K (Higher) |
| Maximum Operating Temperature | Up to 1400degC | Up to 600degC |
| Density | 160 - 320 kg/m3 (Lightweight) | 2500 - 2600 kg/m3 (Heavier) |
| Chemical Stability | Excellent at high temperatures | Moderate; susceptible to alkalis |
| Mechanical Strength | Good tensile strength, flexible | Brittle, lower tensile strength |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Typical Applications | High-temp insulation, aerospace, industrial furnaces | Building insulation, low-temp thermal barriers |
Introduction to Thermal Insulators
Thermal insulators such as ceramic fiber and glass matrix materials play a critical role in reducing heat transfer in industrial applications. Ceramic fiber is composed of alumina and silica, providing high-temperature resistance up to 1400degC, excellent thermal shock resistance, and low thermal conductivity around 0.12 W/m*K. Glass matrix insulators, typically based on borosilicate or soda-lime glass, offer moderate temperature resistance up to 600degC with enhanced chemical stability and thermal insulation properties near 0.04 W/m*K.
Overview of Ceramic Fiber Materials
Ceramic fiber materials, composed primarily of alumina, silica, and other refractory oxides, exhibit exceptional thermal stability and low thermal conductivity, making them ideal for high-temperature insulation applications. Their porous structure provides excellent resistance to thermal shock and chemical corrosion compared to glass matrix insulators. These fibers maintain integrity at temperatures exceeding 1200degC, outperforming most glass-based thermal insulators in both durability and insulation efficiency.
Understanding Glass Matrix Composites
Glass matrix composites offer enhanced thermal insulation by combining the low thermal conductivity of glass with reinforced fibers that improve mechanical strength and thermal stability. These composites provide superior resistance to high temperatures and thermal shock compared to traditional ceramic fibers, making them ideal for demanding industrial applications. Understanding the microstructure and fiber-matrix interface is crucial for optimizing thermal performance and durability in glass matrix thermal insulators.
Thermal Conductivity Comparison
Ceramic fiber typically exhibits lower thermal conductivity values, ranging from 0.03 to 0.07 W/m*K, compared to glass matrix materials, which generally have thermal conductivities around 0.1 to 0.2 W/m*K. The intrinsic microstructure of ceramic fibers provides superior resistance to heat flow, making them more effective for high-temperature insulation applications. Glass matrix insulation, while more cost-effective, tends to perform less efficiently in environments where minimal heat transfer is critical.
Temperature Resistance and Limits
Ceramic fiber insulation provides superior temperature resistance, typically withstanding continuous operating temperatures up to 1260degC (2300degF), making it ideal for high-temperature industrial applications. Glass matrix insulation usually has lower temperature limits, generally effective up to 550degC (1022degF), restricting its use to moderate heat environments. The higher melting point and thermal stability of ceramic fibers allow for greater durability and efficiency in extreme heat conditions compared to glass-based insulation.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Ceramic fiber insulation exhibits superior mechanical strength and durability compared to glass matrix materials, maintaining integrity at temperatures exceeding 1200degC due to its crystalline structure and resistance to thermal shock. Glass matrix insulators, while offering good thermal resistance up to around 600degC, tend to suffer from brittleness and reduced mechanical stability under cyclic temperature fluctuations. The enhanced toughness and longer lifespan of ceramic fiber make it the preferred choice for high-temperature industrial applications requiring robust thermal insulation performance.
Weight and Flexibility Factors
Ceramic fiber insulation offers superior lightweight properties compared to traditional glass matrix materials, enhancing ease of installation and reducing structural load. Its inherent flexibility enables better conformity to complex shapes, making it ideal for applications requiring tight sealing and thermal efficiency. Glass matrix insulators tend to be heavier and more rigid, limiting their use where weight reduction and adaptability are critical.
Chemical Stability and Corrosion Resistance
Ceramic fiber thermal insulators exhibit superior chemical stability and corrosion resistance compared to glass matrix materials, maintaining structural integrity in highly acidic or alkaline environments. The inherent inertness of ceramic fibers ensures minimal degradation when exposed to aggressive chemicals and high-temperature oxidative atmospheres. Glass matrix insulators tend to be more susceptible to chemical attack and corrosion, especially under prolonged exposure to moisture and alkaline substances, limiting their effectiveness in harsh industrial applications.
Cost Analysis and Availability
Ceramic fiber insulation typically costs more than glass matrix materials due to higher manufacturing complexity and raw material expenses. Glass matrix insulators offer greater availability and lower cost, benefiting large-scale industrial applications and wide distribution in construction markets. Cost-efficiency and accessibility make glass matrix preferred in budget-sensitive projects, while ceramic fibers are favored for high-temperature, specialized environments.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Application
Ceramic fiber offers superior thermal resistance and lower thermal conductivity compared to glass matrix materials, making it ideal for high-temperature applications above 1000degC. Glass matrix insulators provide excellent chemical stability and cost-effectiveness at moderate temperatures below 600degC, suitable for less demanding thermal environments. Selecting the right material depends on operating temperature, mechanical strength requirements, and exposure to corrosive atmospheres to ensure optimal insulation performance and longevity.
Infographic: Ceramic fiber vs Glass matrix for Thermal insulator
 azmater.com
azmater.com