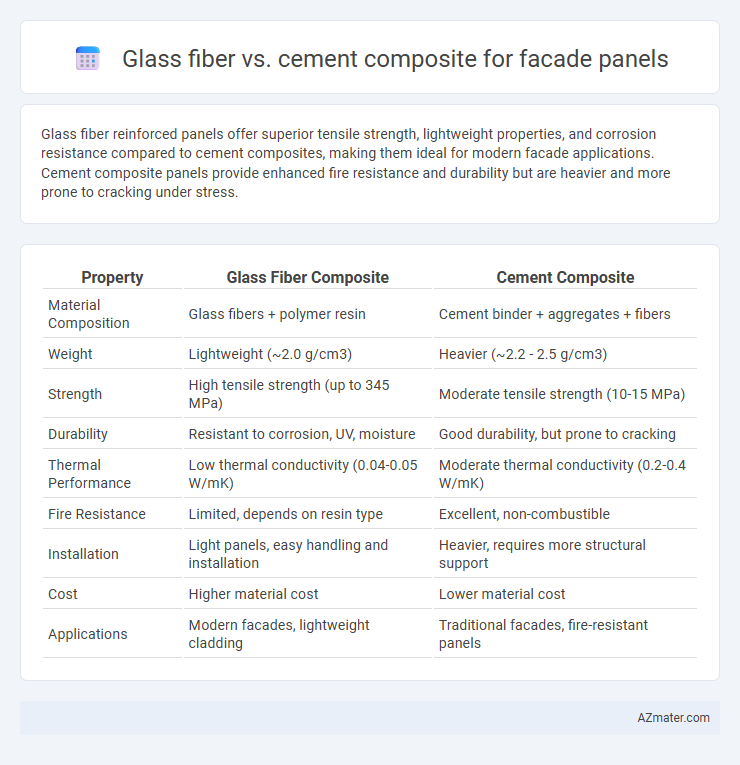
Glass fiber reinforced panels offer superior tensile strength, lightweight properties, and corrosion resistance compared to cement composites, making them ideal for modern facade applications. Cement composite panels provide enhanced fire resistance and durability but are heavier and more prone to cracking under stress.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Glass Fiber Composite | Cement Composite |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Glass fibers + polymer resin | Cement binder + aggregates + fibers |
| Weight | Lightweight (~2.0 g/cm3) | Heavier (~2.2 - 2.5 g/cm3) |
| Strength | High tensile strength (up to 345 MPa) | Moderate tensile strength (10-15 MPa) |
| Durability | Resistant to corrosion, UV, moisture | Good durability, but prone to cracking |
| Thermal Performance | Low thermal conductivity (0.04-0.05 W/mK) | Moderate thermal conductivity (0.2-0.4 W/mK) |
| Fire Resistance | Limited, depends on resin type | Excellent, non-combustible |
| Installation | Light panels, easy handling and installation | Heavier, requires more structural support |
| Cost | Higher material cost | Lower material cost |
| Applications | Modern facades, lightweight cladding | Traditional facades, fire-resistant panels |
Introduction to Facade Panel Materials
Glass fiber and cement composites are popular materials for facade panels due to their durability and versatility. Glass fiber offers high tensile strength, lightweight properties, and excellent resistance to corrosion, making it suitable for intricate designs and modern aesthetics. Cement composites provide robustness, fire resistance, and cost-effectiveness, ideal for structural stability and longevity in building exteriors.
Overview of Glass Fiber Composites
Glass fiber composites for facade panels consist of glass fibers embedded in a resin matrix, providing high strength-to-weight ratio and excellent durability against weathering and corrosion. These composites offer superior flexibility, impact resistance, and ease of installation compared to traditional cement-based panels. Their thermal insulation properties and resistance to chemical degradation make them a preferred choice for modern architectural facades requiring long-lasting performance and aesthetic versatility.
Overview of Cement Composites
Cement composites for facade panels consist of a mixture of cement, aggregates, and reinforcing fibers that enhance durability and load-bearing capacity. These composites provide excellent resistance to weathering, fire, and corrosion, making them suitable for exterior cladding applications. Their high compressive strength and versatility allow for customizable textures and finishes, offering architects robust and aesthetically pleasing facade solutions.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Glass fiber reinforced composites exhibit higher tensile strength and superior impact resistance compared to cement-based composites, making them ideal for facade panels subjected to dynamic loads. Cement composites offer greater compressive strength and stiffness, which can be advantageous for structural stability in facade applications. However, glass fiber composites provide better flexibility and resistance to cracking under stress, resulting in enhanced durability and long-term mechanical performance.
Durability and Weather Resistance
Glass fiber reinforced composites exhibit superior durability and weather resistance for facade panels due to their high tensile strength and resistance to corrosion, moisture, and UV radiation. Cement composites, while robust and fire-resistant, are prone to cracking and degradation over time when exposed to freeze-thaw cycles and prolonged moisture penetration. The longevity of glass fiber panels in harsh environmental conditions typically outperforms cement-based options, making them a preferred choice for sustainable and low-maintenance facades.
Aesthetic Versatility and Design Options
Glass fiber reinforced composite panels offer superior aesthetic versatility due to their ability to be molded into complex shapes and a wide range of colors and finishes, enabling intricate facade designs. Cement composite panels, while durable and strong, provide a more uniform texture and limited color palette, often resulting in a more traditional and less customizable appearance. The inherent flexibility of glass fiber composites in design enables architects to achieve innovative facade solutions that blend function with artistic expression.
Installation and Workability
Glass fiber reinforced facade panels offer superior ease of installation due to their lightweight nature, reducing labor costs and structural load compared to cement composites. Cement composite panels, while heavier and more rigid, require specialized handling and longer curing times, impacting overall project timelines. The enhanced flexibility and dimensional stability of glass fiber panels improve workability, allowing for quicker adjustments and more complex design applications on facades.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Glass fiber reinforced facade panels offer lower embodied carbon compared to cement composites due to less energy-intensive production and the potential for recycling glass fibers. Cement composite panels, while durable, contribute significantly to CO2 emissions during cement manufacturing, which is responsible for approximately 8% of global carbon dioxide emissions. Utilizing glass fiber composites supports circular economy principles and reduces environmental impact, making them a more sustainable choice for facade applications.
Cost Efficiency and Lifecycle Analysis
Glass fiber reinforced concrete (GFRC) facade panels offer superior cost efficiency due to reduced material weight and faster installation times compared to traditional cement composite panels. Lifecycle analysis reveals GFRC panels have enhanced durability and lower maintenance costs, with better resistance to cracking and environmental degradation. Cement composites typically incur higher long-term expenses from repairs and replacements, impacting overall project budget sustainability.
Choosing the Right Facade Panel Material
Glass fiber reinforced panels offer superior tensile strength, lightweight properties, and excellent resistance to corrosion, making them ideal for modern facade applications that demand durability and design flexibility. Cement composites provide robust fire resistance, thermal insulation, and low maintenance costs, suitable for heavy-duty facades requiring long-term structural integrity. Selecting the right facade panel material depends on project-specific factors such as environmental exposure, aesthetic requirements, budget constraints, and installation complexity.
Infographic: Glass fiber vs Cement composite for Facade panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com