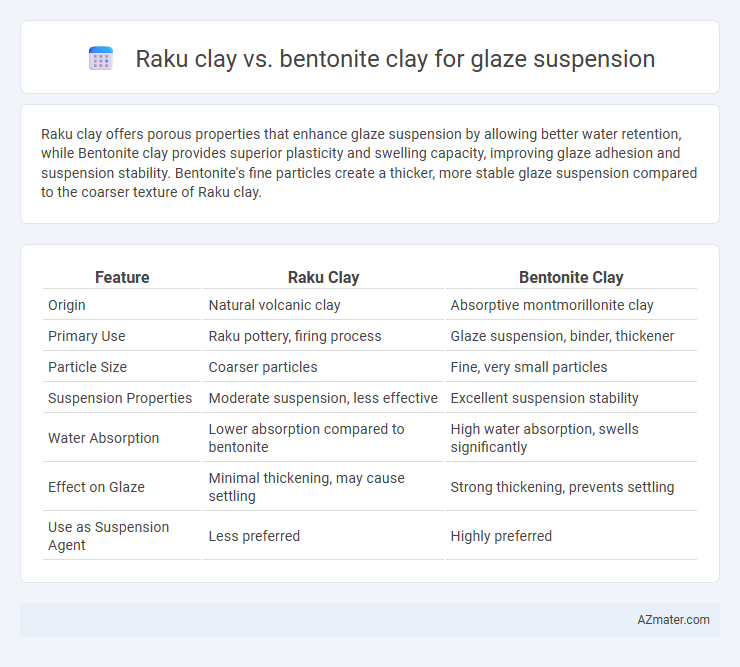
Raku clay offers porous properties that enhance glaze suspension by allowing better water retention, while Bentonite clay provides superior plasticity and swelling capacity, improving glaze adhesion and suspension stability. Bentonite's fine particles create a thicker, more stable glaze suspension compared to the coarser texture of Raku clay.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Raku Clay | Bentonite Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Natural volcanic clay | Absorptive montmorillonite clay |
| Primary Use | Raku pottery, firing process | Glaze suspension, binder, thickener |
| Particle Size | Coarser particles | Fine, very small particles |
| Suspension Properties | Moderate suspension, less effective | Excellent suspension stability |
| Water Absorption | Lower absorption compared to bentonite | High water absorption, swells significantly |
| Effect on Glaze | Minimal thickening, may cause settling | Strong thickening, prevents settling |
| Use as Suspension Agent | Less preferred | Highly preferred |
Introduction: Understanding Glaze Suspension
Raku clay and bentonite clay serve distinct roles in glaze suspension due to their unique particle properties and plasticity. Bentonite clay offers superior suspension stability in glaze formulations because of its fine particle size and swelling capacity, which helps evenly disperse glaze materials for better application and finish. Raku clay, while useful in its own right, typically provides less suspension power, making bentonite the preferred choice for maintaining a homogenous glaze mixture.
What is Raku Clay?
Raku clay is a porous, low-fire clay body specifically designed for raku firing, known for its rapid thermal shock resistance and ability to develop unique surface textures. Bentonite clay, a highly absorbent and swelling clay used primarily as a suspension agent, enhances glaze suspension by maintaining even particle distribution and preventing settling. Unlike bentonite, raku clay influences the final fired texture and durability of ceramic pieces rather than solely improving glaze suspension properties.
What is Bentonite Clay?
Bentonite clay is a highly absorbent natural clay composed primarily of montmorillonite, prized in ceramics for its excellent suspension properties in glazes. It enhances glaze viscosity, preventing materials from settling and ensuring even application in both Raku and traditional firing techniques. Unlike Raku clay, bentonite's fine particle size and swelling capacity make it essential for maintaining homogeneity and stability in glaze mixtures.
Key Chemical and Physical Properties
Raku clay, characterized by its coarse particle size and high grog content, offers excellent thermal shock resistance and a porous texture ideal for glaze suspension, promoting better adhesion and controlled drying. Bentonite clay, rich in montmorillonite with high plasticity and excellent water absorption, enhances suspension stability and viscosity due to its fine particles and strong swelling capacity. The combination of Raku's durability and Bentonite's binding properties optimizes glaze suspension by balancing particle dispersal and rheological behavior during application and firing.
Particle Size and Glaze Suspension Abilities
Raku clay features larger particle sizes compared to Bentonite clay, which contributes to better rheological properties for glaze suspension by preventing settling and promoting even distribution. Bentonite clay, with its extremely fine particles and high swelling capacity, enhances glaze suspension by increasing viscosity and stabilizing the slurry, even at low concentrations. The optimal choice depends on the specific glaze formulation, but Bentonite generally offers superior suspension abilities due to its finer particle size and stronger colloidal properties.
Effects on Glaze Stability and Settling
Bentonite clay offers superior suspension properties due to its high swelling capacity and strong plate-like particle structure, which enhances glaze stability and minimizes settling over time. Raku clay, with its coarser particle size and lower plasticity, provides less effective suspension, leading to faster settling and potential glaze consistency issues. The choice between Bentonite and Raku clay directly impacts the homogeneity and workability of glaze mixtures, with Bentonite preferred for long-lasting suspension and smoother application.
Influence on Glaze Texture and Appearance
Raku clay, known for its coarse texture and porous nature, enhances glaze suspension by allowing better adherence and producing a rough, crackled surface that accentuates natural variations in glaze texture. Bentonite clay, with its fine particles and high plasticity, significantly improves glaze suspension by increasing viscosity, resulting in a smoother, more uniform glaze finish with fewer imperfections. The choice between Raku and Bentonite clays directly influences the glaze's texture and appearance, with Raku promoting rustic, textured effects, while Bentonite ensures refined, consistent layers.
Application Differences in Studio Practices
Raku clay, known for its porous structure, often requires higher proportions in glaze suspension to maintain even viscosity, making it ideal for rapid reduction firing techniques in studio settings. Bentonite clay provides superior plasticity and suspension properties, enabling smoother glaze application and better adherence, especially beneficial for intricate ceramic surfaces and dipping methods. Studio practices favor Bentonite for consistent glaze suspension and Raku clay when an open texture and quick drying are desired, reflecting their distinct operational roles.
Pros and Cons: Raku Clay vs Bentonite Clay
Raku clay offers unique thermal shock resistance and a porous structure that enhances glaze adhesion but may cause warping and cracking during rapid cooling. Bentonite clay provides excellent plasticity and superior suspension qualities for glazes, promoting even application and minimizing settling, yet it can lead to overly thick pastes and drying shrinkage if overused. Choosing between Raku and Bentonite clays for glaze suspension depends on balancing Raku's heat tolerance and texture with Bentonite's suspension efficiency and workability.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Clay for Your Glaze Suspension
Raku clay offers excellent particle dispersion and thermal shock resistance, making it ideal for low-temperature glaze suspensions with rapid firing processes. Bentonite clay provides superior plasticity and high swelling capacity, resulting in stable glaze suspensions with consistent viscosity ideal for commercial and high-volume production. Selecting between Raku and Bentonite depends on firing temperature, suspension stability requirements, and desired glaze finish characteristics.
Infographic: Raku clay vs Bentonite clay for Glaze suspension
 azmater.com
azmater.com