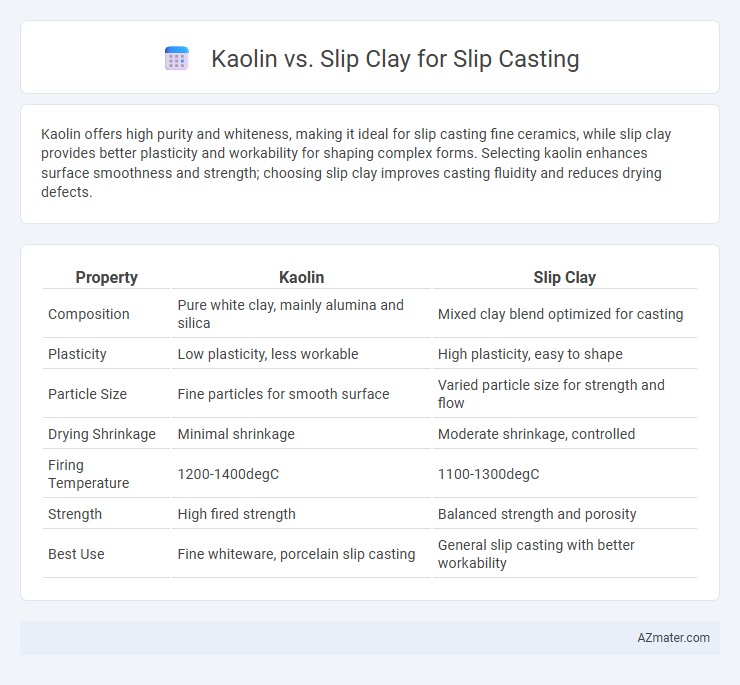
Kaolin offers high purity and whiteness, making it ideal for slip casting fine ceramics, while slip clay provides better plasticity and workability for shaping complex forms. Selecting kaolin enhances surface smoothness and strength; choosing slip clay improves casting fluidity and reduces drying defects.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Kaolin | Slip Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Pure white clay, mainly alumina and silica | Mixed clay blend optimized for casting |
| Plasticity | Low plasticity, less workable | High plasticity, easy to shape |
| Particle Size | Fine particles for smooth surface | Varied particle size for strength and flow |
| Drying Shrinkage | Minimal shrinkage | Moderate shrinkage, controlled |
| Firing Temperature | 1200-1400degC | 1100-1300degC |
| Strength | High fired strength | Balanced strength and porosity |
| Best Use | Fine whiteware, porcelain slip casting | General slip casting with better workability |
Introduction to Slip Casting
Slip casting utilizes liquid clay, or slip, as the fundamental material, where kaolin plays a crucial role due to its high plasticity and fine particle size, ensuring smooth flow and uniformity. Kaolin enhances the slip's viscosity and suspension stability, enabling precise mold filling and detailed surface replication. In contrast, slip clay formulations without sufficient kaolin may result in poor casting quality, increased defects, and uneven drying during the slip casting process.
Defining Kaolin and Slip Clay
Kaolin is a fine, white clay mineral composed mainly of kaolinite, prized for its purity, plasticity, and high refractory properties, making it essential in ceramic production. Slip clay refers to a liquid suspension of fine clay particles, including kaolin and other clays, suspended in water to create a pourable mixture ideal for slip casting. Slip casting utilizes slip clay to form precise ceramic shapes, while kaolin provides the foundational material that enhances the strength and smoothness of the final product.
Key Differences Between Kaolin and Slip Clay
Kaolin, a highly purified white clay, provides exceptional plasticity and strength, making it ideal for fine-detail slip casting and producing smooth, durable ceramic surfaces. Slip clay, a mixed slurry of various clays and water, offers greater fluidity and ease of application but may lack the uniformity and fine particle size of pure kaolin. Key differences include kaolin's high refractory properties and whiteness compared to slip clay's versatility and adjustable consistency for different ceramic applications.
Particle Size and Plasticity Comparison
Kaolin typically has finer particle size compared to slip clay, resulting in smoother slip consistency and better surface detail in slip casting. Slip clay, which contains larger particles, offers higher plasticity, enhancing mold release and shaping flexibility during the casting process. Optimizing the balance between kaolin's fine particles and slip clay's plasticity is crucial for achieving both precision and workability in ceramic slip casting.
Workability in Slip Casting Formulations
Kaolin enhances slip casting workability by improving the plasticity and rheological stability of the slip, allowing for smoother flow and better mold filling. Slip clay, with its finer particle size and higher surface area, offers superior suspension stability and reduced settling, resulting in a more consistent casting layer thickness. Balancing kaolin and slip clay proportions in formulations optimizes slip viscosity and green strength, crucial for defect-free ceramic castings.
Firing Temperatures and Maturation
Kaolin and slip clay differ significantly in firing temperatures and maturation properties for slip casting applications. Kaolin typically matures at higher temperatures, around 1200degC to 1450degC, offering excellent refractory qualities and plasticity suitable for porcelain and fine ceramics. Slip clays, often composed of ball clay blends with kaolin, mature at lower temperatures, approximately 900degC to 1150degC, providing better workability and faster vitrification, ideal for earthenware and terracotta production.
Color and Surface Finish Outcomes
Kaolin provides a bright white color and a smooth, slightly matte surface finish ideal for detailed slip casting, while slip clay often contains impurities that can produce off-white or grayish tones with a rougher texture. The high purity of kaolin ensures consistent translucency and minimal discoloration after firing, whereas slip clays may result in uneven glaze adherence and color variances. Selecting kaolin enhances the final aesthetic quality, delivering crisp surface detail and a more uniform color ideal for fine art ceramics.
Shrinkage and Drying Behavior
Kaolin exhibits lower shrinkage rates during slip casting compared to slip clay, resulting in more dimensionally stable ceramic pieces. Drying behavior in kaolin-based slips is more uniform, reducing the risk of cracks and deformation, while slip clay often experiences uneven drying leading to surface defects. Optimizing the kaolin content in slip casting formulations enhances both drying consistency and minimizes shrinkage-induced stresses.
Cost and Availability Considerations
Kaolin is generally more affordable and widely available than slip clay, making it a preferred choice for cost-sensitive slip casting projects. Slip clay often requires additional processing and refinement, increasing its overall cost and limiting its availability in some regions. Selecting kaolin can optimize budget and material accessibility without compromising the quality of the slip casting process.
Choosing the Right Clay for Your Slip Casting Project
Kaolin offers superior whiteness and fine particle size, making it ideal for delicate slip casting projects requiring smooth surfaces and high detail. Slip clay, containing a blend of clays and additives, provides better plasticity and workability, which is essential for complex shapes and faster drying times. Selecting the right clay depends on the project's finish requirements, mold complexity, and drying schedule to achieve optimal results.
Infographic: Kaolin vs Slip clay for Slip Casting
 azmater.com
azmater.com