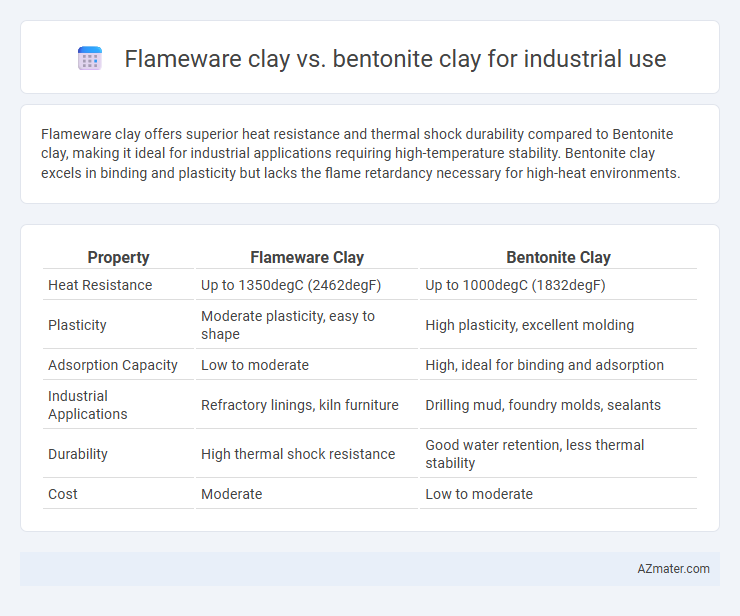
Flameware clay offers superior heat resistance and thermal shock durability compared to Bentonite clay, making it ideal for industrial applications requiring high-temperature stability. Bentonite clay excels in binding and plasticity but lacks the flame retardancy necessary for high-heat environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Flameware Clay | Bentonite Clay |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Resistance | Up to 1350degC (2462degF) | Up to 1000degC (1832degF) |
| Plasticity | Moderate plasticity, easy to shape | High plasticity, excellent molding |
| Adsorption Capacity | Low to moderate | High, ideal for binding and adsorption |
| Industrial Applications | Refractory linings, kiln furniture | Drilling mud, foundry molds, sealants |
| Durability | High thermal shock resistance | Good water retention, less thermal stability |
| Cost | Moderate | Low to moderate |
Introduction to Industrial Clays
Flameware clay offers high refractory properties, making it ideal for industrial applications requiring heat resistance, such as kiln linings and furnace components. Bentonite clay is known for its exceptional swelling capacity and binding strength, commonly used in drilling muds, foundry sands, and sealing applications. Both clays serve distinct industrial functions, with Flameware prized for thermal stability and Bentonite valued for its plasticity and adsorption qualities.
What is Flameware Clay?
Flameware clay is a high-temperature refractory material designed to withstand intense heat without cracking or deforming, commonly used in industrial applications such as kiln linings and furnace components. Unlike Bentonite clay, which is primarily valued for its swelling properties and adsorption capacity in drilling and sealing, Flameware clay contains specific mineral compositions like kaolin and alumina that enhance its heat resistance and thermal stability. Industrial processes demanding durability under extreme thermal conditions benefit from Flameware clay's superior refractory characteristics compared to the more chemically reactive Bentonite clay.
What is Bentonite Clay?
Bentonite clay is a highly absorbent and swelling natural clay composed primarily of montmorillonite, used extensively in industrial applications such as drilling mud, binder in foundry sands, and sealing materials for landfills. Its unique properties include excellent water retention, high cation exchange capacity, and the ability to form a stable gel-like consistency when hydrated, making it indispensable for fluid control and contaminant containment. In comparison with Flameware clay, Bentonite clay offers superior sealing, binding, and adsorption capabilities critical for enhancing the performance and durability of industrial processes.
Chemical Composition Comparison
Flameware clay typically consists of high alumina and silica content, providing excellent refractory properties ideal for high-temperature industrial applications. Bentonite clay, predominantly composed of montmorillonite, features high swelling capacity and cation exchange properties, useful for sealing and binding in various industrial processes. The chemical composition difference, primarily the alumina-silica ratio in Flameware clay versus the smectite group minerals in Bentonite, dictates their distinct performance in thermal resistance and adsorption capabilities.
Thermal Resistance and Durability
Flameware clay offers exceptional thermal resistance, making it ideal for high-temperature industrial applications such as kiln linings and furnace components. Bentonite clay, while valuable for its plasticity and absorbent properties, exhibits lower thermal stability and durability under extreme heat conditions. Industrial processes requiring prolonged exposure to temperatures above 1200degC benefit more from the superior refractory qualities of flameware clay compared to bentonite.
Industrial Applications of Flameware Clay
Flameware clay is prized in industrial applications for its exceptional refractory properties, making it ideal for manufacturing kiln linings, crucibles, and furnace components subjected to extreme heat. Unlike bentonite clay, which primarily serves as a binder or sealing agent, flameware clay withstands thermal shock and high temperatures without deforming, ensuring durability in metallurgical and ceramics industries. Its high alumina content and low thermal conductivity optimize energy efficiency and structural integrity in high-temperature environments.
Industrial Applications of Bentonite Clay
Bentonite clay is widely used in industrial applications due to its exceptional absorbent and swelling properties, making it ideal for drilling mud in oil and gas exploration and as a binder in foundry molds. Flameware clay, while known for its high-temperature resistance, lacks the broad industrial versatility seen in bentonite, particularly in wastewater treatment and pelletizing processes. The strong cation exchange capacity of bentonite enhances its role in environmental remediation and catalysts, solidifying its prominence in various industrial sectors.
Cost-Effectiveness and Availability
Flameware clay, known for its high refractory properties, often comes at a higher cost but offers superior heat resistance for industrial applications like furnace linings, making it cost-effective for high-temperature environments. Bentonite clay, abundant and widely available, is less expensive and primarily used for its swelling and sealing properties in industries such as drilling and foundry molds. The choice between Flameware and Bentonite clay heavily depends on operational temperature requirements and budget constraints, with Bentonite favored for general sealing and cost-sensitive projects and Flameware preferred for intense thermal applications.
Environmental Impact of Both Clays
Flameware clay, known for its refractory properties, typically exhibits lower environmental impact during extraction and processing due to less intensive mining requirements compared to bentonite clay, which involves extensive strip mining leading to significant land disruption and habitat loss. Bentonite clay extraction generates higher water consumption and potential contamination risks from processing chemicals, whereas flameware clay production is generally associated with minimal chemical use and lower water demand. Both clays require careful management to mitigate dust emissions and soil erosion, but the environmental footprint of bentonite is substantially greater due to its higher demand and more resource-intensive mining techniques.
Choosing the Right Clay for Industrial Needs
Flameware clay offers exceptional heat resistance and structural integrity, making it ideal for high-temperature industrial applications such as kiln linings and furnace components. Bentonite clay features superior swelling properties and excellent absorption, which suits it for drilling fluids, sealing, and binding processes in industries like oil and gas and construction. Selecting between Flameware and Bentonite clay depends on specific operational requirements, where thermal stability favors Flameware and absorbent sealing capabilities prioritize Bentonite.
Infographic: Flameware clay vs Bentonite clay for Industrial use
 azmater.com
azmater.com